Types of Anaemia and Their Causes
Explore the different types of anaemia, including iron-deficiency, vitamin-deficiency, and hemolytic anaemia. Learn the specific causes and risk factors for each type.

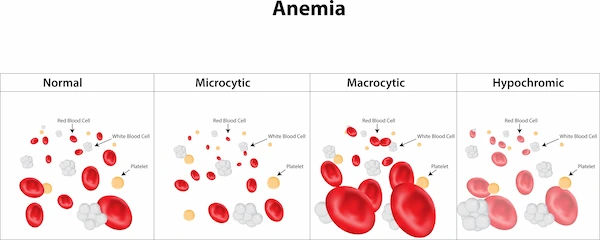
Types of Anaemia and Their Causes
Anaemia is a common health condition that occurs when your body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells (RBCs) or haemoglobin to carry oxygen efficiently to your tissues. This can leave you feeling tired, weak, or short of breath. While anaemia is widespread, it can stem from different causes, and understanding the types can help in proper diagnosis and treatment.
In this article, we’ll explore the different types of anaemia, their causes, symptoms, and ways to manage them effectively.
Common Types of Anaemia and Their Causes
Let us have a look at the common types of anaemia and its causes:
1. Iron-Deficiency Anaemia
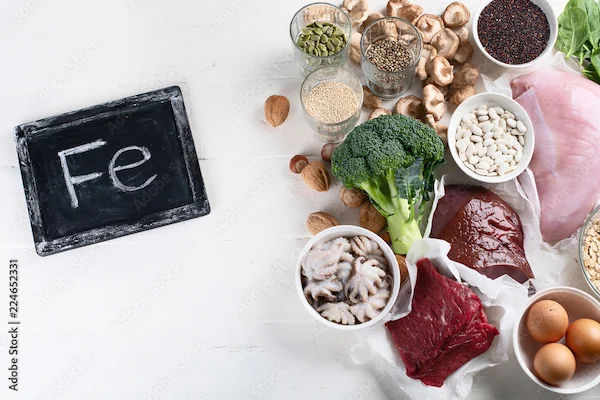
Cause: This is the most common type of anaemia and occurs when your body lacks enough iron to produce haemoglobin. Without sufficient iron, your red blood cells can’t carry oxygen properly.
Possible Reasons:
- Poor diet (low iron intake)
- Blood loss (heavy periods, ulcers, or internal bleeding)
- Pregnancy (increased iron demand)
Symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Brittle nails
Management:
- Eat iron-rich foods (spinach, red meat, lentils, fortified cereals).
- Take iron supplements if prescribed by a doctor.
- Pair iron-rich foods with vitamin C (oranges, tomatoes) to enhance absorption.
2. Vitamin Deficiency Anaemia (B12 & Folate Deficiency)
Cause: Your body needs vitamin B12 and folate (B9) to produce healthy red blood cells. A deficiency in either can lead to anaemia.
Possible Reasons:
- Poor diet (lack of meat, dairy, or leafy greens)
- Pernicious anaemia (an autoimmune condition that affects B12 absorption)
- Digestive disorders (celiac disease, Crohn’s disease)
Symptoms:
- Extreme fatigue
- Tingling in hands and feet (B12 deficiency)
- Mouth ulcers
- Memory difficulties
Management:
- Consume B12-rich foods (eggs, fish, dairy) and folate-rich foods (leafy greens, beans).
- B12 injections may be needed for severe deficiency.
3. Aplastic Anaemia
Cause: A rare but serious condition where the bone marrow fails to produce enough red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Possible Reasons:
- Autoimmune disorders
- Exposure to toxins (pesticides, chemotherapy)
- Viral infections (hepatitis, HIV)
Consult Top Specialists
Symptoms:
- Frequent infections
- Excessive bruising or bleeding
- Persistent fatigue
Management:
- Blood transfusions or bone marrow transplants may be required.
- Immunosuppressive therapy if caused by an autoimmune condition.
4. Hemolytic Anaemia
Cause: This occurs when red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be produced.
Possible Reasons:
- Inherited conditions (sickle cell anaemia, thalassemia)
- Autoimmune disorders
- Infections (malaria)
Symptoms:
- Jaundice (yellowish skin)
- Dark-colored urine
- Rapid heart rate
Management:
- Treatment depends on the cause—medications, blood transfusions, or spleen removal in severe cases.
5. Anaemia of Chronic Disease
Cause: Long-term illnesses like kidney disease, cancer, or rheumatoid arthritis can interfere with red blood cell production.
Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Inflammation-related symptoms
Management:
- Treating the underlying disease is key.
- Sometimes, erythropoietin (a hormone that stimulates RBC production) is prescribed.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience persistent fatigue, dizziness, pale skin, or unusual shortness of breath, consult a doctor. A simple blood test (Complete Blood Count - CBC) can diagnose anaemia and its type.
You can book a consultation or schedule a test easily through Apollo 24|7 for quick diagnosis and treatment.
Lifestyle Tips to Prevent or Manage Anaemia
1. Eat a Balanced Diet: Include iron, vitamin B12, and folate-rich foods.
2. Avoid Iron Blockers: Tea, coffee, and calcium-rich foods can reduce iron absorption if taken with meals.
3. Stay Hydrated: Helps in maintaining healthy blood volume.
4. Exercise Moderately: Improves circulation but avoid overexertion if severely anaemic.
Conclusion
Anaemia is manageable once the underlying cause is identified. If you suspect you have anaemia, don’t ignore the symptoms—early diagnosis and treatment can make a big difference in your energy levels and overall health.
Book a consultation with a specialist on Apollo 24|7 today and take the first step towards better health!
By understanding the types and causes of anaemia, you can take proactive steps to stay healthy and energised.
Consult Top Specialists
Consult Top Specialists

Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam
General Practitioner
3 Years • MD (Physician)
Visakhapatnam
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Andhra Pradesh, Visakhapatnam
(100+ Patients)

Dr. Mohammed Huzef Ul Arifeen
General Practitioner
3 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Telangana, Hyderabad

Dr. Praveen Kumar Mukka
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
21 Years • MBBS, MD General Medicine
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Telangana, Hyderabad

Dr. Syed Yaseen Ahmed
General Practitioner
7 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad

Dr. Shesham Srinidhi
General Practitioner
5 Years • MD(physician)
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad
(100+ Patients)