Difference Between Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Confused between osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis? Learn the key differences in causes, symptoms, and treatments to manage joint pain effectively.

Written by Dr. J T Hema Pratima
Reviewed by Dr. D Bhanu Prakash MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Last updated on 5th Aug, 2025

Arthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. However, not all arthritis is the same. The two most common types—Osteoarthritis (OA) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)—have different causes, symptoms, and treatments. If you or a loved one is experiencing joint pain, understanding these differences can help in managing the condition better.
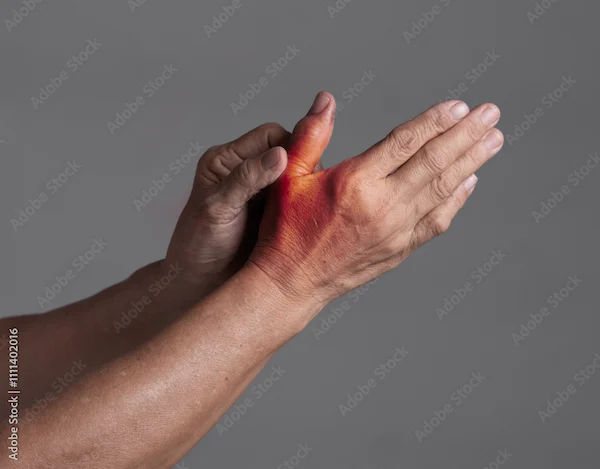
What is Osteoarthritis (OA)?
Osteoarthritis is often called "wear-and-tear" arthritis because it occurs due to the gradual breakdown of cartilage (the cushion between bones) over time. It usually affects older adults but can also develop due to joint injuries or obesity.
Common Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Joint pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest.
Stiffness, especially after waking up or sitting for long periods.
Swelling around the affected joints.
Reduced flexibility and a grating sensation when moving the joint.
Bony growths (spurs) may develop, causing visible joint deformities.
Joints Most Affected by OA
Knees
Hips
Hands (especially fingers and thumbs)
Spine
Causes & Risk Factors
Aging – Cartilage naturally wears down over time.
Joint injuries – Previous fractures or ligament tears increase risk.
Obesity – Extra weight puts stress on joints.
Genetics – Family history may play a role.
How to Manage Osteoarthritis
Exercise regularly (low-impact activities like swimming, walking).
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint stress.
Use hot/cold therapy for pain relief.
Take pain relievers (like acetaminophen or NSAIDs) as prescribed.
Physical therapy can improve joint function.
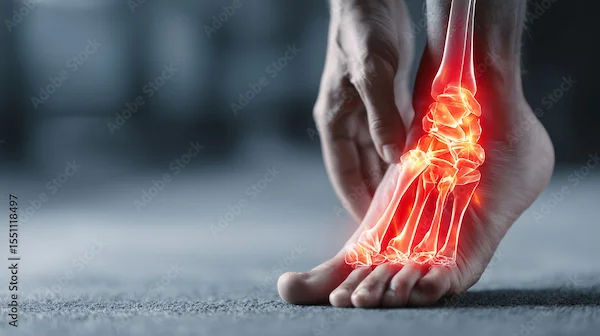
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Unlike OA, Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own joints, causing inflammation. RA can affect people at any age, even young adults.
Consult Top Specialist
Common Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Symmetrical joint pain (both sides of the body, e.g., both hands).
Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes.
Fatigue, fever, and general weakness.
Swollen, warm, and tender joints.
Progressive joint damage leading to deformities if untreated.
Joints Most Affected by RA
Hands and wrists
Feet
Knees
Shoulders
Elbows
Causes & Risk Factors
Autoimmune response – The immune system attacks joint lining (synovium).
Genetics – Family history increases risk.
Smoking – Can trigger RA in susceptible individuals.
Hormonal changes – More common in women.
How to Manage Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early diagnosis & treatment are crucial to prevent joint damage.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) slow disease progression.
Anti-inflammatory medications reduce pain and swelling.
Regular exercise (gentle stretching, yoga) helps maintain mobility.
Healthy diet (anti-inflammatory foods like fish, nuts, and leafy greens).
Stress management (RA flare-ups can worsen with stress).
Key Differences Between OA and RA
| Factor | Osteoarthritis (OA) | Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) |
| Cause | Wear-and-tear of cartilage | Autoimmune disorder |
| Age of Onset | Usually after 50 | Can occur at any age (even 30s-40s) |
| Joint Involvement | Asymmetrical (one side) | Symmetrical (both sides) |
| Morning Stiffness | Less than 30 minutes | More than 30 minutes |
| Systemic Symptoms | No fever/fatigue | Fatigue, fever, weakness |
| Treatment Focus | Pain management, mobility | Reducing inflammation, slowing disease |
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience persistent joint pain, swelling, or stiffness, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis. Early treatment can prevent further damage, especially in RA.
Diagnostic Tests May Include:
X-rays or MRI (to check joint damage).
Blood tests (for RA markers like rheumatoid factor).
Joint fluid analysis (to rule out infections or gout).
If you suspect arthritis, Apollo 24|7 offers expert consultations and diagnostic tests to help you get the right treatment.
Conclusion
While both Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis cause joint pain, they are different conditions requiring different treatments. OA is a degenerative disease linked to aging, while RA is an autoimmune disorder needing early intervention.
Key Takeaways:
OA: Wear-and-tear, affects older adults, manageable with lifestyle changes.
RA: Autoimmune, affects any age, needs medical treatment to prevent damage.
Early diagnosis improves quality of life, don’t ignore persistent joint pain.
If you need guidance, book a consultation with a rheumatologist or orthopedic specialist on Apollo 24|7 for personalized care. Stay active, eat well, and take control of your joint health!
Consult Top Specialist
Consult Top Specialist

Dr. Suvadeep Sen
Critical Care Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, MD, FNB (CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE), EDIC
Mumbai
Apollo Hospitals CBD Belapur, Mumbai
Dr. Gaddam Manoj
General Practitioner
1 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Aaradhya clinic, Hyderabad

Dr. Mainak Baksi
General Practitioner
13 Years • MBBS , MD (MPH)
Howrah
Mainak Baksi Clinic, Howrah
(50+ Patients)

Dr Summaiya Banu
General Practitioner
8 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad
(175+ Patients)

Dr. M L Ezhilarasan
General Practitioner
6 Years • MBBS
Visakhapatnam
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Andhra Pradesh, Visakhapatnam