Kodo Millet in Ayurveda: Benefits, Uses, and Side Effects
Explore kodo millet benefits, Ayurveda uses, and millet nutrition. Learn how to cook it, who should be cautious, and the side effects to know.
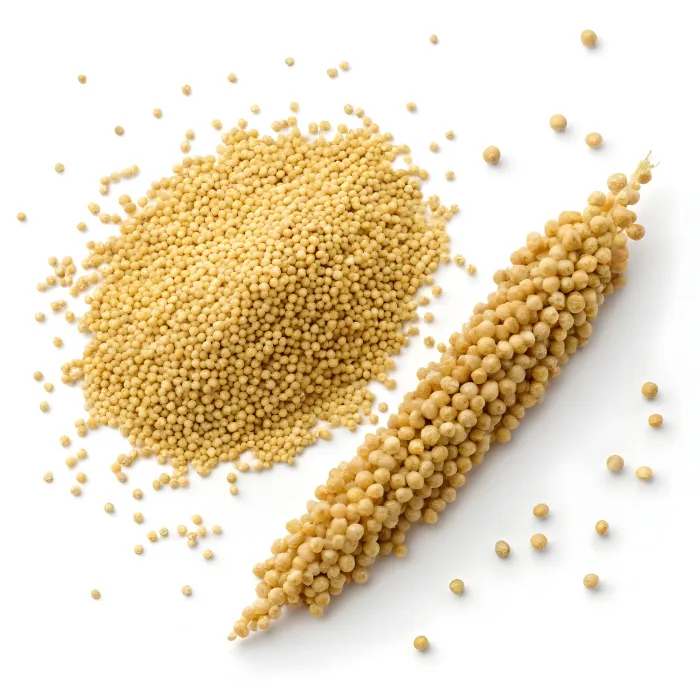


Introduction
Curious about kodo millet benefits and millet nutrition? You’re not alone. As more people shift towards wholesome, minimally processed foods, millets have steadily returned to the spotlight, especially within Ayurveda-inspired eating patterns that value simplicity, balance and seasonal nourishment. Kodo millet, also known as kodra, varagu or haraka, is a small whole grain valued for its fibre content, versatility and naturally gluten-free nature. It cooks quickly, adapts to both savoury and sweet recipes and fits easily into modern healthy eating goals. While Ayurveda has traditionally encouraged the inclusion of whole grains such as millets, contemporary nutrition research examines how grains like kodo millet may support heart health, blood sugar balance, gut health and overall wellbeing.
This guide brings together traditional insights and evidence-informed explanations to help you understand the potential benefits of kodo millet, how to use it in everyday meals, its possible side effects and who may need to exercise caution. The aim is to provide a clear, practical overview so you can confidently include kodo millet as part of a balanced, varied diet. If you have any existing medical conditions, it is always wise to speak with your healthcare provider for personalised advice. Consult a Top Ayurveda Doctor for Personalised Advice
What Is Kodo Millet?
Here are some basics of kodo millet:
- A small, ancient whole grain cultivated mainly in parts of Asia and Africa.
- Naturally gluten-free and commonly used in place of rice or couscous.
- Mild, nutty flavour suitable for porridge, pilaf, salads, upma, khichdi and dosas.
- Retains the bran, germ and endosperm, making it a true whole grain.
Kodo millet is valued for its resilience as a crop. It grows well in challenging climates, which is one reason it has been cultivated for centuries. In the kitchen, it tends to be easy to prepare and adapts readily to different cuisines, making it a useful addition for modern home cooks looking for nutritious grain alternatives.
Kodo Millet in Ayurveda: The Traditional View
Ayurveda encourages the consumption of whole, natural, seasonal foods that promote digestive ease and internal balance. Millets, including kodo millet, often feature in lighter, cleansing-style meals, particularly when people want to reduce reliance on refined grains. Ayurveda does not classify kodo millet as a cure for specific medical conditions, but views whole grains as grounding, nourishing and supportive of long-term digestive strength. The system highlights mindful cooking practices such as soaking and using gentle spices to support digestion. However, Ayurvedic dietary suggestions should be combined with modern nutrition knowledge for decisions related to disease prevention or management.
Kodo Millet Benefits at a Glance
Research typically examines millets as a group rather than kodo millet alone, but the findings are relevant because most whole millets share similar nutrient profiles. The benefits include:
- Heart health support through fibre, minerals and antioxidant-rich compounds.
- Better blood sugar balance compared with many refined grains.
- Digestive support due to high fibre content.
- Weight-friendly because fibre increases satiety and helps regulate appetite.
- Naturally gluten-free, making it suitable for gluten-free diets when cross-contact is controlled.
Why Whole Grains Matter: Millet Nutrition in Context?
Understanding millet nutrition is easier when viewed through the broader lens of whole-grain science. As a whole grain, kodo millet typically provides:
- Dietary fibre that supports heart and gut health.
- B vitamins, including niacin and vitamin B6.
- Minerals such as magnesium, manganese and iron.
- Natural plant compounds like polyphenols with antioxidant activity.
These nutrients contribute to metabolic health, immunity, energy production and digestive function. Levels vary depending on variety, growing conditions, storage and preparation. For example, flaked or puffed versions may have different glycaemic effects compared with intact cooked grains. Cooking methods, such as soaking and fermenting, can also enhance digestibility and nutrient availability.
How to Use Kodo Millet in Everyday Meals?
Kodo millet's everyday meal uses are:
Simple Ways to Get Started
- Use as a rice replacement served with lentils, beans or curries.
- Prepare a warm breakfast porridge with milk or fortified plant milk, nuts and fruit.
- Make upma or khichdi with vegetables, dal and gentle spices.
- Toss into salads and grain bowls with chopped vegetables, herbs, lemon and olive oil.
- Add to dosa or idli batters; fermentation improves texture and digestibility.
Cooking Basics
- Rinse thoroughly to remove dust and bitterness.
- Soak for 2 to 4 hours if you prefer improved digestibility and reduced antinutrient levels.
- Use approximately 1 part millet to 2 to 2.5 parts water or broth and simmer until tender.
- Adjust cooking time and liquid depending on your preferred texture.
- Toasting briefly before adding water deepens flavour.
Kodo millet cooks fairly quickly compared with many other whole grains, making it suitable for busy households. Its fluffy, separate texture when cooked makes it easy to incorporate into lunch or dinner meals without much preparation.
Smart Pairings for Balanced Plates
Some smart pairing ideas are:
- Combine with protein such as lentils, beans, tofu, eggs, yoghurt, fish or lean meats.
- Add healthy fats, including nuts, seeds, avocado or extra virgin olive oil.
- Fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables for volume and fibre.
- Use spices and herbs to enhance flavour without relying heavily on salt.
Pairing kodo millet with protein and healthy fats helps moderate the glycaemic response and extends satiety. This is particularly useful for individuals looking to maintain balanced energy levels throughout the day.
Portion and Frequency Tips
Portion and frequency tips are:
- Aim to consume whole grains regularly as part of weekly meals.
- If managing blood sugar, keep portions moderate and check your response where recommended by your clinician.
- Rotate among different whole grains to ensure variety in nutrients and flavour.
Millet Nutrition: Evidence-Based Benefits Explained
Evidence-based benefits are:
Fibre and Heart Health
- Whole grains rich in fibre are associated with reduced cardiovascular disease risk.
- Fibre helps lower LDL cholesterol.
- Gut-friendly fibre supports microbial diversity, which plays a role in heart and metabolic health.
Blood Sugar and Reduced Diabetes Risk
- Replacing refined grains with intact whole grains is linked to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Minimally processed grains tend to have a lower glycaemic impact.
- Pairing with protein and fats further improves post-meal glucose stability.
Weight Management
- The natural fibre content in whole grains increases fullness.
- This can help with portion control and support weight management goals.
- Whole grains provide steady energy, discouraging overeating or snacking.
Nutrient Density
- Whole grains retain vitamins, minerals and phytonutrients that are lost in refined grains.
- These nutrients support metabolism, bone health and immune function.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Kodo millet is generally safe when consumed as part of a balanced diet, but there are a few considerations. Possible side effects and precautions may include:
- Thyroid concerns: Millets contain goitrogenic compounds. In very large amounts, especially with low iodine intake, they may impact thyroid function. Those with thyroid conditions should ensure adequate iodine and discuss frequency with a clinician.
- Mineral absorption: Phytates in whole grains may reduce iron and zinc absorption.
- Soaking, sprouting and fermenting, as well as eating vitamin C-rich foods, can help counteract this.
- Gas or bloating: Increasing fibre suddenly may cause digestive discomfort. Introduce gradually and stay well hydrated.
- Allergies: Millet allergies are rare but possible. Seek medical help if you notice itching, swelling or hives.
- Blood sugar considerations: Millets still contribute carbohydrates. Portion control and balanced plates remain important for people monitoring glucose.
Who Might Want to Be Cautious?
Caution is to be observed in:
- Individuals with hypothyroidism should avoid consuming millet excessively without ensuring sufficient iodine intake.
- People with chronic kidney disease who follow mineral-restricted diets may need guidance on portion sizes.
- Those with coeliac disease should choose guaranteed gluten-free millet products to avoid cross-contact.
- Anyone following a specific medical diet should speak with their care team for personalised guidance.
Kodo Millet in Special Diets
The special diet with kodo millet is:
Gluten-Free Diets
- Naturally gluten-free and suitable for coeliac or gluten-sensitive individuals when cross-contact is controlled.
Plant-Forward or Vegetarian Diets
- Pair well with legumes to achieve complementary amino acids.
- Useful for creating balanced, satisfying meals.
Low-Glycaemic Eating
- Use intact grains rather than processed millet products.
- Balance with protein and healthy fats for improved glycaemic outcomes.
Practical Shopping and Storage Tips
Practical shopping and storage tips include:
- Choose whole, hulled kodo millet from reputable brands.
- If gluten-free certification is required, look for labels guaranteeing no cross-contact.
- Store in an airtight container in a cool, dry cupboard.
- Refrigerate or freeze for a longer shelf life due to the natural oils present in whole grains.
Quick Start: A Simple Kodo Millet Bowl
A simple bowl recipe is:
- Base: 1 cup cooked kodo millet
- Add: 1/2 cup cooked lentils or chickpeas
- Veggies: Roasted or sautéed vegetables of choice
- Dress: Olive oil, lemon juice, herbs and a small pinch of salt
- Top: Toasted seeds or nuts for added crunch.
Conclusion
Kodo millet is a nutritious, versatile whole grain that fits easily into many modern eating styles while supporting digestive health, metabolic balance and overall wellbeing. Its mild flavour and quick cooking time make it suitable for everyday meals, and its naturally gluten-free nature expands its usefulness for people with specific dietary needs. When used mindfully, alongside balanced portions of protein, vegetables and healthy fats, it can contribute to long-term health goals. With thoughtful preparation and variety in your diet, kodo millet can be a wholesome and enjoyable addition to your kitchen. Consult a Top Ayurveda Doctor for Personalised Advice
Consult a Top Ayurveda Doctor for Personalised Advice

Dr. Pepsy Jose
Panchakarma Practitioner
14 Years • BAMS, MD Ayurveda (Panchakarma)
Bengaluru
AYURRHYTHM HOLISTIC CLINIC AND PANCHAKARMA THERAPY, Bengaluru

Dr. Shiv Prakash Singh
Ayurveda Practitioner
19 Years • BAMS
Kolkata
Vedhive Ayurveda College Street, Kolkata

Dr. Anjan Das
Ayurveda Practitioner
8 Years • Ayurvedacharya ( B.A.M.S )
Dumdum
Vedhive Ayurveda Clinic, Dumdum

Dr. Rik Sadhukhan
Ayurveda Practitioner
8 Years • BAMS
Kolkata
Vedhive Ayurveda, Ballygunge, Kolkata
Consult a Top Ayurveda Doctor for Personalised Advice

Dr. Pepsy Jose
Panchakarma Practitioner
14 Years • BAMS, MD Ayurveda (Panchakarma)
Bengaluru
AYURRHYTHM HOLISTIC CLINIC AND PANCHAKARMA THERAPY, Bengaluru

Dr. Shiv Prakash Singh
Ayurveda Practitioner
19 Years • BAMS
Kolkata
Vedhive Ayurveda College Street, Kolkata

Dr. Anjan Das
Ayurveda Practitioner
8 Years • Ayurvedacharya ( B.A.M.S )
Dumdum
Vedhive Ayurveda Clinic, Dumdum

Dr. Rik Sadhukhan
Ayurveda Practitioner
8 Years • BAMS
Kolkata
Vedhive Ayurveda, Ballygunge, Kolkata
More articles from General Medical Consultation
Frequently Asked Questions
1) Is kodo millet good for people with diabetes?
Kodo millet can be part of a diabetes-friendly diet when eaten in moderate portions and combined with protein, healthy fats and vegetables. Individual responses vary, so people monitoring their glucose may want to check readings after meals and adjust portions accordingly.
2) Is kodo millet gluten-free?
Yes. Millet is naturally gluten-free, but people with coeliac disease should choose certified gluten-free products to avoid cross-contact during processing or packaging.
3) How often can I eat kodo millet?
You can include kodo millet regularly as part of your weekly whole grain rotation. Some people enjoy millet-based meals daily, while others prefer variety with oats, brown rice, quinoa and other millets. Those with thyroid concerns should speak to a healthcare provider about the appropriate frequency.
4) Are there side effects from eating kodo millet?
Most people tolerate it well. Side effects can include temporary bloating when increasing fibre, reduced mineral absorption due to phytates and potential thyroid considerations in very high intakes combined with low iodine consumption. Allergies are rare but can occur.
5) What is the best way to cook kodo millet?
Rinse well, optionally soak for 2 to 4 hours, then simmer using roughly 1 part millet to 2 to 2.5 parts water until tender. Toasting beforehand adds flavour, and the cooked grain can be used anywhere you would normally use rice or couscous.