Causes, Diet, and Treatment of Gallstones
Gallstones can cause pain and complications, but understanding the causes, dietary changes, and treatment options is key to management. Learn how to prevent and treat gallstones with this comprehensive guide.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula MBBS
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Gallstones are a common health issue that affects many people, often causing pain and discomfort. If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with gallstones, you might have questions about what they are, why they form, and how to manage them. This article will explain everything in simple terms, helping you understand the causes, dietary changes, and treatment options available.
What Are Gallstones?
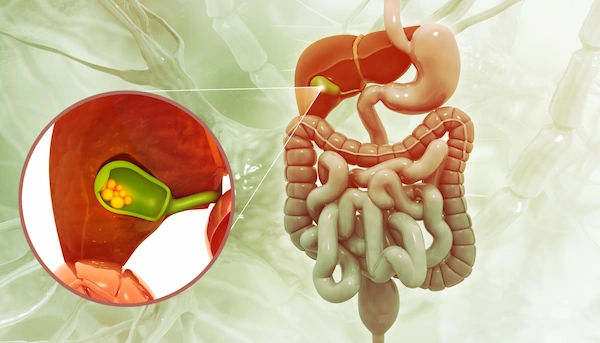
Gallstones are small, hard deposits that form in the gallbladder—a small organ located under the liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid that helps break down fats. Gallstones can vary in size—some are as tiny as a grain of sand, while others can be as large as a golf ball.
There are two main types of gallstones:
1. Cholesterol stones (most common) – Made mostly of undissolved cholesterol.
2. Pigment stones – Made of bilirubin, a substance produced when red blood cells break down.
What Causes Gallstones?
Gallstones develop when there’s an imbalance in the substances that make up bile. Some common causes include:
Too much cholesterol in bile – If your liver excretes more cholesterol than bile can dissolve, it can form stones.
Bile contains too much bilirubin – Conditions like liver cirrhosis or blood disorders can increase bilirubin levels.
Gallbladder doesn’t empty properly – If bile stays in the gallbladder too long, it can become concentrated and form stones.
Risk Factors for Gallstones
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing gallstones:
Gender – Women are more prone due to hormones like estrogen.
Age – People over 40 have a higher risk.
Obesity – Excess weight increases cholesterol in bile.
Rapid weight loss – Crash diets can cause the liver to release extra cholesterol.
Pregnancy – Hormonal changes slow gallbladder emptying.
Diabetes – High triglycerides (a type of fat) increase risk.
Family history – Genetics can play a role.
Symptoms of Gallstones
Many people with gallstones don’t experience symptoms (silent gallstones). However, if a stone blocks a bile duct, it can cause:
Sudden, intense pain in the upper right abdomen (gallbladder attack).
Pain between the shoulder blades or in the right shoulder.
Nausea or vomiting.
Indigestion, bloating, or gas.
Jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes) if a stone blocks the bile duct.
If you experience severe pain, fever, or yellow skin, seek medical help immediately, as this could indicate complications like infection or pancreatitis.
Diet and Lifestyle Tips to Manage Gallstones
While diet alone cannot dissolve gallstones, making healthy food choices can help prevent new ones from forming and reduce symptoms.
Foods to Eat
Highfiber foods – Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes help digestion.
Healthy fats – Olive oil, avocados, and nuts (in moderation).
Lean proteins – Fish, skinless poultry, and plantbased proteins like beans.
Low fat dairy – Skim milk, yogurt, and low fat cheese.
Hydration – Drink plenty of water to keep bile flowing smoothly.
Consult a General Physician for the best advice
Foods to Avoid
Fried and fatty foods – Burgers, fries, and processed snacks can trigger attacks.
Refined carbs – White bread, pastries, and sugary foods.
High cholesterol foods – Fatty meats, butter, and full fat dairy.
Rapid weightloss diets – Avoid extreme fasting or very lowcalorie diets.
Lifestyle Changes
Maintain a healthy weight – Gradual weight loss (1-2 lbs per week) is safer.
Exercise regularly – Helps digestion and weight management.
Eat smaller, frequent meals – Prevents bile buildup in the gallbladder.
Treatment Options for Gallstones
If gallstones cause pain or complications, treatment may be necessary.
1. Medications
Ursodeoxycholic acid – Helps dissolve small cholesterol stones over months/years (not always effective).
2. Surgery (Most Common Treatment)
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy – Minimally invasive removal of the gallbladder (recovery is quick, and most people live normally without it).
3. NonSurgical Procedures
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) – Removes stones from bile ducts without gallbladder removal.
When to See a Doctor?
Consult a doctor if you have:
Persistent abdominal pain.
Fever with chills.
Yellow skin or eyes.
Dark urine or pale stools.
If you suspect gallstones, Apollo 24|7 offers expert consultations and diagnostic tests. You can easily book an appointment online for personalized care.
Final Thoughts
Gallstones can be painful, but with the right diet, lifestyle changes, and medical care, they can be managed effectively. If you experience symptoms, don’t ignore them—early treatment can prevent complications. Stay mindful of your diet, maintain a healthy weight, and seek medical advice when needed.
For expert guidance, consider booking a consultation with a specialist at Apollo 24|7 to get the right diagnosis and treatment plan. Stay healthy and take care!
Would you like to schedule a test or speak with a doctor? Visit Apollo24|7 today for quick and reliable healthcare support.
Consult a General Physician for the best advice
Consult a General Physician for the best advice

Dr. Vivek D
General Physician
4 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr Syed Mateen Pasha
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Harshendra Jaiswal
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS , MD (General medicine)
Kolkata
108 DHANA DHANVANTARI Clinic, Kolkata
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Syed Ismail Ali
General Practitioner
7 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad
Dr. Thandra Ramoji Babu
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS, DNB(General Medicine)
Warangal
Sai Ram multi-specialty hospital, Warangal
.webp)