Ovarian Cyst Causes & Symptoms
Ovarian cyst is a gynaecological issue. Learn how to recognize its signs and explore effective diagnosis and management options for better health.

Written by
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
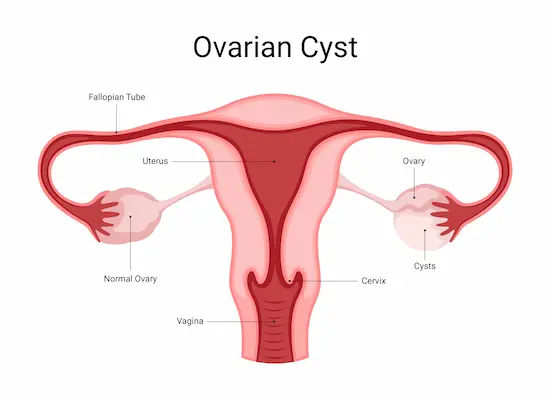
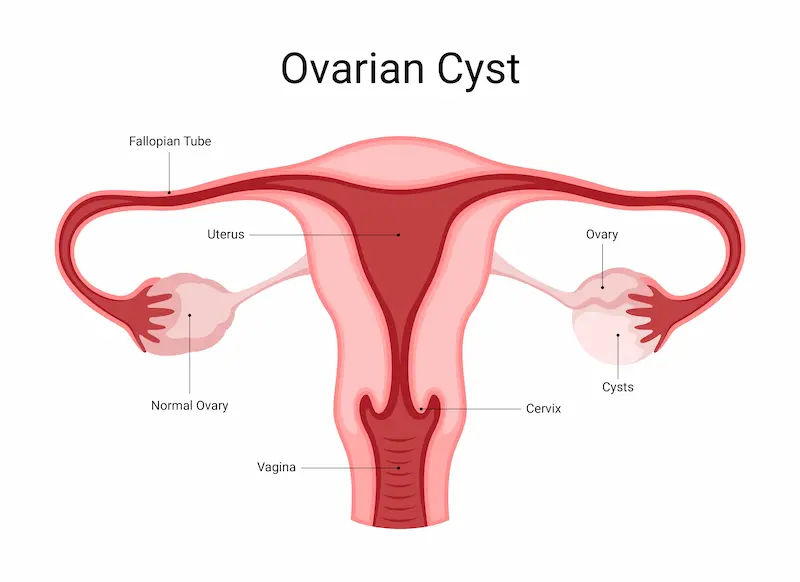
Ovarian cysts are one of the most common gynaecological disorders in women. These fluid-filled sacs or pocket-like structures form in the ovaries, usually without noticeable symptoms. The ovaries are vital reproductive organs that produce eggs and excrete hormones like oestrogen and progesterone. These hormones control the menstrual cycle and fertility in women, and conditions such as ovarian cysts may form due to a disturbance in these normal processes. Thus, it is essential to know the symptoms and treatments of this disease as it is vital for the reproductive health and overall well-being of women.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are two types of ovarian cysts: functional and pathological. Usually, functional cysts are non-malignant and disappear on their own after the completion of some menstrual cycles. However, pathological cysts may become malignant and need medical attention.
Moving on, functional cysts have two types –
Follicular Cysts: This occurs when a follicle (a sac containing an egg) fails to rupture to release the egg during ovulation. Instead, the follicle keeps growing, and a cyst is formed.
Corpus Luteum Cysts: After the egg is released, the follicle usually transforms into a corpus luteum structure. If the corpus luteum does not degenerate, and instead fills with fluid, it can get produce a cyst which is typically harmless.
Similarly, pathological Cysts have three types –
Dermoid Cysts: These have tissue like skin, hair, or teeth and develop from the reproductive cells that produce eggs.
Endometriomas: These are a type of ovarian cyst formed when endometrial tissue (the tissue lining the uterus) grows on the ovaries. These cysts are filled with old, dark blood and are commonly associated with endometriosis, often causing pain and potentially affecting fertility.
Cystadenomas: It grows on the surface of the ovary and may be filled with fluid or mucus.
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian Cysts can be formed due to various biological and medical factors:
Hormonal Factors: Hormonal disturbance is the prominent cause of ovarian cysts. Functioning cysts can result from disrupting the release of reproductive hormones, particularly oestrogen and progesterone. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are also the result of long-term hormonal malfunctions causing multiple small cysts.
Pregnancy: During early pregnancy, cysts may develop to supply the growing embryo with the required hormones. These cysts are usually harmless and dissolve spontaneously, but they might need to be monitored.
Pelvic Infections: Endogenous severe pelvic infections can ascend to the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Such infections can cause pus-filled or fluid-filled cysts that need to be treated.
Common Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Most ovarian cysts are asymptomatic; however, some can result in significant discomfort or complications. Identifying the signs is crucial for early diagnosis. So, some of the common symptoms for identifying ovarian cysts are –
Abdominal Pain
A common symptom is pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic region, varying from mild to severe.
Bloating and Fullness
If the cyst becomes larger and pushes against nearby organs, an individual may experience feelings of heaviness, pressure, or bloating in her abdomen.
Menstrual Irregularities
Hormonal imbalance due to the presence of cysts can cause irregular menstrual cycles, resulting in heavier or lighter flows than usual, spotting, or missed periods.
Pain During Intercourse
Large or deep-seated cysts can cause discomfort or pain during and/or after sex, particularly if a cyst is pressing on adjacent tissues or organs.
Diagnostic Methods
Proper diagnosis is crucial in understanding what kind of ovarian cyst one is dealing with and identifying the effective treatment approach. Here are the options –
Ultrasound: The most common and reliable imaging modality to diagnose ovarian cysts is ultrasound. It shows detailed images of the cyst’s size, location, and composition (fluid-filled, solid, or mixed).
Blood Tests: Blood tests that, for example, measure CA-125 levels can help identify whether a cyst is benign or malignant. CA-125 is a molecule that’s often elevated in ovarian cancer but can also be elevated for a host of other reasons.
Pelvic Examination: A routine pelvic exam can help identify changes in the size or shape of the ovaries. The doctor may recommend additional imaging or tests if a cyst is suspected.
Pregnancy test: A positive pregnancy report indicates that an individual has a corpus luteum cyst.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
Identifying warning signs and getting an early medical evaluation will prevent complications and enable effective management. So, here are some indications of medical interventions that women should keep an eye out for –
If abdominal or pelvic pain is constant, getting worse, or interfering with everyday tasks, it should be evaluated by a medical professional.
A ruptured cyst can cause sudden, severe pain, nausea, and vomiting. It also causes bleeding in the pelvis. This is a medical emergency that needs urgent intervention.
Severe and sudden symptoms like fever, dizziness, or rapid breathing may signal the occurrence of ovarian torsion, in which the ovary twists and cuts off its blood supply. This, too, is an emergency that requires urgent care. Also, losing appetite and weight without trying requires medical attention.
Treatment Options
Managing ovarian cysts varies according to the size and type of cysts, the patient’s overall health, and associated symptoms. So, here are some notable treatment options –
Most small, asymptomatic cysts disappear spontaneously in a few months. But, ultrasounds can be performed to monitor them.
Hormonal treatment or birth control medications become helpful when the patient feels pain from the cysts. Hormonal treatment cannot eliminate the cyst, but it prevents the formation of new ones.
Over-the-counter or prescription pain relief drugs help relieve discomfort caused by cysts.
Larger, symptomatic, or suspected cancerous cysts may require surgery.
So, there are two types of surgery for removing ovarian cysts –
Laparoscopy: Used to remove smaller cysts in a minimally invasive procedure.
Laparotomy: An open or invasive surgical procedure used for larger cysts or a suspected malignancy.
Possible Complications
Complications of untreated ovarian cysts can have serious effects on a woman’s health and fertility. Here are some major concerns –
Ovarian Torsion: Large cysts can twist the ovary and sever its blood supply. It causes severe pelvic pain, nausea, and vomiting. This condition needs emergency surgery to avoid tissue death and potential loss of ovarian function.
Rupture: Cyst rupture indicates a cyst that bursts open. The larger cysts are more likely to tear and cause internal bleeding and severe pain that may need surgical intervention.
Impact on Fertility: Some variants of the cyst may affect fertility and make it harder to conceive, for example, endometriosis and cysts seen with PCOS.
Prevention and Lifestyle Adjustments
Healthy lifestyle habits and annual examinations might also reduce the risk of ovarian cysts.
Regular Health Check-ups: Cysts can be detected early through routine pelvic exams and ultrasounds, allowing opportunities for timely intervention and preventing complications.
Good Diet and Exercise: Hormonal regulation through a healthy diet and exercise can help decrease the occurrence of conditions such as PCOS. Also, cutting back on processed foods and eating nutrient-dense foods promotes ovarian health. Thus, one should prefer fibre, lean proteins, and anti-inflammatory foods.
Heat Therapy: Applying a heating pad or hot water bottle on the lower abdomen reduces cyst pain and menstrual cramping.
Conclusion
Ovarian cysts are common and sometimes complicated, ranging from functional cysts to pathological ones that have more serious implications. While hormonal imbalance is the primary cause, there are other lifestyle reasons as well that lead to this condition. But, timely detection via ultrasound, blood tests, and pelvic exam is vital for effective treatment and prevention of complications such as ovarian torsion or infertility. Also, regular check-ups, a good diet, and a proper lifestyle can prevent cyst formation. Therefore, with proper knowledge and action, women can handle these cysts properly, ensuring the health of their reproductive system and themselves.
Consult Top Gynaecologist
Consult Top Gynaecologist
Dr. K Anusha
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
4 Years • MBBS, DGO
Yemmiganur
SRINIVASAA HOSPITAL, Yemmiganur

Dr. Mona Yadav
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
19 Years • MBBS, MD (Obstetrics & Gynaecology)
Dombivli
Nulife multispeciality, Dombivli

Dr. Parul Sharma
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
8 Years • MBBS, MS (Obstetrics & Gynaecology)
New Delhi
THE DOCTORS NESST, New Delhi
Dr. J Aswini Sowndarya
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
4 Years • MBBS, MS Obstetrics & Gynaecology, FMAS, FART
Rajamahendravaram
Tholat Memorial Multi Speciality Hospital, Rajamahendravaram

Dr. Debajyoti Goswami
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
10 Years • MBBS,D.G.O(DNB),Adv. Infertility Tech.(AIIMS),Fellowship in Diabetes(U.K),Comprehensive Abortion Care(Govt. Of W.B), Certificate in Clinical Embryology(AIIMS, BHUBANESWAR)
Bankura
D.G Clinic, Bankura
(25+ Patients)