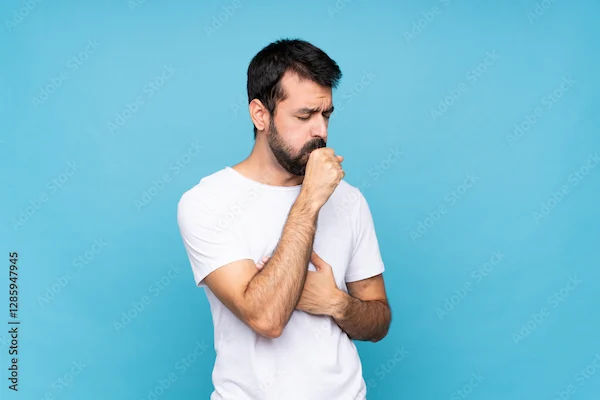
Whooping Cough Overview: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments
Learn about whooping cough (pertussis), including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Understand how it spreads, who is at risk, and the importance of vaccination and early care

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. Mohammed Kamran MBBS, FIDM
Last updated on 26th Aug, 2025
.webp?tr=q-80,f-webp,w-350,dpr-2,c-at_max 700w)
Whooping cough, also known as pertussis, is a highly contagious respiratory infection that can cause severe coughing fits. It gets its name from the "whooping" sound people often make when gasping for air after a coughing episode. While it can affect people of all ages, it is especially dangerous for infants and young children.
In this article, we’ll discuss the symptoms, causes, treatments, and prevention tips for whooping cough in simple terms so you can stay informed and take the right steps if needed.
What is Whooping Cough?
Whooping cough is caused by a type of bacteria called Bordetella pertussis. This infection spreads easily through coughing and sneezing, making it highly contagious. The illness progresses in stages, starting with mild cold-like symptoms before developing into severe coughing spells.
Consult a Top Pulmonologist
Why is it Dangerous?
- Whooping cough can be dangerous in the following cases,
- In babies, whooping cough can lead to serious complications like pneumonia, seizures, or even death.
- Older children and adults may experience prolonged coughing that disrupts daily life.
- Unvaccinated individuals are at higher risk of severe illness.
Symptoms of Whooping Cough
Whooping cough symptoms develop in stages:
1. Early Stage (1-2 weeks)
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Mild fever
- Mild, occasional cough
- Sneezing and watery eyes
At this stage, it can be mistaken for a common cold.
2. Severe Stage (1-6 weeks or longer)
- Intense coughing fits that may end with a "whooping" sound when breathing in
- Vomiting after coughing
- Exhaustion from coughing episodes
- Difficulty breathing, especially in infants
3. Recovery Stage (weeks to months)
- Coughing gradually decreases but may linger for weeks.
- Fatigue and weakness may persist.
Note: Infants may not cough but instead have pauses in breathing (apnea), which is a medical emergency.
Causes of Whooping Cough
Whooping cough is caused by the Bordetella pertussis bacteria. It spreads when an infected person coughs or sneezes, releasing tiny droplets into the air. You can get infected by:
- Breathing in contaminated air
- Touching a surface with bacteria and then touching your mouth or nose
Who is at Risk?
Below are the people at risk of whooping cough,
- Unvaccinated or partially vaccinated infants and children (most vulnerable)
- Teens and adults whose vaccine protection has weakened over time
- Pregnant women (can pass it to newborns)
- People with weakened immune systems
How is Whooping Cough Diagnosed?
If you or your child has persistent coughing, especially with a "whooping" sound, consult a doctor. Diagnosis may involve:
- Medical history and symptom review
- Nasal or throat swab test (to detect bacteria)
- Blood tests (to check for infection)
Early diagnosis helps in managing symptoms and preventing spread.
Treatment for Whooping Cough
Below are a few treatment options for whooping cough,
1. Antibiotics
- Doctors prescribe antibiotics (like azithromycin or erythromycin) to kill the bacteria and reduce contagiousness.
- Starting treatment early can shorten illness duration.
2. Home Care & Symptom Relief
- Stay hydrated – Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Use a humidifier – Moist air helps ease coughing.
- Rest – Avoid exertion to reduce coughing fits.
- Small, frequent meals – Helps if vomiting occurs after coughing.
3. Hospital Care (for severe cases)
Infants or those with breathing difficulties may need hospitalization for:
- Oxygen therapy
- IV fluids
- Monitoring for complications
Prevention: How to Protect Yourself & Others
Below are a few ways to prevent whooping cough,
1. Vaccination is Key
- DTaP vaccine – Given to children at 2, 4, 6 months, and boosters at 15-18 months and 4-6 years.
- Tdap vaccine – Recommended for teens and adults (especially pregnant women) to maintain immunity.
2. Practice Good Hygiene
- Wash hands frequently.
- Cover your mouth when coughing or sneezing.
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals.
3. Protect Newborns
- Pregnant women should get the Tdap vaccine during the third trimester to pass antibodies to the baby.
- Keep infants away from people with cough or cold symptoms.
When to See a Doctor?
Seek medical help if:
- A cough lasts more than two weeks.
- Coughing causes vomiting or difficulty breathing.
- An infant has pauses in breathing or turns blue.
If you suspect a whooping cough, consult a doctor immediately. Early treatment can prevent complications.
Need Help?
If you’re concerned about whooping cough symptoms, book a consultation with an expert on Apollo 24|7 for quick diagnosis and treatment. Stay safe and protect your family with timely vaccinations!
Final Thoughts
Whooping cough is a serious but preventable illness. Vaccination remains the best defense, especially for infants and pregnant women. If you or a loved one has persistent coughing, don’t ignore it, early medical care can make a big difference.
Consult a Top Pulmonologist
Consult a Top Pulmonologist

Dr. P Sravani
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
3 Years • MBBS, MD
Visakhapatnam
Apollo Clinic Vizag, Visakhapatnam

Dr. Hyder
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS, MD (PULMONOLOGY)
Guntur
Kalam chest and multi-speciality clinic, Guntur

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(125+ Patients)

Dr. K Prasanna Kumar Reddy
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
16 Years • MBBS, DTCD (TB&CHEST), DNB (PULM MED), FCCP
Hyderabad
Apollo Medical Centre Kondapur, Hyderabad
Dr. Aakanksha Chawla
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
9 Years • MD (Pulmonary Medicine), IDCCM, IFCCM (Indian Fellowship in Critical Care Medicine)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(250+ Patients)
Consult a Top Pulmonologist

Dr. P Sravani
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
3 Years • MBBS, MD
Visakhapatnam
Apollo Clinic Vizag, Visakhapatnam

Dr. Hyder
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS, MD (PULMONOLOGY)
Guntur
Kalam chest and multi-speciality clinic, Guntur

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(125+ Patients)

Dr. K Prasanna Kumar Reddy
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
16 Years • MBBS, DTCD (TB&CHEST), DNB (PULM MED), FCCP
Hyderabad
Apollo Medical Centre Kondapur, Hyderabad

Dr. Aakanksha Chawla
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
9 Years • MD (Pulmonary Medicine), IDCCM, IFCCM (Indian Fellowship in Critical Care Medicine)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(250+ Patients)

.webp)

