Understanding Childhood Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Treatment, And Management
Childhood type 1 diabetes is a rapidly developing autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Learn about its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.

Written by
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
Type 1 childhood diabetes develops when a child's body stops producing insulin, requiring insulin pumps or injections. In this condition, families learn to manage it through carbohydrate counting and blood sugar monitoring. While there's no cure, numerous advanced tools have improved the quality and management of life for affected children.
Type 1 childhood diabetes is an autoimmune condition that often develops due to genetics. Read more to get a clear understanding of this condition and learn how to lead a healthier life.
Causes and Risk Factors of Childhood Type 1 Diabetes
Childhood type 1 diabetes develops when the immune system destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Two main factors play a major role which include:
It can be triggered by a genetic condition that affects how the immune system works, causing it to attack insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Environmental factors such as living conditions, infections, or unknown triggers may activate the immune system to destroy beta cells, leading to diabetes.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes in Children
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually begin mildly and worsen over days, weeks, or months as the pancreas produces less insulin. Some of the early signs of type 1 diabetes include:
Frequent urination (bedwetting in children)
Excessive thirst and hunger
Fatigue and blurred vision
Unexplained weight loss
Slow healing of infections or wounds
Here are some of the major differences in symptom presentation in children versus adults listed in the table:
Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes in Children
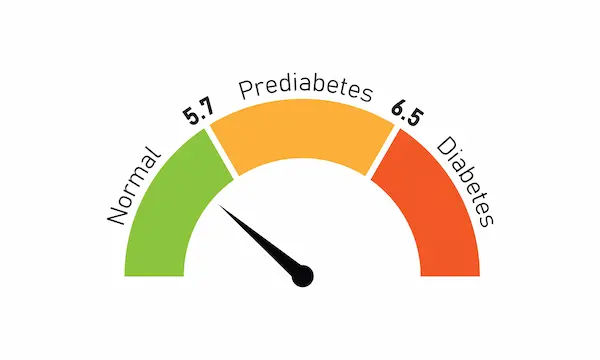
Childhood type 1 diabetes is relatively simple to diagnose. The healthcare provider asks for certain tests in case a child suspects a few symptoms of type 1 diabetes. This mainly includes:
Blood glucose test
Glycosylated hemoglobin test (A1c)
Antibody test
Basic metabolic panel
Urinalysis
Arterial blood gas
It is essential to consult a healthcare provider and get tested for type 1 diabetes as soon as possible. Early diagnosis is important as if it gets delayed, untreated type 1 diabetes can even lead to a life-threatening condition known as DKA (Diabetic Ketoacidosis).
Treatment Options for Childhood Type 1 Diabetes
Children with type 1 diabetes are generally required to take synthetic insulin multiple times a day to manage their blood sugar levels and stay healthy. Managing type 1 childhood diabetes is quite personalised and complex, as many factors affect sugar levels. Some of the essential parts of managing it may involve:
Insulin therapy
Monitoring blood glucose
Counting carbohydrates
Dietary and Lifestyle Recommendations
Proper diet and a better lifestyle play a major role in any diabetes treatment plan. One must focus on balanced nutrition, and regular physical activity can help control blood sugar levels effectively.
Balanced nutrition plays a major role in managing diabetes, but a child doesn’t need a strict diabetes diet.
Their meals should include low-fat and nutritious foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
A dietitian can help create a meal plan that suits the child’s health and preference requirements and also teaches how to count carbohydrates for insulin dosing.
Physical activity is important for children with type 1 diabetes but can also affect blood sugar levels
Adjusting insulin or meals as required and checking blood sugar more often with new physical activities is essential.
Aiming for 60 minutes of physical activity regularly and considering exercising together can help manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Challenges and Management Strategies
Managing childhood type 1 diabetes involves emotional and physical challenges. But, with the proper support and management, these can be handled effectively.
Coping with daily insulin injections in childhood type 1 diabetes can be tough but manageable with proper routine and parental support.
Encouraging the child while making injections comfortable and involving them in their care helps reduce fear. Over time, it becomes a regular part of a child's life.
Type 1 diabetes can affect a child's emotions, causing feelings or irritability of being indifferent due to severe treatment and injections.
Children with diabetes may even face anxiety and depression. It is better to look for signs like behaviour changes or sadness.
Counselling and support groups for children and parents can help cope with these challenges. Proper diabetes management ensures a healthy, long life for a child.
Potential Complications of Childhood Type 1 Diabetes
Since blood circulates throughout the entire body, poorly managed childhood type 1 diabetes with consistently high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can affect multiple parts of the body. Potential complications include:
Eye issues like retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma
Foot problems, including infections and ulcers
Heart disease
High blood pressure
Kidney disease
Oral health problems
Nerve damage (neuropathy)
Skin conditions like infections and dryness
Stroke
Type 1 diabetes is a severe condition that requires daily planning, attention, and care. Here are some preventive measures to help manage all of the complications effectively:
Taking insulin and other medication regularly
Checking blood sugar often
Consulting healthcare providers regularly
Consulting an ophthalmologist
Consulting endocrinologist regularly
Taking care of mental health
Staying educated
Having a sick day plan
Finding community
Technological Advancements in Diabetes Management
Recent innovations have significantly improved the management of diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes. These advanced technologies make managing diabetes more efficient while providing better control over blood sugar levels. Some of the essential advancements include:
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Smart insulin pens
Insulin pumps
Artificial pancreas systems
Closed-loop system
Resources and Support Systems for Families
The American Diabetes Association recognised the education program for diabetes patients to provide the knowledge, confidence, and skills to manage diabetes. Federal law also protects children with diabetes, requiring schools to make necessary adjustments to ensure they receive proper education.
A person can easily reach out to a healthcare provider, diabetes specialist, or dietitian in case they have any concerns. In addition, many support groups for families are available. A person can also find support online through:
ADA (The American Diabetes Association)
JDRF (Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation)
These organisations offer education camps and support programs for children and teens with diabetes.
Conclusion
Understanding childhood type 1 diabetes is essential for managing its causes, treatment, and ongoing care. With proper insulin management, regular monitoring, and a healthy lifestyle, children with type 1 diabetes can lead fulfilling lives. Early detection and consistent support are key to preventing complications and ensuring long-term health.
Consult Top Endocrinologists
Consult Top Endocrinologists

Dr. Anand Ravi
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(175+ Patients)

Dr. Arunava Ghosh
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS,MD(GENL.MED.),DM(ENDOCRINOLOGY)
Kolkata
VDC Clinic, Kolkata
Aditya Singh
Endocrinologist
8 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
Apollo One Electronic City, Bengaluru

Dr Venkata Naga Sai Tribhushan Rambhatla
General Physician
3 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru