Guide to Diabetes Management Through Lifestyle Changes
Manage your diabetes effectively with our comprehensive guide. Learn how diet, exercise, and healthy habits can help you control blood sugar and improve your quality of life.

Written by Dr. Siri Nallapu
Reviewed by Dr. D Bhanu Prakash MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Receiving a diabetes diagnosis can feel overwhelming, but it's important to know that it's a condition you can powerfully manage and even thrive with. While medication plays a role, the true foundation of effective diabetes management lies in the daily choices you make. This comprehensive guide is designed to empower you with actionable knowledge and strategies for diabetes control through sustainable lifestyle changes. We will move beyond generic advice and delve into the "how" and "why" behind nutrition, exercise, weight management, and other critical factors. Whether you're newly diagnosed or looking to refine your approach, this article will provide you with the tools to take charge of your health, improve your wellbeing, and reduce the risk of complications. Let's embark on this journey to a healthier you.
Understanding Diabetes: The Basics
What is Diabetes?
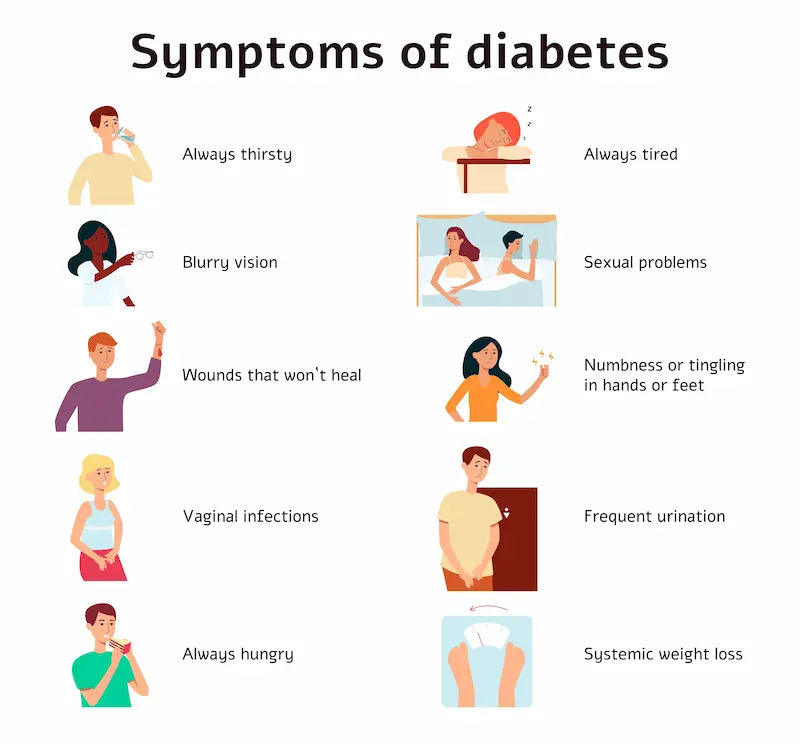
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. When you eat, most of the food is broken down into sugar (glucose) and released into your bloodstream. When your blood sugar goes up, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. Insulin acts like a key, allowing the blood sugar into your body’s cells for use as energy. With diabetes, your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use it as well as it should, leading to too much blood sugar staying in your bloodstream.
Type 1 vs. Type 2 Diabetes: Know the Difference
Understanding your type is crucial for management.
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with Type 1 require daily insulin administration. It is often diagnosed in children and young adults.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, where the body doesn't use insulin well and can't keep blood sugar at normal levels. It is closely linked to lifestyle factors and often develops over many years. It can be managed with diet, exercise, oral medication, and sometimes insulin.
The Crucial Role of Insulin
Think of insulin as the key that unlocks your cells. Without it, or if the key doesn't work properly (insulin resistance), glucose piles up in the blood. This state of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia), over time, can cause serious health problems like heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease. Effective diabetes management focuses on keeping this blood sugar within a target range.
The Cornerstone of Control: Mastering Your Diet
What you eat is arguably the single most significant factor in controlling your blood sugar. It's not about deprivation; it's about making smart, strategic choices.
Building Your Plate: The Diabetes Plate Method
The American Diabetes Association recommends a simple visual tool: the plate method.
1. NonStarchy Vegetables (½ your plate): Spinach, broccoli, carrots, tomatoes, peppers. These are low in carbs and high in fiber and nutrients.
2. Lean Protein (¼ of your plate): Chicken, fish, tofu, eggs, legumes. Protein helps you feel full and has minimal impact on blood sugar.
3. Carbohydrates (¼ of your plate): This is where your attention should be. Choose highfiber, complex carbs like brown rice, quinoa, wholewheat bread, or sweet potato.
Consult Top Specialists
Carbohydrate Counting: A Practical Skill
Since carbs have the biggest impact on your blood glucose, learning to count them is a powerful skill. It involves keeping track of the grams of carbohydrates you eat and drink. Using this alongside your blood glucose monitoring can help you determine how different foods and portions affect your levels, giving you more flexibility and control.
Superfoods for Blood Sugar Stability
Incorporate these foods to lower blood sugar naturally:
- Leafy Greens: Low in calories and digestible carbs.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega3 fats, which reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
- Chia Seeds & Flaxseeds: Packed with fiber, which can improve blood sugar control.
- Greek Yogurt: High in protein and probiotics, linked to improved blood sugar control.
- Nuts: A study published in BMJ Open found that eating nuts daily could help control
blood sugar and lipid levels in people with Type 2 diabetes.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
Minimize intake of:
- Sugar Sweetened beverages (soda, juice)
- Refined carbs (white bread, pasta, pastries)
- Trans fats (found in margarine, packaged snacks)
- Highly processed foods
Get Moving: The Power of Physical Activity
Exercise is like a free dose of medicine for diabetes. It makes your cells more sensitive to insulin, meaning your body needs less insulin to usher sugar into the cells.
How Exercise Lowers Blood Sugar?
When you exercise, your muscles use glucose for energy. This happens both during and after the activity, helping to lower your blood sugar levels. Regular exercise for type 2 diabetes can also help you lose weight and reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease.
Crafting Your Exercise Routine
Aim for a mix:
- Aerobic Exercise: At least 150 minutes per week of moderate intensity activity (brisk walking, cycling, swimming) spread over at least 3 days.
- Strength Training: At least 2 sessions per week. Building muscle gives your body more places to store glucose. Focus on major muscle groups.
Tips for Staying Safe During Workouts
- Check your blood sugar before, during, and after exercise.
- Stay hydrated.
- Keep a fast-acting carbohydrate (like glucose tablets) handy in case your blood sugar drops too low (hypoglycemia).
- Wear proper footwear to protect your feet.
The Scale Matters: Weight Management Strategies
The Link Between Weight and Insulin Resistance
Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, increases insulin resistance. This means your body's cells don't respond effectively to insulin. Losing even a modest amount of weight—5% to 7% of your body weight—can significantly improve insulin sensitivity. For someone who weighs 200 pounds, that's just 10 to 14 pounds.
Sustainable Weight Loss Tips for Diabetics
Focus on gradual loss through the diet and exercise principles above. Crash diets are dangerous and ineffective long term. Tracking your food intake, practicing mindful eating, and ensuring you're in a slight calorie deficit are proven strategies for diabetes weight loss.
Beyond Food and Exercise: Holistic Lifestyle Tweaks
Stress Management: Cortisol and Blood Sugar
When you're stressed, your body releases hormones like cortisol, which can cause your blood sugar to rise. Chronic stress can make diabetes management a constant challenge. Incorporate stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or hobbies you enjoy.
The Importance of Quality Sleep
Poor sleep can disrupt key hormones, making you hungrier and increasing cravings for high carb foods. It also increases insulin resistance. Aim for 79 hours of quality sleep per night.
Breaking Bad Habits: Smoking and Alcohol
- Smoking: Increases the risk of all diabetes-related complications, including heart and kidney disease. Quitting is one of the best things you can do.
- Alcohol: Can cause either high or low blood sugar. If you drink, do so in moderation and always with food. Monitor your blood sugar closely.
Monitoring and Medication: Working with Your Doctor
The Importance of Regular Blood Sugar Checks
Self monitoring provides real-time feedback on how your lifestyle choices affect your glucose levels. It helps you make informed decisions about food, activity, and medication. Your doctor will advise you on how often to check.
Understanding Your HbA1c
This is a blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 23 months. It's the gold standard for assessing diabetes management. A general goal for many people is to keep it below 7%, but your doctor will set a personal target for you. Apollo24|7 offers a convenient home collection for tests like HbA1c, making it easier to track your progress.
Adhering to Your Medication Plan
If your doctor has prescribed medication (oral or insulin), take it exactly as directed. These medications are designed to work in tandem with your lifestyle efforts. If your condition does not improve after trying these methods, book a physical visit to a doctor with Apollo24|7 to discuss adjusting your management plan.
Quick Takeaways: Key Points for Diabetes Management
- Food is Medicine: Fill half your plate with nonstarchy vegetables and focus on complex carbs and lean protein.
- Move Daily: Aim for 150 mins of aerobic exercise and 2 strength sessions per week.
- Mind Your Weight: Losing 57% of body weight can dramatically improve insulin sensitivity.
- Check and Track: Regularly monitor your blood sugar and know your HbA1c target.
- Sleep and Destress: Prioritize quality sleep and manage stress through mindfulness.
- Partner with Your Doctor: Adhere to medication plans and maintain regular checkups.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes is a lifelong journey, not a sprint. It's built on a foundation of consistent, daily lifestyle changes that empower you to take control of your health. By mastering your nutrition, embracing physical activity, managing your weight, and tending to your mental wellbeing, you can not only manage your blood sugar levels but also dramatically enhance your overall quality of life and reduce the risk of future complications. Remember, you are the most important member of your healthcare team. Start with one or two changes from this guide, build momentum, and don't hesitate to seek support from healthcare professionals, dietitians, or diabetes educators. If you have concerns about your symptoms or management plan, consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for personalized guidance. You have the power to shape your health journey.
Consult Top Specialists
Consult Top Specialists

Dr. Vivek D
General Physician
4 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Sudhashree R
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MRCEM
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr Aakash Andgi
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
9 Years • MBBS MD
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Zulkarnain
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS, PGDM, FFM
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Swarna Deepak K
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
20 Years • MBBS: MD (Internal Medicine) MRCP (UK), EDIC (European Diploma in Critical Care), IDCCM, IFCCM (Critical Care), FID (Royal Liverpool Academy)
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
(425+ Patients)
Consult Top Specialists

Dr. Vivek D
General Physician
4 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Sudhashree R
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
13 Years • MBBS, MRCEM
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr Aakash Andgi
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
9 Years • MBBS MD
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Zulkarnain
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS, PGDM, FFM
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Swarna Deepak K
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
20 Years • MBBS: MD (Internal Medicine) MRCP (UK), EDIC (European Diploma in Critical Care), IDCCM, IFCCM (Critical Care), FID (Royal Liverpool Academy)
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
(425+ Patients)
More articles from Diabetes
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you reverse Type 2 diabetes with lifestyle changes?
While 'reversal' is a debated term, Type 2 diabetes can often be put into remission through significant lifestyle changes. This means achieving normal blood sugar levels without medication. It is most achievable through substantial weight loss, particularly early after diagnosis.
What are the best fruits for a diabetic to eat?
Berries (strawberries, blueberries), cherries, apples, and pears are excellent choices due to their high fiber and lower glycemic index. Portion control is key. It's best to eat whole fruit rather than fruit juice.
How often should I check my blood sugar?
The frequency depends on your type of diabetes, your treatment plan, and how stable your levels are. Some may need to check multiple times a day (especially if on insulin), while others with well-controlled Type 2 might check less frequently. Your doctor will provide a personalized schedule.
Can I still eat sugar if I have diabetes?
Yes, but in strict moderation and as part of a healthy meal plan. It's not about complete elimination, but about understanding how it affects your blood sugar and accounting for it in your carbohydrate count for the day.
What are the warning signs of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)?
Shakiness, sweating, dizziness, hunger, irritability, fast heartbeat, and confusion. It's crucial to treat it immediately with 1520 grams of a fastacting carbohydrate, like glucose tablets or juice.