A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Back Pain
Discover the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for back pain. Learn effective management strategies and prevention tips for a healthier back.

Written by
Last updated on 3rd Jul, 2025
Introduction
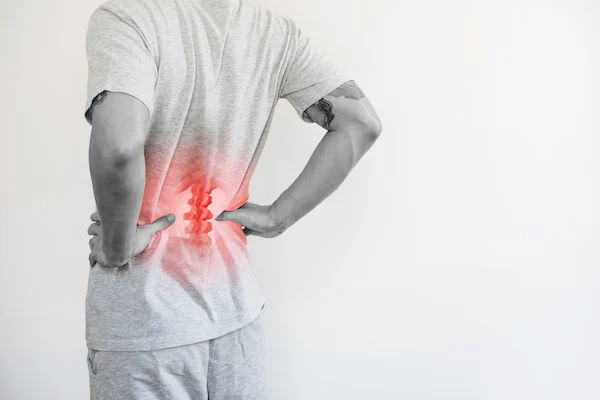
Back pain is a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It can range from a dull ache to a sharp, debilitating pain that interferes with daily activities. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for back pain is essential for anyone who has experienced or wants to prevent it. In this blog, we will explore the nature of back pain, its causes, how to manage it, and strategies for prevention.
What is Back Pain?
Back pain is a term used to describe discomfort or pain in the back. It can occur in various areas, including the lower, middle, and upper back. It can be classified into two main types: acute and chronic. Acute back pain typically lasts a few days to a few weeks and is often the result of an injury or strain. Chronic back pain, on the other hand, persists for three months or longer and may be due to underlying health conditions.
According to statistics, back pain is one of the leading causes of disability worldwide. It can affect people of all ages, but it is more common in adults aged 30 to 50. Factors such as lifestyle, occupation, and overall health can influence the likelihood of experiencing back pain.
Anatomy of the Back
It is helpful to know a bit about the anatomy of the back to understand back pain better. The spine comprises 33 vertebrae stacked on each other, forming a flexible column. Between these vertebrae are intervertebral discs, which act as shock absorbers and allow for movement. The spine also houses the spinal cord, a bundle of nerves that transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
When any of these structures are damaged or strained, it can lead to pain. For example, a herniated disc can press on nearby nerves, causing pain that radiates down the legs. Similarly, muscle strains or ligament sprains can result from lifting heavy objects or sudden movements.
Common Causes of Back Pain
There are many potential causes of back pain; understanding these can help in prevention and treatment. Some of the most common causes include:
Muscle or Ligament Strain: Muscle or ligament strain is one of the most frequent causes of back pain. This can occur due to heavy lifting, awkward movements, or sudden twists. Over time, poor posture can also contribute to muscle strain.
Bulging or Ruptured Discs: The intervertebral discs can become damaged due to wear and tear, leading to bulging or ruptured discs. When this happens, the disc can press on nearby nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs.
Arthritis: Arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, can affect the lower back. This condition causes the cartilage that cushions the joints to wear down, leading to pain and stiffness.
Skeletal Irregularities: Conditions such as scoliosis and an abnormal spine curvature can lead to back pain. These irregularities can place additional stress on the back muscles and ligaments.
Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis weakens bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. Compression fractures in the spine can result in significant back pain.
Other Factors: Age, lifestyle, and occupation can also contribute to back pain. For instance, individuals who sit for long periods or engage in repetitive movements may be at a higher risk.
Recognising Symptoms
Back pain can manifest in various ways. Common symptoms include:
Dull, aching pain in the lower back
Sharp or stabbing pain
Pain that radiates down the legs
Stiffness or limited range of motion
Muscle spasms
It is essential to pay attention to these symptoms. If back pain persists for over a few weeks, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, unexplained weight loss, or bowel or bladder issues, it is crucial to seek medical attention.
Diagnostic Procedures
If you experience persistent back pain, a healthcare professional may perform a physical examination and ask about your medical history. They may also recommend diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause of your pain. Standard diagnostic procedures include imaging tests like:
X-rays: These can help identify fractures or structural issues in the spine
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This test provides detailed images of soft tissues, including discs and nerves, helping to identify herniated discs or other issues
CT Scans: These can offer a more detailed view of the spine and surrounding structures
In some cases, nerve studies or blood tests may be necessary to rule out other conditions or assess nerve function.
Treatment Options
Once the cause of back pain is identified, various treatment options are available. These can be broadly categorised into conservative treatments, alternative therapies, and surgical options.
1. Conservative Treatments
Non-surgical treatments can effectively manage back pain and improve mobility.
Rest and Activity Modification: Taking a break from activities that aggravate the pain is essential. However, prolonged bed rest is not recommended, as it can lead to stiffness and muscle weakness. Gradually returning to normal activities is crucial.
Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a tailored exercise program to strengthen the back and core muscles, improve flexibility, and promote better posture. This can significantly reduce pain and prevent future episodes.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, muscle relaxants or prescription medications may be necessary.
Heat and Cold Therapy: Heat can help relax tense muscles, while cold packs can reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain. Alternating between the two can provide relief.
2. Surgical Options
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be considered. Surgical options can include:
Discectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of a herniated disc to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves.
Spinal Fusion: This surgery involves joining two or more vertebrae to provide stability and reduce pain.
Laminectomy: This procedure removes a portion of the vertebra to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Discussing the risks and benefits of surgery with a healthcare professional is essential, as surgery is typically considered a last resort.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing back pain is often more effective than treating it. Here are some strategies to help reduce the risk:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Making simple lifestyle changes can go a long way in preventing back pain.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put additional strain on the back. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight.
Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens the muscles supporting the back. Focus on exercises that improve core strength, flexibility, and overall fitness.
Proper Posture: Maintaining good posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can significantly reduce the risk of back pain. Be mindful of your body mechanics throughout the day.
2. Workplace Ergonomics
A well-designed workspace can prevent strain and discomfort.
Ergonomic Workspace: An ergonomic workspace can help prevent back pain. Ensure your chair supports your lower back and your computer screen is at eye level to avoid straining your neck.
Take Breaks: If you sit long, take regular breaks to stand, stretch, and move around. This can help alleviate tension and improve circulation.
3. Home Care Tips
Practising safe lifting techniques, using a supportive mattress, and adopting proper sleeping positions can significantly reduce strain on the back and promote spinal health in daily life.
Safe Lifting Techniques: When lifting heavy objects, bend at the knees and keep the object close to your body. Avoid twisting your back while lifting.
Supportive Mattress: A good quality mattress with adequate support can help maintain proper spinal alignment during sleep. Consider your sleeping position when choosing a mattress.
Proper Sleeping Positions: Sleeping on your side with a pillow between your knees can help maintain spinal alignment. Placing a pillow under your knees can also provide support if you prefer sleeping on your back.
Living with Back Pain
For those who experience chronic back pain, coping mechanisms and support systems are essential.
Psychological Aspects: Chronic pain can affect mental health. It is essential to address the psychological aspects of living with pain. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Mindfulness can help individuals focus on the present moment and reduce pain-related anxiety. Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can also be beneficial.
Conclusion
Back pain is a prevalent issue that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding its causes, recognising symptoms, and exploring treatment options are crucial steps in managing this condition. By implementing prevention strategies and seeking support, individuals can take control of their back health and improve their quality of life. If you or someone you know is struggling with persistent back pain, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Consult Top Orthopaedicians
Consult Top Orthopaedicians
Dr. Anil Sharma
Orthopaedician
42 Years • MBBS, MS Orthopedics
New Delhi
AAKASH MEDSQUARE, New Delhi

Dr. Anil Pradeep Jadhav
Orthopaedician
23 Years • MBBS MS (Ortho)
Nashik
Apollo Hospitals Nashik, Nashik
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Manoj Dinkar
Orthopaedician
15 Years • MBBS, Dip (Orthopaedics)
New Delhi
THE DOCTORS NESST, New Delhi

Dr. Pradeep Lucas
Orthopaedician
7 Years • MBBS, Diploma in Orthopaedics, Fellowship in DFSI
Bengaluru
Revival Multispeciality Clinic, Bengaluru

Dr. Mriganka Ghosh
Orthopaedician
11 Years • MD (Physician), DNB (Orthopaedics)
Howrah
Dr Mriganka Mouli Ghosh, Howrah