Diabetes: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment & Types
Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting blood sugar regulation. Effective treatment includes lifestyle changes, medications, insulin therapy, and regular monitoring. Learn about managing diabetes to improve health and prevent complications.

Written by
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). If left untreated, it can cause serious health complications. Understanding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for diabetes is essential. The condition manifests in various forms, each with unique characteristics and management approaches.
From its causes and symptoms to treatment options, managing diabetes is possible. Discover how the right knowledge and approach can pave the way to a healthier life.
Types of Diabetes & Its Global Prevalence
According to the WHO (World Health Organisation), about 830 million people worldwide are suffering from diabetes. It is a prevalent condition involving the hormone insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Diabetes has two types:
Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong disorder in which the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells.
Type 2 diabetes develops when the body fails to produce enough insulin or when cells do not react properly to insulin.
Another type of temporary diabetes is gestational diabetes, which develops during pregnancy. It often goes away after childbirth.
Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetes
Diabetes is caused by an excess of glucose in the bloodstream, irrespective of its type. However, the explanation for the elevated blood glucose levels varies according to the type of diabetes. Some of the genetic factors that cause diabetes include:
Having a parent, sister, or brother with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Autoimmune disease
Genetic mutations
For type 2 diabetes, lifestyle and dietary habits can have a significant influence on the development. Key factors include:
Unhealthy Diet: Regular consumption of red meat, sweets, and fried foods can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise contributes to obesity and insulin resistance, both of which are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Other common contributing factors for type 2 diabetes include:
Being overweight or obese
Being 45 years of age or older
Having a family member with type 2 diabetes
Exercising less than three times a week
Having nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Giving birth to a child weighing more than 4 kilograms or experiencing gestational diabetes
Symptoms of Diabetes
The severity of diabetes symptoms is directly linked to the level of elevated blood sugar. It is possible that some patients, particularly those with prediabetes, gestational diabetes, or type 2 diabetes, may not have symptoms. The symptoms of type 1 diabetes appear fast and are usually more severe.
Some of the common diabetes symptoms include:
Feeling exhausted and weak
Feeling irritable or experiencing other mood swings
Having blurry eyesight
Feeling thirstier than usual
Urinating frequently
Losing weight without trying
Consult Top Diabetologist
Diagnosis of Diabetes
The diagnostic criteria and tests for type 1, type 2, and prediabetes are as follows:
Older than age 35
Women who have had gestational diabetes
Anyone who is infected with HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
BMI (body mass index) of 25 or higher
Anyone who has been diagnosed with prediabetes
Tests done to diagnose diabetes include:
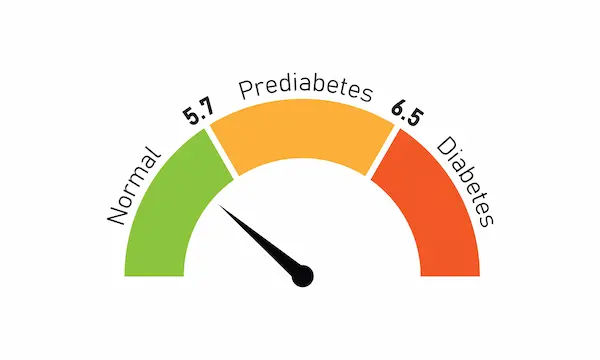
HbA1C (Glycated Hemoglobin)
Random blood sugar test
Fasting blood sugar test
Glucose tolerance test
Diabetes should be diagnosed as early as possible. If left untreated, it's likely to get worse and can lead to long-term health problems.
Check Your Sugar Levels
Complications Associated with Diabetes
If it is not controlled, diabetes can cause a host of complications, which can be categorised into short-term and long-term. The short-term complications of diabetes include:
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): Causes shakiness, sweating, confusion, or loss of consciousness. Common triggers include excess insulin, skipping meals, or alcohol.
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar): Symptoms include thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. If left untreated, it can potentially lead to diabetic ketoacidosis.
If left untreated, the long-term effects of diabetes include:
Heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease
Nerve damage from diabetes (diabetic neuropathy)
Kidney damage from diabetes (diabetic nephropathy)
Eye damage from diabetes (diabetic retinopathy)
Foot damage
Skin and mouth disorders
Hearing impairment
Treatment Options for Diabetes
Diabetes management includes a plan involving medication and lifestyle changes as well as regular testing of the blood sugar levels.
Blood sugar can be controlled with a healthy diet. Eating whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, processed foods, and carbs is recommended.
Physical activity is an integral part of reducing blood sugar levels. One should aim to walk, cycle, or swim for at least 30 minutes a day.
Medications and therapy are also often prescribed for diabetes, such as:
Oral Hypoglycemics: They help lower blood sugar and are usually prescribed to people with type 2 diabetes.
Insulin Therapy: It involves injecting insulin to successfully regulate blood sugar levels, which is essential for those with type 1 diabetes.
Advanced Treatments for Diabetes
One advanced treatment for diabetes is insulin pump therapy, which releases insulin into the body and helps control high blood sugar levels. Another option people opt for includes Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM).
CGM is a wearable device that monitors the blood glucose (sugar) levels over time. It monitors the glucose level in the interstitial fluid beneath the skin 24 hours a day while wearing the device.
Managing Diabetes with Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet is essential for blood sugar management. A diabetic diet includes:
Nonstarchy vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, and green beans.
Avoiding or limiting added sugars and refined grains, such as white bread, rice, and pasta.
Cutting down on highly processed foods and focusing on whole foods.
It isn’t always clear how to plan the perfect diet. In such cases, a dietitian or nutritionist can help in optimising the diet as per the needs.
Preventing Diabetes and Its Complications
As diabetes complications are lifelong, prevention is crucial. Reducing the risk of diabetes and its complications involves:
Engaging in regular physical activity and having a healthy diet are paramount.
Consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels and routine health check-ups help in the early detection and management of potential complications.
Community-based programs promoting healthy lifestyles and providing education on diabetes prevention can significantly reduce the incidence of diabetes.
A Holistic Approach to Living with Diabetes
Managing diabetes can be challenging and emotionally draining. Mental health issues left untreated can make diabetes management more difficult. One must engage with community and support groups for practical advice.
Getting to consistent medical appointments is vital so that diabetes is preventable and complications can be monitored. Timely adjustments to treatment plans can help patients attain positive health outcomes.
Conclusion
Diabetes impacts millions globally, and with no cure available, prevention becomes essential. Maintaining a nutritious diet, staying active, and managing stress are key steps to take. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can lead healthier lives and minimise the effects of diabetes on their well-being.
Consult Top Diabetologist
Consult Top Diabetologist

Dr. Utsa Basu
Diabetologist
14 Years • MBBS , MD
Barasat
Diab-Eat-Ease, Barasat
(75+ Patients)

Dr Bhargav Vuppumalla
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS MD GENERAL MEDICINE
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr. Arif Ahmed
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
9 Years • MBBS, MD (Genl. Med.)
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Swaroopa Rani
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
9 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine)
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr. Chaithanya R
Internal Medicine Specialist Diabetologist
16 Years • MBBS, MD Internal Medicine, Fellowship in Diabetes(UK), CCEBDM(PHFI)
Bangalore
Apollo Clinic Bellandur, Bangalore
(75+ Patients)
Consult Top Diabetologist

Dr. Utsa Basu
Diabetologist
14 Years • MBBS , MD
Barasat
Diab-Eat-Ease, Barasat
(75+ Patients)

Dr Bhargav Vuppumalla
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS MD GENERAL MEDICINE
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr. Arif Ahmed
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
9 Years • MBBS, MD (Genl. Med.)
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Swaroopa Rani
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
9 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine)
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr. Chaithanya R
Internal Medicine Specialist Diabetologist
16 Years • MBBS, MD Internal Medicine, Fellowship in Diabetes(UK), CCEBDM(PHFI)
Bangalore
Apollo Clinic Bellandur, Bangalore
(75+ Patients)