Understanding Ectopic Pregnancy
Know all about ectopic pregnancy, what it is, and how different from uterine pregnancy, recognising signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options and more


Introduction
An ectopic pregnancy is a serious and potentially life-threatening early pregnancy complication that requires immediate medical attention. Unlike a typical pregnancy, where the fertilised egg implants and grows inside the uterus, an ectopic pregnancy occurs when the egg implants somewhere else, most commonly in a fallopian tube. Understanding the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy is crucial for every woman of childbearing age. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from the earliest warning signs and risk factors to diagnosis, treatment options, and recovery, empowering you with knowledge to seek timely care.
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
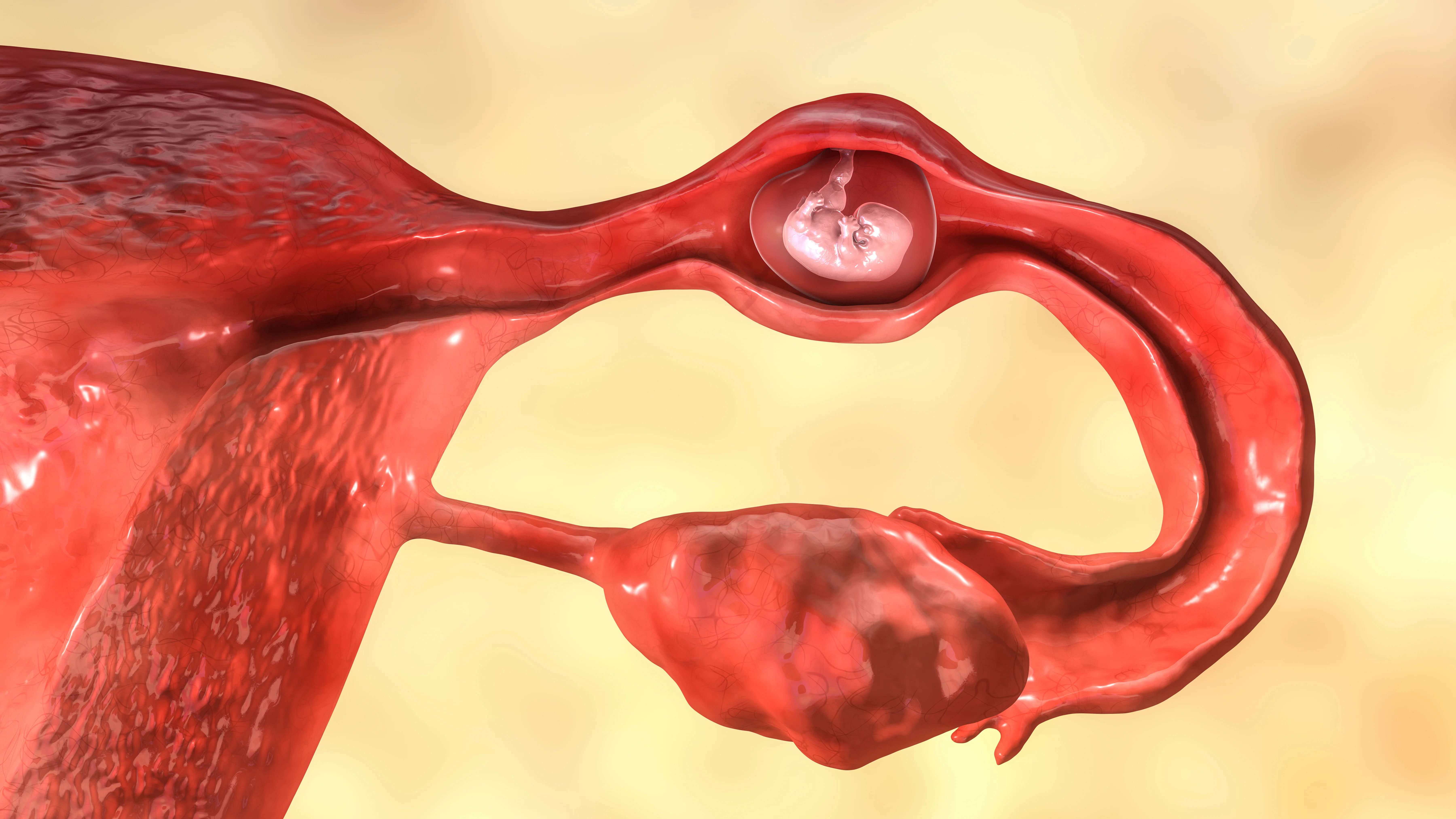
An ectopic pregnancy, often called a tubal pregnancy, is any pregnancy that implants outside the main cavity of the uterus. The word "ectopic" literally means "out of place." In over 95% of cases, the implantation happens in one of the fallopian tubes. However, it can also rarely occur in other areas like the ovary, abdominal cavity, or the cervix. Unfortunately, there is no way for a pregnancy to survive in these locations. The tissues outside the uterus are not designed to stretch and nourish a growing embryo, making the situation unsustainable and dangerous for the mother.
How an Ectopic Pregnancy Differs from a Uterine Pregnancy
In a viable uterine pregnancy, the fertilized egg travels through the fallopian tube and implants into the nutrient-rich
lining of the uterus (the endometrium). Here, it has ample space to develop into an embryo and a placenta. In an ectopic pregnancy, the egg gets stuck on its journey. Often, this is due to a damaged or misshapen fallopian tube. It implants in the tube's lining and begins to grow. Since the tube is narrow and not elastic, it will eventually stretch to its limit, causing pain and potentially rupturing, which leads to severe internal bleeding. This fundamental difference in
location is what makes an ectopic pregnancy a medical emergency rather than a viable pregnancy.
Recognising the Signs: Symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy
Early on, an ectopic pregnancy often feels like a normal pregnancy, with typical signs like a missed period, breast tenderness, and nausea. However, warning signs usually appear between the 4th and 12th weeks of pregnancy. It's vital to listen to your body and seek medical advice for any unusual symptoms.
Early Warning Signs
It includes:
- Abdominal or Pelvic Pain: This is the most common symptom. It might be sharp, stabbing, or persistent on one side of
the abdomen. The pain can vary in intensity. - Vaginal Bleeding: Unlike a normal period, this bleeding is often different—it might be lighter or heavier, and the blood
can be a unique watery, dark brown color sometimes described as "prune juice." - Gastrointestinal Discomfort: Pain in the shoulder tip (caused by internal bleeding irritating nerves) and pain when passing urine or stools.
Symptoms of a Rupture (A Medical Emergency)
If the fallopian tube ruptures, the symptoms become severe and life-threatening. This requires immediate emergency care.
- Sudden, Severe, Sharp Abdominal Pain: This is often described as a tearing sensation.
- Dizziness, Lightheadedness, or Fainting: Caused by significant internal blood loss.
- Signs of Shock: Rapid heartbeat, pale and clammy skin, and a feeling of extreme weakness.
If you experience any symptoms of a rupture, seek emergency medical attention without delay.
Who is at Risk? Understanding Ectopic Pregnancy Risk Factors
Any sexually active woman of childbearing age can experience an ectopic pregnancy. However, certain factors increase
the risk by causing scarring or damage to the fallopian tubes, which can hinder the egg's journey. Key risk factors include:
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: A history of one ectopic pregnancy increases the risk of another.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): This is a major risk factor. PID, often caused by infections like chlamydia or
gonorrhea, can cause scarring in the tubes. - Smoking: Chemicals in cigarettes can damage the tubes' ability to move the embryo.
- Fertility Treatments: IVF and other assisted reproductive technologies carry a slightly higher risk.
- Tubal Surgery: Previous surgery on the tubes, including a reversal of tubal ligation.
- Endometriosis: This condition can cause scarring within the pelvis.
- Being 35 or Older: Maternal age is associated with a higher risk.
Consult a Gynaecology Expert for Personalised Advice
How is an Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected based on symptoms, a doctor will perform a series of tests to confirm it. Apollo24|7 offers convenient home collection for essential tests like hCG monitoring, which can be a crucial part of early diagnosis.
The Role of hCG Blood Tests
The pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is key. In a healthy uterine pregnancy, hCG levels typically double every 48-72 hours in early pregnancy. In an ectopic pregnancy, hCG levels often rise more slowly or plateau. A doctor will order two blood tests 48 hours apart to track this pattern.
Transvaginal Ultrasound: The Key Diagnostic Tool
This ultrasound provides a clear view of the uterus and fallopian tubes. By around the 6th week of pregnancy, a doctor should be able to see a gestational sac within the uterus. If the transvaginal ultrasound shows an empty uterus despite positive pregnancy tests and rising hCG, it strongly suggests an ectopic pregnancy. Sometimes, the doctor can directly
visualise the ectopic mass in the tube.
Treatment Options for an Ectopic Pregnancy
Unfortunately, an ectopic pregnancy cannot proceed normally. The goal of treatment is to remove the ectopic tissue to protect the mother's life and health and preserve her future fertility. The choice between methotrexate for ectopic pregnancy and surgery depends on the specific circumstances.
Medication Treatment (Methotrexate)
- This is a non-surgical option using a drug called methotrexate, which stops the growth of rapidly dividing cells, including the pregnancy cells.
- Who is a Candidate for Methotrexate? This option is suitable if the ectopic pregnancy is detected early, before rupture, and if the hCG levels are relatively low (typically under 5,000 mIU/mL). The patient must be stable with no signs of
heavy bleeding.
Surgical Treatment (Laparoscopy)
Surgery is necessary if the tube has ruptured, if the patient is unstable, or if methotrexate is not suitable. The standard procedure is a laparoscopy (keyhole surgery).
Salpingostomy vs. Salpingectomy: What's the Difference?
In a salpingostomy, the surgeon makes a small incision in the fallopian tube to remove the ectopic tissue while leaving the tube intact. In a salpingectomy, the entire affected fallopian tube is removed. The choice depends on the extent of the damage and the condition of the other tube.
Recovery and Aftercare: What to Expect
Recovery is both physical and emotional.
Physical Healing Timeline
Recovery from laparoscopic surgery is relatively quick, with most women resuming normal activities within a few weeks. If you received methotrexate, you will need to avoid alcohol, certain vitamins (like folic acid), and sunlight exposure for a period, as advised by your doctor.
Monitoring hCG Levels to Zero
Whether treated with medication or surgery, your doctor will continue to monitor your hCG levels with blood tests until they return to zero. This ensures that all ectopic tissue has been successfully removed.
Emotional Recovery and Support
The loss of a pregnancy, coupled with the emergency nature of the event, can be profoundly traumatic. Feelings of grief,
sadness, anxiety, and fear about the future are completely normal. It is essential to:
- Allow yourself to grieve.
- Seek support from your partner, family, friends, or a professional counselor.
- Connect with support groups where you can share your experience with others who understand.
Future Pregnancy After an Ectopic Pregnancy
Having one ectopic pregnancy does not mean you cannot have a healthy pregnancy in the future. Many women go on
to have successful pregnancies. Your chances depend on the health of your remaining fallopian tube. It is crucial to:
- Wait: Doctors typically recommend waiting at least 3-6 months after methotrexate or 2-3 menstrual cycles after surgery
before trying to conceive again. - Seek Early Monitoring: In your next pregnancy, contact your doctor immediately for early monitoring through blood
tests and an ultrasound to confirm the pregnancy is in the uterus.
Conclusion
An ectopic pregnancy is an unexpected and challenging experience, but understanding its signs, risks, and treatments is your first line of defense. While the diagnosis can be frightening, modern medicine provides effective and often fertility-sparing treatments. The most critical action you can take is to listen to your body and seek prompt medical attention for any concerning symptoms during early pregnancy. Consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for prompt and professional guidance.
Consult a Gynaecology Expert for Personalised Advice
Consult a Gynaecology Expert for Personalised Advice

Dr. Sai Lakshmi Daayana
Gynaecological Oncologist
18 Years • MBBS, MRCOG
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
(225+ Patients)

Dr. Revathi S Rajan
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
24 Years • MBBS, DGO, DNB.FFMM
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Sreeparna Roy
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
8 Years • MBBS , MS (OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY), Fellowship in Infertility, Endoscopy & Ultrasonography), Fellowship in Laparoscopy & Hysteroscopy,DRM
Kolkata
Dr Utsa Basu Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Swati Shah
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • DNB Surgical Oncology, certified Robotic Cancer Surgeon
Ahmedabad
Apollo Hospitals Gandhinagar, Ahmedabad
(25+ Patients)

Dr Shefali Sardana
Medical Oncologist
18 Years • MBBS, MD (Medicine), DNB (Medical Oncology)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
Consult a Gynaecology Expert for Personalised Advice

Dr. Sai Lakshmi Daayana
Gynaecological Oncologist
18 Years • MBBS, MRCOG
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
(225+ Patients)

Dr. Revathi S Rajan
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
24 Years • MBBS, DGO, DNB.FFMM
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Sreeparna Roy
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
8 Years • MBBS , MS (OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY), Fellowship in Infertility, Endoscopy & Ultrasonography), Fellowship in Laparoscopy & Hysteroscopy,DRM
Kolkata
Dr Utsa Basu Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Swati Shah
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • DNB Surgical Oncology, certified Robotic Cancer Surgeon
Ahmedabad
Apollo Hospitals Gandhinagar, Ahmedabad
(25+ Patients)

Dr Shefali Sardana
Medical Oncologist
18 Years • MBBS, MD (Medicine), DNB (Medical Oncology)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
More articles from ectopic pregnancy
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can an ectopic pregnancy be saved or moved to the uterus?
No, unfortunately, it is not possible to save an ectopic pregnancy or move it to the uterus. The implantation site cannot support the embryo's growth, and leaving it in place is dangerous for the mother. Medical or surgical intervention is necessary.
2. How long after methotrexate treatment do I have to wait to try to get pregnant again?
It is generally recommended to wait at least 3-6 months after methotrexate treatment. This allows the drug to completely leave your system and for your body to rebuild its folate reserves, which are crucial for a healthy future pregnancy.
3. What are the chances of having another ectopic pregnancy?
Your risk increases after having one. While about 1 in 50 pregnancies are ectopic in the general population, your risk may rise to roughly 1 in 10 after a previous ectopic. However, this also means you have a 90% chance of your next pregnancy being in the uterus.
4. Is it possible to have a period during an ectopic pregnancy?
No, you will not have a true period. However, vaginal bleeding is a very common symptom of an ectopic pregnancy. This bleeding can sometimes be mistaken for a period, which is why it's important to take a pregnancy test if the bleeding seems unusual or if you have other symptoms.
5. Does having a tubal ligation (getting your 'tubes tied') prevent ectopic pregnancy?
While tubal ligation is highly effective at preventing pregnancy, if a pregnancy does occur after this procedure, it has a significantly higher chance of being ectopic. This is because the procedure can sometimes create a partial blockage where an egg can still be fertilised but get stuck.