Types and Symptoms of Arteriosclerosis
Know and learn what arteriosclerosis is, its types, symptoms, management and prevention.

Written by Dr. Vasanthasree Nair
Reviewed by Dr. J T Hema Pratima MBBS, Fellowship in Diabetes Mellitus
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
Introduction
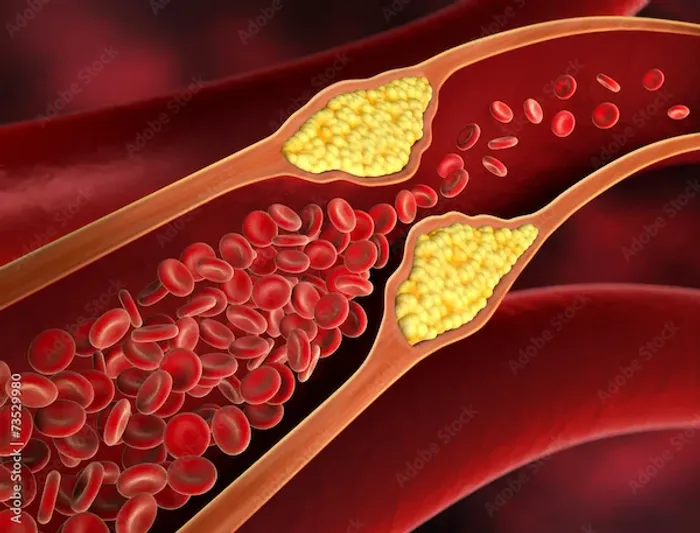
Arteriosclerosis is a common condition that affects the arteries—the blood vessels responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood from your heart to the rest of your body. Over time, these arteries can become stiff, narrow, or blocked, which can lead to serious health problems.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with arteriosclerosis, it’s important to understand the condition, risks, treatment and management.
The article will discuss what arteriosclerosis is, its types, causes, management, prevention and treatment.
What Is Arteriosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis is a broad term that refers to the thickening and hardening of the arteries. This condition restricts blood flow, making it harder for your heart to pump blood efficiently. With time, reduced blood flow can lead to complications like heart disease, stroke, or even organ damage.
There are various types of arteriosclerosis, each affecting the arteries in slightly different ways.
Types of Arteriosclerosis
1. Atherosclerosis
This is the most common type, where fatty deposits (plaque) build up inside the artery walls. Over time, these plaques harden and narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow. If a plaque ruptures, it can cause a blood clot, leading to a heart attack or stroke.
2. Arteriolosclerosis
This type affects the smaller arteries (arterioles) and is often linked to high blood pressure or diabetes. The walls of these tiny arteries thicken, reducing blood flow to organs like the kidneys, eyes, and brain.
3. Mönckeberg’s Arteriosclerosis
Unlike atherosclerosis, this type involves calcium deposits in the middle layer of the artery walls. While it doesn’t usually block blood flow, it makes the arteries stiff and less flexible.
Common Symptoms of Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis often develops slowly, and many people don’t notice symptoms until the condition is advanced. The symptoms depend on which arteries are affected:
1. Coronary Artery Disease (Heart Arteries)
Chest pain (angina) – A feeling of pressure, tightness, or discomfort in the chest.
Shortness of breath – Mainly during physical activity.
Heart attack – Sudden, severe chest pain, nausea, sweating, or pain radiating to the arm, jaw, or back.
2. Carotid Artery Disease (Neck Arteries Leading to the Brain)
Weakness or numbness – Usually on one side of the body.
Slurred speech or difficulty speaking (signs of a stroke).
Sudden vision problems – Blurred or lost vision in one eye.
3. Peripheral Artery Disease (Legs and Arms)
Leg pain while walking – Often relieved by rest (claudication).
Coldness or numbness in the legs or feet.
Slow-healing wounds on the feet or legs.
4. Kidney Artery Disease
High blood pressure that’s hard to control.
Kidney failure – Swelling in legs, fatigue, or changes in urination.
What Causes Arteriosclerosis?
Several factors contribute to the development of arteriosclerosis, including:
High cholesterol (especially LDL or "bad" cholesterol).
High blood pressure (puts extra strain on artery walls).
Smoking (damages the inner lining of arteries).
Diabetes (high blood sugar harms blood vessels).
Obesity and lack of exercise.
Family history of heart disease.
Ageing (arteries naturally stiffen over time).
Consult Specialist Cardiologist expert advice for Treatment of Arteriosclerosis.
How to Manage and Prevent Arteriosclerosis?
While some risk factors (like age and genetics) can’t be changed, many lifestyle changes can help slow or even reverse arteriosclerosis:
1. Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet
Reduce saturated fats (found in fried foods, red meat, and full-fat dairy).
Increase fibre intake (whole grains, fruits, vegetables).
Choose healthy fats (olive oil, nuts, fish rich in omega-3s).
Limit salt to control blood pressure.
2. Stay Active
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise (walking, swimming, cycling) most days.
Exercise improves circulation and helps maintain a healthy weight.
3. Quit Smoking
Smoking damages arteries and speeds up plaque buildup.
Seek support from doctors or smoking cessation programs if needed.
4. Manage Chronic Conditions
Keep blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes under control with medications if prescribed.
Regular check-ups help monitor these conditions.
5. Reduce Stress
Chronic stress can raise blood pressure.
Try relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
6. Get Regular Health Screenings
Blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar tests can catch problems early.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience any symptoms like chest pain, leg pain while walking, sudden weakness, or vision changes, seek medical help immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent serious complications.
Final Thoughts
Arteriosclerosis is a serious but manageable condition. By understanding the types, recognising symptoms early, and making healthy lifestyle changes, you can protect your heart and blood vessels. Small steps today can lead to a healthier tomorrow!
Consult Specialist Cardiologist expert advice for Treatment of Arteriosclerosis.
Consult Specialist Cardiologist expert advice for Treatment of Arteriosclerosis.

Dr. Tripti Deb
Cardiologist
40 Years • MBBS, MD, DM, FACC, FESC
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
Dr Moytree Baruah
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS, PGDCC
Guwahati
Apollo Clinic Guwahati, Assam, Guwahati

Dr. Zulkarnain
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS, PGDM, FFM
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(175+ Patients)

Dr. Vijayachandra Reddy Y
Cardiologist
27 Years • MD, DM, MRCP, FACC, FCSI, CCDS, FSCAI
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(1275+ Patients)