Understanding Gangrene and Its Treatment Options
Know about gangrene, know what it is, different types, symptoms, causes, risk factors and treatment options. Learn how to prevent it and more.

Written by Dr. J T Hema Pratima
Reviewed by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam MD (Physician)
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
Introduction
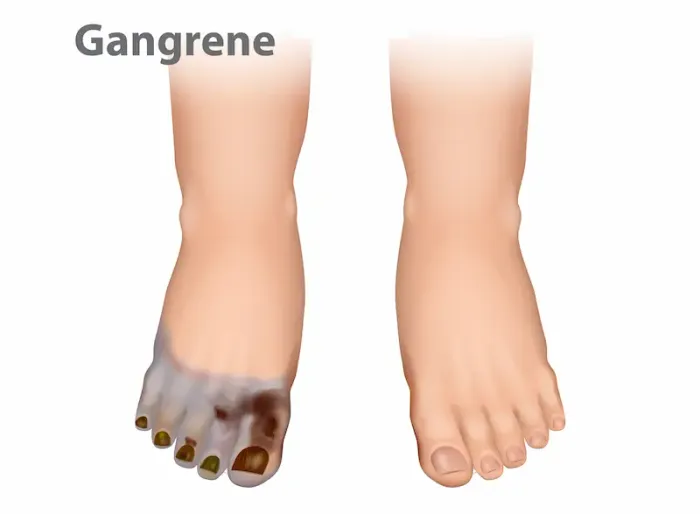
Gangrene is a serious medical condition that occurs when body tissues die due to a lack of blood flow or a severe bacterial infection. It can affect any part of the body, but is most common in the fingers, toes, arms, and legs. If left untreated, gangrene can lead to life-threatening complications. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help in early detection and better management.
What is Gangrene?
Gangrene happens when a part of the body loses its blood supply, causing the tissue to die. This can occur due to injury, infection, or underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or peripheral artery disease.
There are different types of gangrene, including:
1. Dry Gangrene – Develops slowly due to poor blood circulation, often seen in people with diabetes or atherosclerosis. The affected area becomes dry, shrivelled, and dark.
2. Wet Gangrene – Caused by bacterial infection, leading to swelling, blisters, and a foul-smelling discharge. It progresses rapidly and requires immediate treatment.
3. Gas Gangrene – A severe type caused by bacteria that produce toxins, leading to gas bubbles under the skin. It is a medical emergency.
4. Internal Gangrene – Affects internal organs like the intestines or gallbladder, usually due to blocked blood flow.
Consult a Surgeon/General Practitioner for Personalised Advice
Symptoms of Gangrene
Recognising the signs early can prevent complications. Common symptoms include:
• Skin changes: Discolouration (blue, black, red, or purple) in the affected area.
• Pain or numbness: Sudden or severe pain, followed by loss of sensation.
• Swelling and blisters: Fluid-filled blisters with a foul odour (in wet gangrene).
• Fever and fatigue indicate infection spreading in the body.
• Cold or pale skin: Poor circulation makes the area feel cold.
If you notice these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
Causes and Risk Factors
Gangrene develops due to:
• Poor blood circulation (common in diabetes, atherosclerosis, or smoking).
• Severe injuries or burns that damage blood vessels.
• Infections (especially untreated wounds).
• Frostbite (extreme cold can block blood flow).
Risk factors include:
• Diabetes (high blood sugar damages blood vessels).
• Obesity.
• Smoking (narrows blood vessels).
• Weakened immune system (due to HIV, chemotherapy, etc.).
Treatment Options
Early treatment is crucial to prevent tissue death and the spread of infection. Treatment depends on the type and severity of gangrene.
1. Medications
• Antibiotics (for bacterial infections).
• Pain relievers (to manage discomfort).
• Clot-dissolving drugs (if blood flow is blocked).
2. Surgical Treatments
• Debridement: Removing dead tissue to prevent infection spread.
• Amputation: In severe cases, removing the affected limb may be necessary.
• Vascular Surgery: Restoring blood flow through bypass surgery or angioplasty.
3. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
• Breathing pure oxygen in a pressurised chamber helps heal infected wounds by increasing oxygen supply.
4. Lifestyle Changes
• Control diabetes: Keep blood sugar levels in check.
• Quit smoking: Improves blood circulation.
• Healthy diet: Eat foods rich in vitamins and minerals to promote healing.
• Regular exercise: Enhances blood flow.
Prevention Tips
The prevention tips include:
• Proper wound care: Clean cuts or injuries immediately and keep them dry.
• Monitor chronic conditions: Manage diabetes, high cholesterol, or heart disease.
• Avoid extreme cold: Protect hands and feet in freezing weather.
• Regular check-ups: Especially if you have circulation problems.
When to See a Doctor?
Seek emergency care if you experience:
• Sudden, severe pain in a limb.
• Skin discolouration with foul odour.
• Fever along with a non-healing wound.
Early intervention can save lives and limbs.
Final Thoughts
Gangrene is a serious but treatable condition if detected early. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to protect your health. If you or a loved one is at risk, prioritise regular medical check-ups and adopt a healthy lifestyle to prevent complications.
Consult a Surgeon/General Practitioner for Personalised Advice
Consult a Surgeon/General Practitioner for Personalised Advice

Dr Syed Mateen Pasha
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Anand Ravi
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Vivek D
General Physician
4 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Syed Ismail Ali
General Practitioner
7 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad

Dr. Johnson. S
General Practitioner
7 Years • MBBS MD(Preventive and social Medicine)
Pune
Apollo Clinic, Nigdi, Pune
Consult a Surgeon/General Practitioner for Personalised Advice

Dr Syed Mateen Pasha
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Anand Ravi
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Vivek D
General Physician
4 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Syed Ismail Ali
General Practitioner
7 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad

Dr. Johnson. S
General Practitioner
7 Years • MBBS MD(Preventive and social Medicine)
Pune
Apollo Clinic, Nigdi, Pune
.webp)



