Skin Care
From Medicines To Exercises, Top Tips To Manage Psoriasis
3 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 18 April 2023, Updated on - 19 June 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
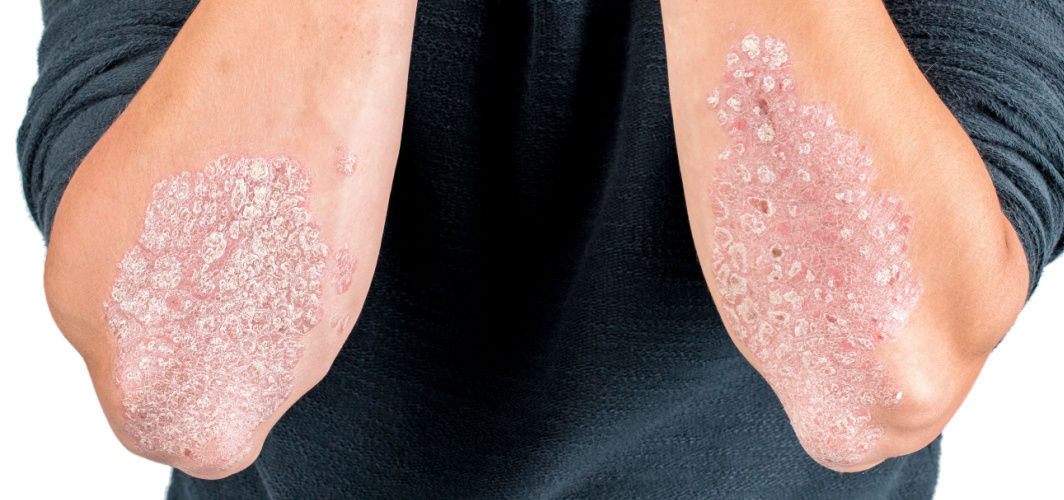
We often experience itching and rashes, especially during the summer season. While in most cases it occurs due to a fungal infection, intense itching, along with scaly patches or cracked skin, may indicate a serious skin condition, such as psoriasis. Very often, people are born with genetic combinations that predispose them to psoriasis, however, it can occur to anyone. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder where the rate of skin cell division increases rapidly. While there is no cure for the condition, here are some of the management strategies that can lessen the ordeal.
1. Avoid Physical injuries
A simple cut or burn could be enough to hyperactivate the immune system. Hence, try to avoid such injuries as much as possible. However, if you ever get injured, don’t let your wounds turn infectious.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Studies indicate that drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes can act as potential triggers of the condition. One should quit both and adopt healthy habits such as eating a well-balanced diet, exercising regularly and meditating to help lower stress, which is another potential trigger of Psoriasis.
3. Personal care
Take regular baths and keep the skin clean as much as possible. Use non-fragrant, mild, hypoallergenic products to reduce the risk of skin irritation. Apply a thick layer of moisturizer post-bathing to lock the hydration.
4. Diet
Avoid red meat, dairy products and refined sugar as they can trigger psoriasis. Indulge in foods like fish, legumes (beans and lentils), olive oil, low-fat dairy and whole grains as they help combat inflammation.
For queries on what to eat and not to eat to manage psoriasis better,
5. Medications:
-
Topical Therapy: It is the primary management for low and moderate levels of the disorder. In this treatment, the recommended medication is applied to the skin and allows it to seep inside the body. A combination of corticosteroids and Vitamin D3 equivalents like Calcipotriol are used.
- Systemic therapy: If the topical therapy fails, the patient is asked to go for systemic therapy. This could be divided under several heads:
- Radiation Therapy: In this therapy, ultraviolet radiation is used. The narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) is primarily (even for teenagers and pregnant women) used since it has zero risk of malignancy. However, there are other options like broadband UVB and psoralen plus UVA.
- Non-Biologic therapy: The problem with radiation therapy is the risk of cancer development and availability. Therefore, patients can be given medications such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, Apremilast, and Acitretin to reduce inflammation.
- Biologic therapy: If all other options fail, biologic therapy is the last resort. Several drugs like infliximab (most effective), ustekinumab, adalimumab and etanercept have been proven to be quite effective in reducing the risk of a flare-up.
It would always be wise to use a combination of treatment strategies instead of religiously sticking to one particular regimen. Additionally, special care is required if the patient has high blood pressure, as the drugs used in its management can act as a potential trigger. Since psoriasis is a lifelong disease, the treatment should be based on improving the symptoms and reducing the frequency of flare-ups. If you have been dealing with psoriasis and need expert advice,
Consult An Apollo Dermatologist
Medically reviewed by Dr Sonia Bhatt.
Skin Care
Leave Comment
Recommended for you

Skin Care
Anti-Ageing Supplements Myths: 6 False Facts You Should Know Now
These days most people are searching for the newest methods to maintain healthy, glowing and radiant skin without ageing. But do anti-ageing supplements work? Let us find out.

Skin Care
6 Ways To Manage Sweating During Summers
It can get difficult to manage sweating during the hot summer months. Fortunately, there’s a lot you can do to prevent your body from sweating too much. So, read on to learn about some effective strategies to help you sweat less this summer.

Skin Care
Which Face Serum To Choose? Know The Ingredients & Their Health Benefits
Face serums are concentrated formulas with antioxidants, vitamins and other active ingredients that are designed to penetrate deep into the skin and repair the damage. Know the ingredients to understand which face serum will suit your purpose.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Recommended for you

Skin Care
Anti-Ageing Supplements Myths: 6 False Facts You Should Know Now
These days most people are searching for the newest methods to maintain healthy, glowing and radiant skin without ageing. But do anti-ageing supplements work? Let us find out.

Skin Care
6 Ways To Manage Sweating During Summers
It can get difficult to manage sweating during the hot summer months. Fortunately, there’s a lot you can do to prevent your body from sweating too much. So, read on to learn about some effective strategies to help you sweat less this summer.

Skin Care
Which Face Serum To Choose? Know The Ingredients & Their Health Benefits
Face serums are concentrated formulas with antioxidants, vitamins and other active ingredients that are designed to penetrate deep into the skin and repair the damage. Know the ingredients to understand which face serum will suit your purpose.
