Ways to Reduce Body Heat and Understand Temperature
Discover effective ways to reduce body heat and maintain a healthy temperature. Learn about common causes of increased body heat and practical tips to stay cool and comfortable.

Written by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula
Reviewed by Dr. Vasanthasree Nair MBBS
Last updated on 11th Aug, 2025

Introduction
Feeling too hot or experiencing an unusually high body temperature can be uncomfortable and sometimes even concerning. While our bodies naturally regulate temperature, certain factors like weather, diet, or health conditions can cause excessive heat buildup. In this article, we’ll explore simple ways to reduce body heat and understand what influences our temperature.
Understanding Body Temperature
Our body maintains an average temperature of around 98.6°F (37°C), but it can vary slightly depending on activity levels, time of day, and individual differences. When the body overheats, it may lead to:
Excessive sweating
Fatigue and dizziness
Headaches
Dehydration
Heat rash or redness
If body temperature rises too much (above 104°F or 40°C), it can lead to heatstroke, a serious condition requiring immediate medical attention.
Health topic carousel:
Doctor's speciality: General Physician
Text: Consult a Top General Physician for the best advice
Common Causes of Increased Body Heat
Several factors can contribute to excessive body heat, including:
1. Hot Weather – High temperatures and humidity make it harder for the body to cool down.
2. Spicy or Fried Foods – Certain foods increase metabolic heat.
3. Dehydration – Lack of water reduces sweating, making it difficult to regulate temperature.
4. Strenuous Exercise – Intense physical activity raises internal heat.
5. Certain Medications – Some drugs affect temperature regulation.
6. Medical Conditions – Fever, hyperthyroidism, or infections can elevate body heat.
Simple Ways to Reduce Body Heat
Simple and effective ways to cool down and keep your body temperature in check naturally:
1. Stay Hydrated
Water helps regulate body temperature by promoting sweating. Drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily. You can also try:
Coconut water (rich in electrolytes)
Buttermilk (cooling and probiotic)
Herbal teas (like peppermint or chamomile)
2. Eat Cooling Foods
Include hydrating and cooling foods in your diet, such as:
Cucumber (high water content)
Watermelon (natural coolant)
Yoghurt (soothes digestion)
Leafy greens (help detoxify)
Avoid spicy, fried, or oily foods that increase body heat.
3. Wear Light, Breathable Clothing
Choose loose, cotton clothes that allow air circulation. Dark colors absorb heat, so opt for light shades.
4. Take Cool Showers or Use Cold Compresses
A quick cool shower or a damp cloth on the forehead, neck, and wrists can bring instant relief.
5. Avoid Peak Sun Hours
Stay indoors between 10 AM – 4 PM when the sun is strongest. If you must go out, wear a hat and use sunscreen.
6. Use Fans or Air Conditioning
Keep your living space cool with proper ventilation. If you don’t have AC, place a bowl of ice in front of a fan for a DIY cooler.
7. Practice Relaxation Techniques
Stress and anxiety can raise body temperature. Try:
Deep breathing exercises
Meditation or yoga
Adequate sleep
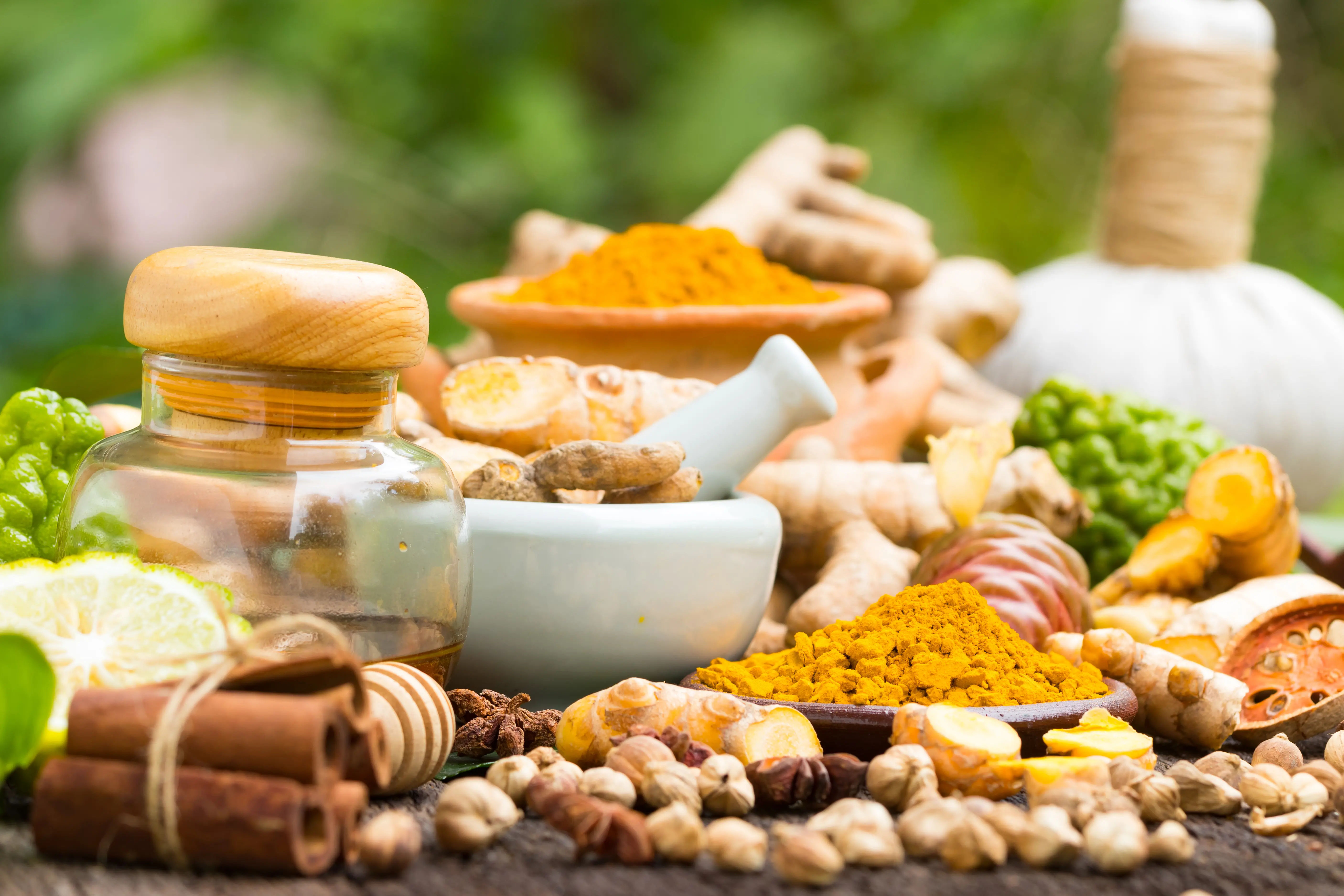
8. Herbal Remedies
Some natural ingredients help cool the body:
Aloe vera juice (detoxifying)
Mint leaves (add to water or chutneys)
Fennel seeds (soak overnight and drink the water)
When to Seek Medical Help?
While most cases of body heat can be managed at home, consult a doctor if you experience:
Persistent high fever (above 103°F)
Confusion or fainting
Rapid heartbeat
Severe dehydration (dry mouth, no urination)
These could be signs of heatstroke or an underlying health issue that needs professional care.
Final Thoughts
Managing body heat is often about simple lifestyle adjustments: staying hydrated, eating right, and avoiding excessive sun exposure. If you frequently feel overheated without an obvious cause, it’s best to consult a doctor to rule out any medical conditions.
Health topic carousel:
Doctor's speciality: General Physician
Text: Consult a Top General Physician for the best advice