Sugar Test Names and Types Explained
Confused about sugar tests? Learn the names, types, and what each test measures, from fasting blood sugar to HbA1c, to manage or detect diabetes early and effectively.
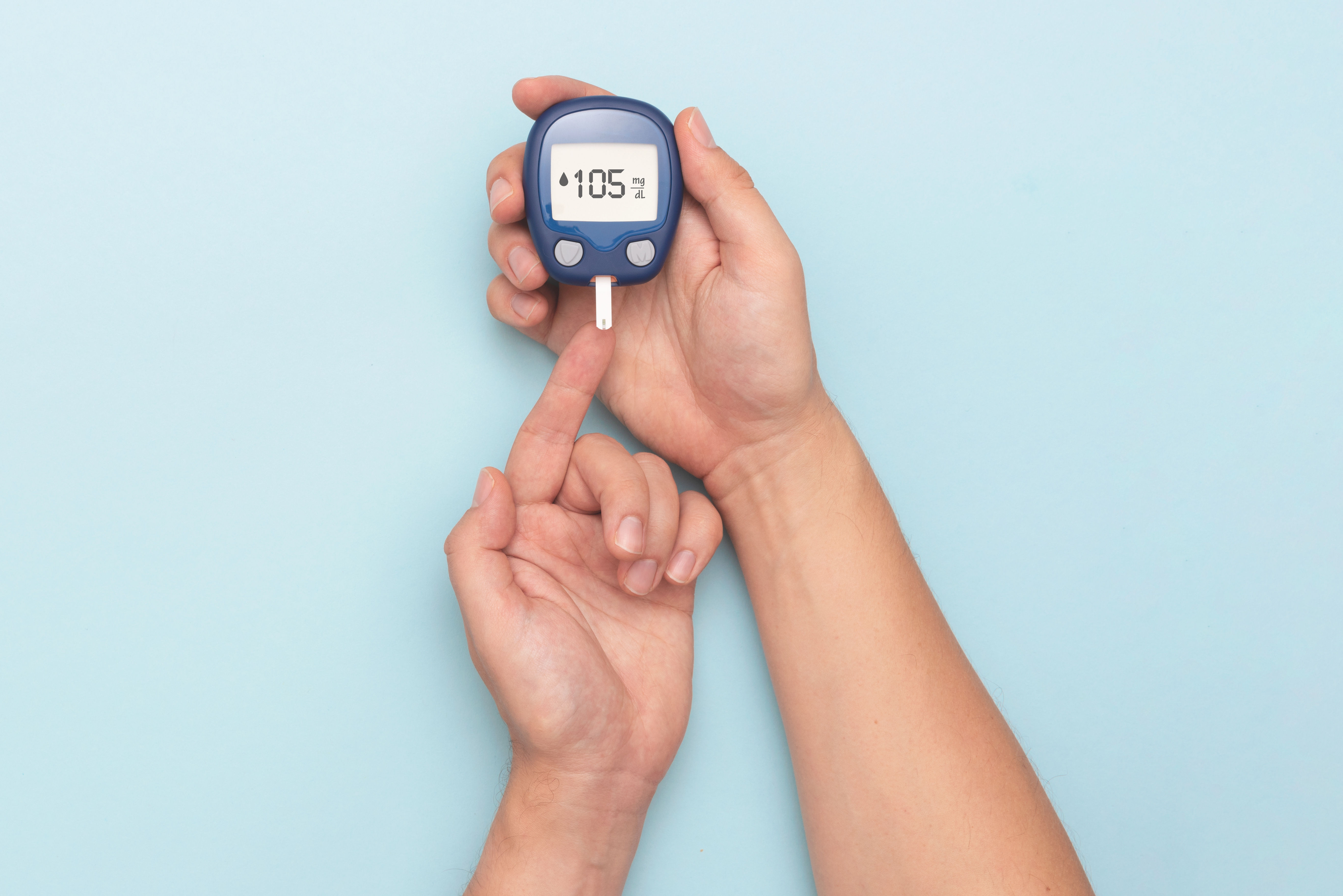


If you or a loved one has been advised to get a sugar test, you might be wondering what these tests are, why they’re needed, and what the different types mean. Understanding these tests can help you take better control of your health. Let’s break it down in simple terms.
Why Are Sugar Tests Important?
Sugar (glucose) tests help determine how well your body processes sugar, which is crucial for diagnosing and managing diabetes or prediabetes. High blood sugar levels over time can damage your organs, nerves, and blood vessels. Early detection through these tests allows for timely treatment and lifestyle changes.
Common Types of Sugar Tests
Here are the most common blood sugar tests you may come across:
1. Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Test
What it measures: Your blood sugar level after fasting (not eating) for at least 8 hours.
Why it’s done: Helps diagnose diabetes or prediabetes.
Normal range: 70–99 mg/dL
Prediabetes: 100–125 mg/dL
Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
Tip: Schedule this test in the morning after an overnight fast for accurate results.
2. Postprandial Blood Sugar (PPBS) Test
What it measures: Blood sugar levels 2 hours after eating a meal.
Why it’s done: Checks how your body processes sugar after food.
Normal range: Below 140 mg/dL
Prediabetes: 140–199 mg/dL
Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or higher
Tip: Eat a normal meal before this test—no extreme overeating or fasting.
3. Random Blood Sugar (RBS) Test
What it measures: Blood sugar level at any time of the day, regardless of meals.
Why it’s done: Helps detect high blood sugar in emergencies.
Normal range: Below 200 mg/dL
Diabetes concern: 200 mg/dL or higher with symptoms (like excessive thirst, frequent urination).
4. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
What it measures: How your body handles a glucose load over 2–3 hours.
Why it’s done: Often used to diagnose gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy).
Process:
Fast overnight.
Drink a sugary solution.
Blood is tested at intervals (usually 1, 2, and sometimes 3 hours).
Normal range (after 2 hours): Below 140 mg/dL
Prediabetes: 140–199 mg/dL
Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or higher
Tip: Avoid heavy exercise before this test, as it can affect results.
5. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Test
What it measures: Average blood sugar levels over the past 2–3 months.
Why it’s done: Gives a long-term picture of blood sugar control.
Normal range: Below 5.7%
Prediabetes: 5.7%–6.4%
Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
Tip: No fasting is needed for this test—it can be done anytime.
Get Your Health Assessed Here
6. Glycated Albumin (GA) or Fructosamine Test
What it measures: Average blood sugar over 2–3 weeks (shorter-term than HbA1c).
Why it’s done: Useful for people with haemoglobin disorders (like anaemia) where HbA1c may not be accurate.
Who Should Get Tested?
You may need a sugar test if you have:
Symptoms of diabetes (frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, blurred vision).
A family history of diabetes.
High blood pressure or cholesterol.
Been diagnosed with prediabetes.
Gestational diabetes risk (pregnant women).
How to Prepare for a Sugar Test?
Follow fasting instructions if required.
Stay hydrated (water is fine).
Avoid heavy exercise before the test.
Inform your doctor about any medications you’re taking.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
If your test results indicate high blood sugar, here are some ways to manage it:
Diet Tips:
Eat more fibre (whole grains, vegetables, fruits).
Avoid sugary drinks and processed foods.
Choose lean proteins (fish, chicken, lentils).
Lifestyle Changes:
Exercise regularly (walking, yoga, swimming).
Maintain a healthy weight.
Get enough sleep (7–8 hours).
Medical Care:
Take prescribed medications (if needed).
Monitor blood sugar levels at home (if advised).
Regular follow-ups with your doctor.
When to See a Doctor?
If your test results show high blood sugar, consult a doctor immediately. Early intervention can prevent complications like heart disease, kidney damage, or nerve problems.
Book a Sugar Test with Apollo 24|7
Worried about your sugar levels? Apollo 24|7 offers convenient at-home blood sugar tests and expert consultations. You can:
Schedule a test from the comfort of your home.
Consult a doctor online for personalised advice.
Conclusion
Understanding sugar tests helps you stay informed and proactive about your health. If you have any concerns, don’t hesitate to get tested and seek medical advice.
Get Your Health Assessed Here