Diabetes in Children Types, Symptoms, Management
Know about diabetes in children, types, symptoms, and how it affects children. Learn how to manage children with diabetes.

Written by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam
Reviewed by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula MBBS
Last updated on 26th Aug, 2025

Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). While it is commonly associated with adults, children can also develop diabetes. As a parent or caregiver, understanding the types, symptoms, and management of diabetes in children is crucial for early detection and proper care.
Types of Diabetes in Children
The two main types of diabetes that affect children are:
1. Type 1 Diabetes
• What is it? Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Without insulin, glucose cannot enter cells, leading to high blood sugar levels.
• Who is affected? It is the most common type of diabetes in children and can develop at any age.
• Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but genetics and environmental factors may play a role.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
• What is it? Unlike Type 1, Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin.
• Who is affected? It was once rare in children but is now increasing due to rising obesity rates and unhealthy lifestyles.
• Causes: Risk factors include family history, poor diet, lack of physical activity, and excess weight.
Consult the Best Endocrinologist for Personalised Advice
Common Symptoms of Diabetes in Children
Early detection is key to managing diabetes effectively. Watch out for these symptoms:
• Frequent urination – The body tries to remove excess sugar through urine.
• Excessive thirst – Due to fluid loss from frequent urination.
• Increased hunger – The body cannot use glucose for energy, leading to constant hunger.
• Unexplained weight loss – Despite eating more, children may lose weight.
• Fatigue and irritability – Lack of glucose in cells leads to low energy.
• Blurred vision – High blood sugar affects the eye lenses.
• Slow-healing wounds – Poor circulation and high sugar levels delay healing.
If your child shows these signs, consult a doctor immediately. Early diagnosis can prevent complications.
How does Diabetes affect children’s Health?
If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious health problems, including:
Short-term complications:
• Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) – Can cause dizziness, confusion, or fainting.
• Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) – A life-threatening condition where the body produces excess acids (ketones).
Long-term complications:
• Heart disease
• Kidney damage
• Nerve damage
• Vision problems
Managing Diabetes in Children
While diabetes is a lifelong condition, proper management can help children lead healthy lives. Here’s how:
1. Healthy Eating Habits
• Focus on balanced meals with whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables.
• Limit sugary foods and processed snacks.
• Monitor carbohydrate intake to manage blood sugar levels.
2. Regular Physical Activity
• Exercise helps the body use insulin more effectively.
• Encourage at least 60 minutes of play or sports daily.
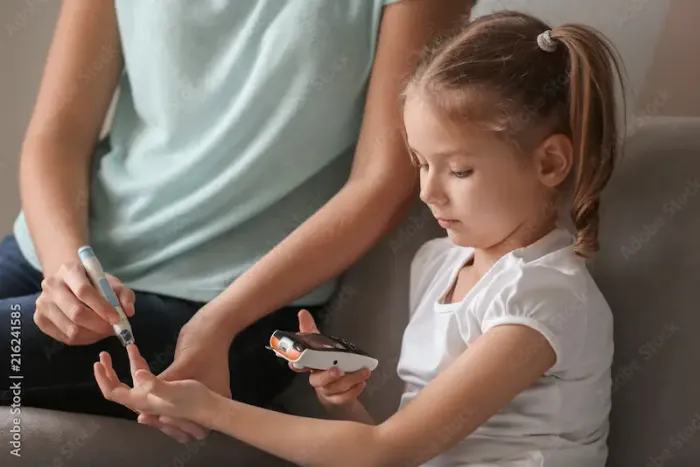
3. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
• Regular checks help adjust insulin doses and diet.
• Use a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) as advised by the doctor.
4. Insulin Therapy (for Type 1 Diabetes)
• Children with Type 1 diabetes need insulin injections or an insulin pump.
• Parents and older children should learn how to administer insulin safely.
5. Oral Medications (for Type 2 Diabetes)
• Some children with Type 2 diabetes may need oral medications like metformin.
6. Emotional Support
• Living with diabetes can be stressful for children.
• Encourage open conversations and consider joining support groups.
When to See a Doctor?
If your child shows symptoms of diabetes, consult a paediatrician or endocrinologist. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
Final Thoughts
Diabetes in children requires careful management, but with the right care, children can live full and active lives. By maintaining a healthy diet, staying active, and monitoring blood sugar levels, parents can help their children manage diabetes effectively.
Consult the Best Endocrinologist for Personalised Advice
Consult the Best Endocrinologist for Personalised Advice

Dr. Shrikrishna V Acharya
Endocrinologist
25 Years • MBBS, MD, DM(Endocrinology), MRCP (Endocrinology)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Anand Ravi
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Nithin Reddy Modhugu
Endocrinologist
6 Years • MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DNB (Endocrinology)
Hyderabad
Dr. Nithin's Endocrine Clinic, Hyderabad
(100+ Patients)

Dr. Shruthi B
Endocrinologist
20 Years • MBBS,MD ( GEN MED) DM (ENDOCRIONOLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
Consult the Best Endocrinologist for Personalised Advice

Dr. Shrikrishna V Acharya
Endocrinologist
25 Years • MBBS, MD, DM(Endocrinology), MRCP (Endocrinology)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Anand Ravi
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Nithin Reddy Modhugu
Endocrinologist
6 Years • MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DNB (Endocrinology)
Hyderabad
Dr. Nithin's Endocrine Clinic, Hyderabad
(100+ Patients)

Dr. Shruthi B
Endocrinologist
20 Years • MBBS,MD ( GEN MED) DM (ENDOCRIONOLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru