Appendicitis Guide: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Know about appendicitis, causes, symptoms, when to go to er, risk factors, diagnosis and treatment options for appendictis and more.

Written by Dr. Mohammed Kamran
Reviewed by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai MBBS
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction:
A sudden, sharp pain in your abdomen could be a stomach bug or something more serious. Appendicitis is a medical emergency that strikes without warning, causing inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch attached to your large intestine. If left untreated, an inflamed appendix can rupture, spilling dangerous bacteria into your abdominal cavity. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about appendicitis, from recognising the first subtle signs to understanding surgical treatment and recovery. Knowing this information is crucial, as prompt action can prevent serious complications and save lives.
What Is Appendicitis? The Basics Explained
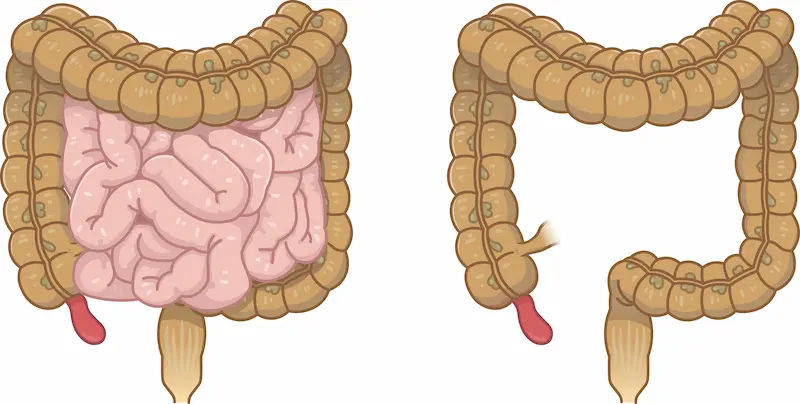
The appendix is a small, finger-shaped tube projecting from the colon on the lower right side of the abdomen. For years, it was considered a useless evolutionary remnant. While its exact mechanism is yet to be known. Studies suggest it may serve as a reservoir for beneficial gut bacteria. Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes blocked, leading to inflammation, bacterial overgrowth, and infection.
The blockage can be caused by hardened stool, enlarged lymphoid follicles, a foreign body, or even a tumour. As pressure builds inside the appendix, blood flow is compromised, and the tissue begins to die. Without timely treatment, the appendix can perforate or burst within 48 to 72 hours of symptoms starting. This is why understanding appendicitis symptoms is a critical piece of health knowledge for everyone.
Consult a Gastroenterologist for Personalised Advice
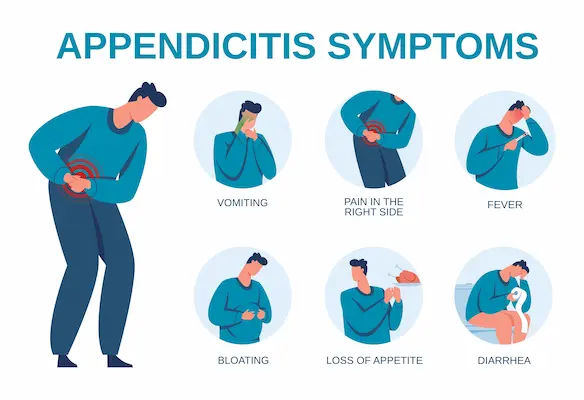
Recognising the Signs: Appendicitis Symptoms
Early detection is the key to a simple recovery. The symptoms of appendicitis can often be mistaken for other ailments, but they follow a distinct and telling pattern.
The Classic Symptom Progression
The most hallmark sign of appendicitis is abdominal pain that begins around the navel or upper abdomen and then, over several hours, migrates to the lower right quadrant, localising at a spot called McBurney's point (midway between the navel and the top of the hip bone). This pain typically worsens with movement, coughing, or sneezing.
Other common symptoms include:
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting (often after the pain begins)
- A low-grade fever that may worsen
- Abdominal swelling
- Inability to pass gas
- A sense that a bowel movement might relieve the discomfort (though it doesn't).
Symptoms in Special Cases: Children and Pregnant Women
Diagnosis can be trickier in young children and pregnant women. A child may only show vague symptoms like a bloated stomach and fatigue. In pregnant women, the pain may be located higher in the abdomen because the appendix is pushed upward by the growing uterus, making it easy to confuse with pregnancy-related discomfort.
When to Go to the ER: Red Flag Signs
If you or a loved one experiences pain that migrates to the lower right abdomen, coupled with any of the symptoms above, seek emergency medical care immediately. Do not eat, drink, or use pain medications, antacids, or laxatives, as these can worsen the situation or complicate diagnosis. Waiting to see if the pain goes away is the most dangerous course of action when dealing with a potential ruptured appendix.
What Causes Your Appendix to Become Inflamed?
The causes include:
Common Culprits: Blockage and Infection
The primary trigger for appendicitis is obstruction. The most frequent causes of this blockage are:
- Appendicoliths (Fecaliths): Hardened pieces of stool that become lodged in the cavity of the appendix.
- Lymphoid Hyperplasia: The wall of the appendix contains lymphoid tissue that can swell in response to infections elsewhere in the body (e.g., gastrointestinal viruses or other infections), blocking the opening.
- Foreign Bodies & Parasites: Less commonly, foreign objects, seeds, or even intestinal worms can cause an obstruction.
Once blocked, bacteria that normally reside inside the appendix multiply rapidly, leading to infection, inflammation, and pus formation.
Risk Factors: Are You More Susceptible?
While appendicitis can affect anyone, it most commonly occurs in people between the ages of 10 and 30. A family history of appendicitis may slightly increase your risk. There is no proven link to diet or specific lifestyle factors, though some studies suggest a diet low in fibre and high in processed foods might contribute to the formation of fecaliths.
How is Appendicitis Diagnosed? The Medical Process
Diagnosing appendicitis can be challenging because its symptoms overlap with many other conditions. Doctors use a multi-pronged approach.
The Physical Exam: Key Tests Doctors Use
A physician will first press on your abdomen to check for tenderness and rigidity. They will look for specific signs:
- Rebound Tenderness: Pain that is worse when the doctor quickly releases pressure than when pressing down.
- Rovsing's Sign: Pain in the lower right abdomen when pressure is applied to the lower left side.
- Psoas Sign: Pain when extending the right hip, suggesting an inflamed appendix is irritating the psoas muscle.
Imaging Tests: CT Scans, Ultrasounds, and MRIs
To confirm their suspicion, doctors will often order imaging.
- Abdominal CT Scan: The most common and accurate test for diagnosing appendicitis in adults, providing detailed cross-sectional images.
- Ultrasound: Often used for children and pregnant women to avoid radiation exposure. It can effectively identify an inflamed appendix.
- MRI: Another radiation-free option, primarily used for pregnant women when ultrasound results are inconclusive.
Ruling Out Other Conditions: Differential Diagnosis
- The doctor must rule out other issues that mimic appendicitis pain, such as kidney stones, urinary tract infections, ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancy, or inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease). Blood tests will also show an elevated white blood cell count, indicating infection.
The Gold Standard: Appendicitis Treatment Options
The standard treatment for appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix, known as an appendectomy.
Appendectomy: Surgical Removal Explained
This is one of the most common emergency surgeries performed. The surgery is performed under general anaesthesia and is highly effective. The urgency of the surgery depends on whether the appendix has ruptured.
Laparoscopic vs. Open Surgery: What's the Difference?
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy: The most common approach. The surgeon makes several small incisions and uses a camera (laparoscope) and specialised instruments to remove the appendix. Benefits include less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery.
- Open Appendectomy (Laparotomy): Requires a single larger incision in the lower right abdomen. This approach is necessary if the appendix has ruptured and the infection has spread, allowing the surgeon to clean the abdominal cavity thoroughly.
Antibiotics Alone: Is Non-Surgical Treatment an Option?
- In some very specific cases of uncomplicated appendicitis, treatment with intravenous antibiotics alone may be an option. However, current research shows a high recurrence rate (nearly 40% within a year), making surgery the definitive and most recommended treatment to prevent future episodes and complications.
The Road to Recovery: What to Expect After Surgery
Recovery time depends on the type of surgery and whether the appendix ruptured.
Immediate Post-Op: Hospital Stay and Pain Management
- After a laparoscopic procedure, you may go home within 24 hours. An open surgery or a case involving a rupture may require a hospital stay of 2 to 4 days to receive intravenous antibiotics. Pain is managed with medication.
Healing at Home: Activity and Diet Guidelines
It includes:
- Activity: Avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and intense exercise for 3 to 5 days after laparoscopic surgery or 10 to 14 days after open surgery. Walking is encouraged to prevent blood clots and aid healing.
- Diet: Start with clear liquids and gradually advance to bland, easy-to-digest foods like toast, rice, and bananas. Constipation is common after surgery, so drink plenty of water and consider a stool softener if needed.
Potential Complications to Watch For
- While rare, contact your doctor if you experience signs of infection: fever, redness/swelling at the incision site, worsening abdominal pain, or persistent nausea/vomiting. These could indicate an abscess or other complication.
Can Appendicitis Be Prevented?
There is no guaranteed way to prevent appendicitis. However, some evidence suggests that a diet high in fibre from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help reduce the risk by promoting regular bowel movements and minimising the chance of fecalith formation. Ultimately, the best "prevention" is awareness knowing the early signs of appendicitis and seeking immediate medical care.
Conclusion: Listen to Your Body and Act Fast
Appendicitis is a swift and serious condition, but it is also highly treatable when caught early. The most important takeaway is to trust your instincts. If you experience abdominal pain that starts around your navel and shifts to your lower right side, don't wait it out. Seek emergency care immediately. Prompt diagnosis and treatment via an appendectomy are incredibly effective, and most people make a full recovery with no long-term consequences. Your health is paramount listening to your body's signals is the first and most crucial step in protecting it.
Consult a Gastroenterologist for Personalised Advice
Consult a Gastroenterologist for Personalised Advice

Dr Bhargav Vuppumalla
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS MD GENERAL MEDICINE
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr. Shivaraj Afzalpurkar
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MD General medicine (Gold medalist), DrNB (Gastroenterology), MNAMS
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Amit Pandita
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS. MD (INTERNAL MEDICINE) DrNB (GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
Dr. Amit Pandita
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS,MD(GENERAL MEDICINE),DNB(MEDICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY)
Noida
Apollo Hospitals Sector 26, Noida

Prof. Dr. M S Revathy
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
22 Years • MBBS, MD(GM), DM (Med. Gastro)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(250+ Patients)
Consult a Gastroenterologist for Personalised Advice

Dr Bhargav Vuppumalla
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS MD GENERAL MEDICINE
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr. Shivaraj Afzalpurkar
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MD General medicine (Gold medalist), DrNB (Gastroenterology), MNAMS
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Amit Pandita
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS. MD (INTERNAL MEDICINE) DrNB (GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
Dr. Amit Pandita
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS,MD(GENERAL MEDICINE),DNB(MEDICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY)
Noida
Apollo Hospitals Sector 26, Noida

Prof. Dr. M S Revathy
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
22 Years • MBBS, MD(GM), DM (Med. Gastro)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(250+ Patients)