Understanding Prediabetes: Causes and Treatments
Prediabetes is a warning sign—but it’s reversible. Learn about the causes, symptoms, and effective lifestyle changes to prevent type 2 diabetes and improve your health.

Written by Dr. Siri Nallapu
Reviewed by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam MD (Physician)
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Prediabetes is a condition where your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. It’s a warning sign that your body is struggling to process sugar efficiently. The good news? Prediabetes is reversible with the right lifestyle changes and early intervention.
In this article, we’ll explore what prediabetes is, its causes, and symptoms, and how you can manage or even reverse it before it progresses to diabetes.
What Is Prediabetes?
Prediabetes means your blood glucose (sugar) levels are elevated, but not in the diabetic range. If left unchecked, it can develop into type 2 diabetes, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other complications.
Key Indicators of Prediabetes
Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS): 100–125 mg/dL
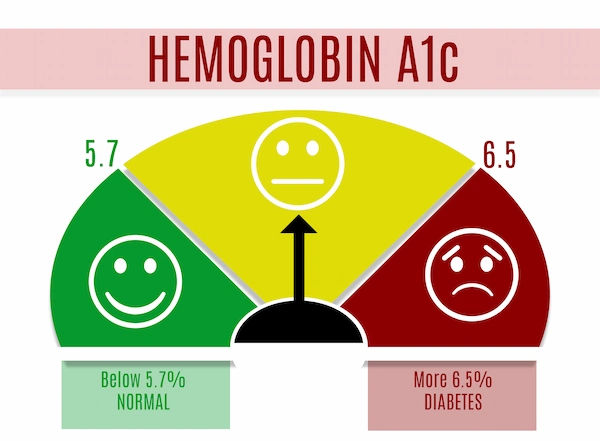
HbA1c (Average Blood Sugar Over 3 Months): 5.7%–6.4%
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): 140–199 mg/dL
If your test results fall in these ranges, your doctor may diagnose you with prediabetes.
Symptoms of Prediabetes
Many people with prediabetes don’t experience noticeable symptoms, which is why it often goes undetected. However, some may notice:
Increased thirst
Frequent urination
Fatigue
Blurred vision
Slow-healing wounds
Darkened skin patches (acanthosis nigricans, often around the neck or armpits)
Since symptoms can be subtle, regular health check-ups are crucial, especially if you have risk factors.
What Causes Prediabetes?
Prediabetes occurs when your body becomes resistant to insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar) or when your pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin. Several factors contribute to this:
1. Insulin Resistance
Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, makes cells less responsive to insulin.
A sedentary lifestyle worsens insulin sensitivity.
2. Genetics & Family History
If a parent or sibling has type 2 diabetes, your risk increases.
3. Poor Diet
High intake of sugary foods, refined carbs, and processed foods can spike blood sugar levels.
4. Lack of Physical Activity
Exercise helps muscles use glucose effectively; inactivity leads to higher blood sugar.
5. Age & Ethnicity
Risk increases after age 45.
Certain ethnic groups (South Asians, African Americans, Hispanics) are more prone.
Get Your Symptoms Checked By An Endocrinologist
6. Other Health Conditions
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), high blood pressure, and high cholesterol are linked to prediabetes.
How Does Prediabetes Affect Your Health?
If ignored, prediabetes can lead to:
Type 2 Diabetes – Higher risk of nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems.
Heart Disease & Stroke – Elevated blood sugar damages blood vessels over time.
Metabolic Syndrome – A cluster of conditions including high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol.
The good news? Prediabetes is reversible with early action!
How to Manage & Reverse Prediabetes
Let’s see how we can manage and reverse prediabetes:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet
Choose whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Limit sugary drinks, refined carbs (white bread, pasta), and processed snacks.
Control portion sizes to avoid blood sugar spikes.
2. Exercise Regularly
Aim for 150 minutes of moderate activity per week (brisk walking, cycling, swimming).
Strength training (twice a week) helps improve insulin sensitivity.
3. Lose Excess Weight
Losing 5–10% of body weight can significantly lower diabetes risk.
4. Get Enough Sleep
Poor sleep affects insulin sensitivity; aim for 7–9 hours per night.
5. Manage Stress
Chronic stress raises blood sugar. Try yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
6. Regular Health Check-ups
Monitor blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
When to See a Doctor?
If you have risk factors or suspect prediabetes, consult a doctor for:
Blood sugar tests
Personalised diet and exercise plans
Medications (if needed, like Metformin)
Early detection and lifestyle changes can prevent diabetes and improve overall health.
Conclusion
Prediabetes is a wake-up call, but it’s also an opportunity to make positive changes. By adopting a healthier lifestyle, you can reverse prediabetes and avoid complications.
If you’re concerned about your blood sugar levels, book a consultation or lab test with Apollo 24|7 for expert guidance and support.
Get Your Symptoms Checked By An Endocrinologist
Get Your Symptoms Checked By An Endocrinologist

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(150+ Patients)

Dr. Shruthi B
Endocrinologist
20 Years • MBBS,MD ( GEN MED) DM (ENDOCRIONOLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
Aditya Singh
Endocrinologist
8 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
Apollo One Electronic City, Bengaluru

Dr. Arunava Ghosh
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS,MD(GENL.MED.),DM(ENDOCRINOLOGY)
Kolkata
VDC Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Chaithanya R
Internal Medicine Specialist Diabetologist
16 Years • MBBS, MD Internal Medicine, Fellowship in Diabetes(UK), CCEBDM(PHFI)
Bangalore
Apollo Clinic Bellandur, Bangalore
(75+ Patients)