Coronavirus Updates
How Does COVID-19 Affect Pregnant Women and Their Babies?
6 min read
By Apollo 24/7, Published on - 14 April 2021, Updated on - 22 October 2022
Share this article
0
3 likes
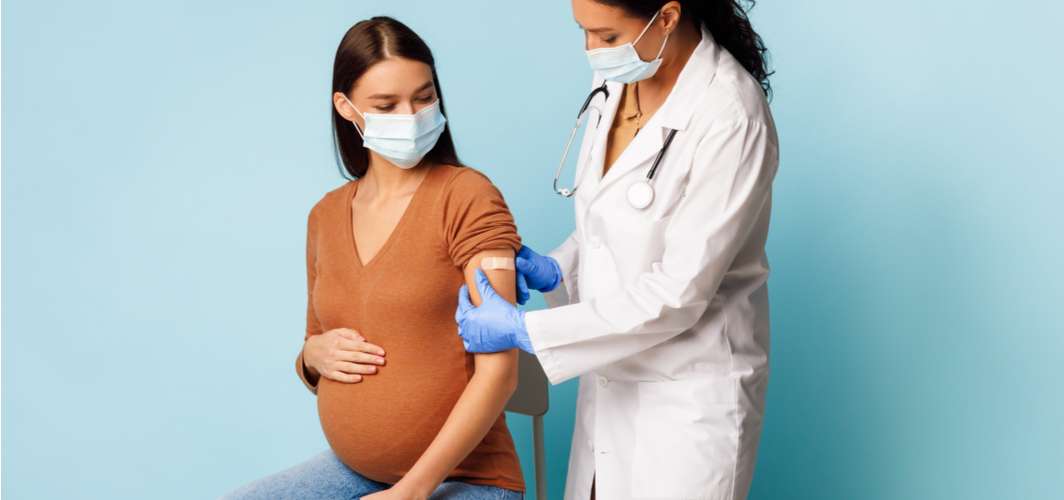

During pregnancy, women need to be careful about their diet, exercise, and overall health as the foetus derives nourishment from the mother. At this time of the pandemic, pregnant women need to be extra cautious of their health as COVID-19 can not only harm the mother but the child as well. While research is still ongoing, various studies have indicated the transfer of COVID-19 infection from an infected mother to their child.
Are pregnant women at risk for severe COVID-19?
Studies done by many health organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO), have established that several changes occur in the bodies and immune system of women during pregnancy, making them immunocompromised. This increases their risk of developing severe COVID-19 illness. Studies that indicate the risk for COVID-19 in pregnant women include:
- A study published in the journal Science Immunology examined 1200 pregnant women with antibodies and found that over 6% of these women got exposed to the SARS-CoV-2 virus while the exposure rate was only 1.4% in the general population. This study concluded that pregnant women are four times more likely to get COVID-19 than others.
- Another study published in the journal Endocrinology concluded that pregnant women diagnosed with COVID-19 have a higher risk of developing blood clots due to the infection as compared to non-pregnant COVID-19 positive women. They further added that these blood clots can damage the placenta and obstruct the blood flow to the foetus, resulting in life-threatening complications for the baby as well as the mother.
- A living systematic review of 192 studies published in the British Medical Journal in September 2020 found that pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 were more likely to require intensive care, mechanical ventilation and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) for breathing. They further added that increased age, high body mass index (BMI), high blood pressure, pre-existing diabetes, and pre-eclampsia were risk factors for severe COVID-19 illness and death in pregnant women.
Can a COVID-positive pregnant woman pass on the virus to the baby?
The exact impact of the COVID-19 virus on pregnant women and their babies is still not known. However, scientists believe that the spike protein of the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, does not bind to ACE2 receptors to enter the womb. It infects the baby by binding to CD147 receptors, which are widely present in the uterus, ovaries and placenta.
Another theory states that when the placenta gets damaged due to blood clots in pregnant women with COVID-19, the vertical transmission of the virus occurs from the mother to the baby. Studies that have found the transfer of COVID-19 from the mother to the child include:
- A meta-analysis published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology in January 2021 found that vertical transmission of the COVID-19 virus seems to occur in the third trimester of pregnancy as the virus was detected in the amniotic fluid and placenta. It further revealed that this infection increased the risk of fetal death.
- The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists in the UK found antibodies against the COVID-19 virus in the serum of newborn babies, which indicated that the virus was passed on to the baby while it was still in the womb.
- A review study published in the British Medical Journal found that as compared to the babies born to COVID-negative women, babies born to pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection were either born before term or required neonatal intensive care unit after being born.
Various studies have indicated that the transmission of the COVID-19 virus from the mother to the unborn baby can be life-threatening for the baby as their immune system is not mature enough to fight the virus.
Should pregnant women be vaccinated for COVID-19?
As per the WHO, since pregnant women have a high risk of developing severe COVID-19 infection, they must be vaccinated after consulting their doctor.
A study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology on 25th March 2021, included a total of 131 women - 84 pregnant, 31 lactating and 16 non-pregnant women. All these women were given two doses of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna mRNA vaccine. The scientists collected the blood and breast milk sample of these women 2 to 6 weeks after taking the vaccine. Scientists also collected blood samples from the umbilical cord of 13 women who delivered a baby after getting the vaccine.
The result of the study showed that:
- Antibodies against the COVID-19 causing virus were found in all the umbilical cord blood and breast milk samples.
- There was a transfer of protective antibodies (against the COVID-19 virus) from the mothers to their babies.
Similarly, several other smaller studies have shown positive effects of different COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant women. However, scientists believe more research is needed to determine the true impact of these vaccines on pregnant women. Pregnant women in countries like the US and UK are being administered the Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, Oxford-Astra-Zeneca or Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen vaccines as they have been considered safe during pregnancy.
However, it is important to note that the Health Ministry of India has stated that pregnant (both confirmed and uncertain) and lactating women will not be given Covishield or Covaxin (the two COVID-19 vaccines being administered in India) until further research is conducted. The Government is expected to announce further guidelines and updates with regards to vaccinations for pregnant women.
Pregnant women should follow strict COVID-appropriate behaviour
As per the WHO, pregnant women should take precautionary measures against COVID-19, which include:
- Not stepping out of the house unless necessary.
- Avoiding physical contact with outsiders.
- Using alcohol-based sanitisers or washing the hands with soap and water frequently.
- Preparing a bag for delivery with all the necessary things that might be required in the hospital.
- Contacting the doctor immediately if they observe any warning signs related to pregnancy such as pain in the abdomen, bleeding, watery discharge and severe headache.
- Continuing the prenatal visits to the doctor until told otherwise.
- Consuming a diet filled with at least 5 portions of fruits and vegetables regularly.
- Adding high-protein foods such as soybean, fish, chicken and pulses to the diet.
- Consuming immunity-boosting foods such as turmeric, citrus fruits, ginger and honey after consulting the doctor.
- Practising meditation and yoga to relieve anxiety and improve sleep.
Takeaway
There have been numerous concerns about mother to child transmission of COVID-19 via the placenta, mother’s body fluids, during delivery, and while breastfeeding. However, more research is required to determine the effects actual impact of COVID-19 on pregnant women and their babies. In the meantime, pregnant women should minimise their risk of infection by wearing masks, distancing physically, and strictly following other COVID-appropriate behaviour. They must consult their doctors if they experience abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding or severe headache. And most of all, they must find ways to put their minds at ease and enjoy a happy and healthy pregnancy.
Coronavirus Updates
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
Coronavirus Updates
Can RT-PCR Tests Detect the Omicron Strain?
Fortunately, Omicron can be detected by certain RT-PCR tests being used all over the world, unlike other SARS-CoV-2 variants whose presence can be ascertained only through genetic sequencing.

Coronavirus Updates
How Do We Prevent the Community Spreading of Coronavirus?
Follow social distancing norms, practice hand hygiene, wear masks, and follow the precautions mentioned in this article to prevent community spread of the Coronavirus.

Coronavirus Updates
What are the Long-Term Health Effects of COVID-19?
It has been found that the after-effects of the COVID-19 linger on in the form of fatigue, heart issues, joint pains, neurological symptoms and other problems.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

COVID-19: The situation on ground [6th July 2021]
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Coronavirus Updates
Can RT-PCR Tests Detect the Omicron Strain?
Fortunately, Omicron can be detected by certain RT-PCR tests being used all over the world, unlike other SARS-CoV-2 variants whose presence can be ascertained only through genetic sequencing.

Coronavirus Updates
How Do We Prevent the Community Spreading of Coronavirus?
Follow social distancing norms, practice hand hygiene, wear masks, and follow the precautions mentioned in this article to prevent community spread of the Coronavirus.

Coronavirus Updates
What are the Long-Term Health Effects of COVID-19?
It has been found that the after-effects of the COVID-19 linger on in the form of fatigue, heart issues, joint pains, neurological symptoms and other problems.