Your Complete Guide to Cochlear Implants How They Work & Who They Help
Discover everything about cochlear implants, how they work, who can benefit, the surgery process, and post-implant rehabilitation to regain the world of sound.

Written by Dr. Mohammed Kamran
Reviewed by Dr. D Bhanu Prakash MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Hearing loss can feel isolating, closing doors to conversations, music, and the subtle sounds of daily life. While hearing aids are a powerful solution for many, they aren't always enough for those with severe to profound hearing loss. This is where cochlear implants come in—a remarkable blend of medical science and technology that can offer a sense of sound to those who receive little to no benefit from conventional aids. This guide will demystify cochlear implants, explaining how they work, who they can help, and what the journey to hearing with one truly entails. Whether you're exploring options for yourself or a loved one, understanding this life-changing technology is the first step towards reconnecting with the world of sound. We'll walk you through everything from candidacy criteria and surgery to activation and the amazing benefits that follow.
What is a Cochlear Implant? It’s More Than a Hearing Aid
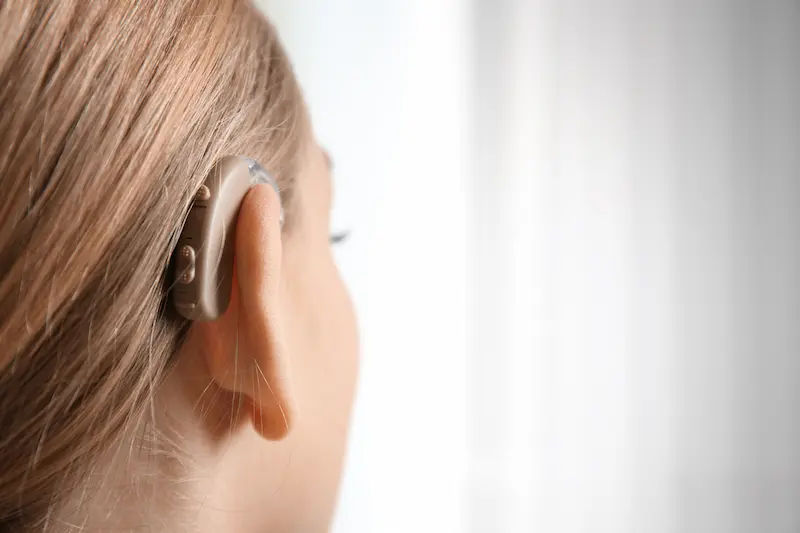
A cochlear implant is a sophisticated electronic medical device that bypasses damaged portions of the ear to directly stimulate the auditory nerve. Unlike hearing aids, which amplify sound, a cochlear implant does the job of the damaged inner ear (cochlea) by converting sound waves into electrical signals the brain can interpret as sound.
This fundamental difference makes it a solution for individuals whose inner ear hair cells are too damaged for amplification to be effective. It's not a "cure" for deafness, but rather a prosthetic device that provides a digital representation of sound, allowing the brain to learn or re-learn how to hear.
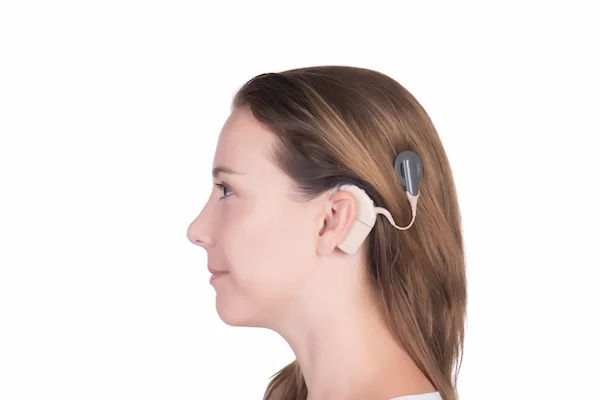
Key Components: The Internal Implant and External Processor
A cochlear implant system consists of two main parts:
1. Internal Implant: This is surgically placed under the skin behind the ear. A thin wire and tiny electrodes are threaded into the cochlea. This component is designed to last a lifetime.
2. External Sound Processor: This is worn on the ear, much like a behind-the-ear hearing aid. It contains a microphone, a battery, and a computer chip that captures sound, processes it into a digital code, and transmits it through the scalp to the internal implant.
Cochlear Implant vs. Hearing Aid: Understanding the Fundamental Difference
Think of it like this: a hearing aid makes a broken speaker louder. A cochlear implant replaces the broken speaker entirely with a new one. Hearing aids are acoustic devices; they make all sounds louder. Cochlear implants are electronic devices; they transform sound into a digital code, allowing for more targeted and clear stimulation of the auditory nerve, which is crucial for understanding speech in noisy environments.
Who is a Candidate for a Cochlear Implant?
Candidacy is determined by a dedicated medical team, but general guidelines are well-established.
Candidacy for Adults with Progressive Hearing Loss
Adults are typically candidates if they:
• Have moderate to profound sensorineural hearing loss in both ears.
• Receive limited benefit from hearing aids (e.g., scoring ≤50% on sentence recognition tests in the ear to be implanted).
• Have a strong desire to be part of the hearing world and are motivated to engage in auditory rehabilitation.
• Have no medical conditions that would increase the risks of surgery.
Candidacy for Children and Infants
For children, early intervention is key. Candidacy often includes:
• Infants as young as 9–12 months with profound hearing loss in both ears.
• Older children with severe hearing loss who show limited progress in auditory and speech development with hearing aids.
• The goal is to provide access to sound during the critical language acquisition period.
The Comprehensive Evaluation Process
Determining cochlear implant candidacy involves a multidisciplinary team approach, including:
• An Audiologist: To conduct extensive hearing tests and hearing aid trials.
• An ENT (Otolaryngologist): To perform a medical evaluation and imaging (CT/MRI scans) to assess the anatomy of the inner ear and ensure surgery is feasible.
• A Speech-Language Pathologist: To evaluate communication skills, especially in children.
• A Psychologist: To assess motivation and expectations, particularly for adults who have lived with hearing loss for a long time.
If you or your child are undergoing this evaluation process and have questions about the medical aspects, consulting an ENT specialist online with Apollo24|7 can provide convenient preliminary guidance.Consult an ENT Specialist for the best advice
The Cochlear Implant Journey: From Surgery to Sound
The path to receiving a cochlear implant is a process, not a single event.
What to Expect During Cochlear Implant Surgery
The surgery is performed under general anaesthesia and typically takes 2–4 hours. The surgeon makes a small incision behind the ear, creates a bony well to secure the implant, and then carefully threads the electrode array into the cochlea. It is considered a safe procedure with a low risk of complications. Most patients go home the same day or after an overnight stay. Recovery involves a few weeks of healing before the external processor is activated.
The "Switch-On" and Auditory (Re)habilitation
About 2–4 weeks after surgery, the "switch-on" or activation appointment occurs. This is a deeply emotional and significant moment. The audiologist fits the external sound processor and activates the electrodes.
• First Sounds: The initial experience of sound is often described as robotic, beeping, or like cartoon characters. This is because the brain must learn to interpret these new electrical signals.
• Mapping Sessions: The audiologist fine-tunes the device's programming ("mapping") over several appointments to ensure optimal sound quality.
• Auditory Rehabilitation: This is the most critical part of the journey. It involves structured therapy and daily practice to train the brain to recognise and understand these new sounds. Success is highly dependent on consistent engagement in this auditory verbal therapy.
Benefits and Realistic Expectations: What Can You Achieve?
The outcomes can be truly transformative, but it's important to have realistic expectations.
Success Stories and Potential Outcomes
Many recipients experience life-changing improvements. Adults often report the ability to understand speech without lip-reading, use the telephone, and enjoy music and social gatherings again. For children implanted early, the goal is to develop spoken language skills on par with their hearing peers, allowing them to attend mainstream schools. Studies show that over 80% of implant users can understand spoken sentences without visual cues when combined with therapy.
Understanding the Risks and Limitations
As with any surgery, there are risks, including infection, numbness, dizziness, and (very rarely) facial nerve injury. The device itself may sometimes fail, requiring revision surgery. Importantly, results vary. While some users achieve exceptional speech understanding, others may primarily get environmental sound awareness and speech-reading support. It does not restore "normal" hearing, and listening in very noisy environments can remain challenging.
Navigating Cost, Insurance, and Financial Assistance
The cost of cochlear implant surgery is significant, often ranging from ₹6,00,000 to ₹12,00,000 per ear in India, covering the device, surgery, and hospital stay. Fortunately, most major health insurance plans in India now provide coverage for cochlear implants as they are recognised as a medically necessary procedure. Additionally, government schemes like the ADIP Scheme (Assistance to Disabled Persons for Purchasing/Fitting of Aids/Appliances) and support from various NGOs can offer substantial financial assistance for hearing implants. It's crucial to work with your hospital's financial counsellor to explore all options.
Living with a Cochlear Implant: Technology and Lifestyle
Once healed and programmed, the implant becomes a part of daily life.
Caring for Your Device and Latest Technological Advancements
Modern processors are rugged, water-resistant (with optional accessories), and incredibly smart. They can connect via Bluetooth directly to phones, TVs, and microphones, streaming sound clearly to the implant. Care involves daily drying of the processor, changing batteries, and protecting it from heavy impact. The field is rapidly evolving, with innovations focusing on improved sound quality in noise, smaller designs, and even built-in fall detection and health monitoring.
Conclusion
A cochlear implant represents one of the most profound achievements in modern medicine, offering not just the ability to hear, but the opportunity to connect, communicate, and engage with the world fully. The journey requires commitment—from the initial evaluation and surgery to the critical rehabilitation afterward—but the potential rewards are immeasurable. If you or someone you love struggles with severe hearing loss and gains limited benefit from hearing aids, taking the step to speak with an audiologist or ENT specialist could open the door to a new chapter. Remember, exploring the possibility of a cochlear implant is an act of hope, and with the right support and information, the world of sound is within reach. If you're considering this path, we recommend starting with a comprehensive hearing evaluation. Apollo24|7 offers convenient access to specialist consultations, including ENTs and audiologists, who can guide you through the initial assessment process from the comfort of your home.Consult an ENT Specialist for the best advice
Consult an ENT Specialist for the best advice

Dr. Ravi Y L
Ent Specialist
15 Years • MBBS, MS (ENT)
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
(175+ Patients)

Dr. Sreeram Valluri
Ent Specialist
15 Years • MBBS, MS ENT, HEAD & NECK SURGERY
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad

Dr. Sreeram Valluri
Ent Specialist
15 Years • MBBS, MS ENT
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir

Dr. Ashwani Kumar
Ent Specialist
11 Years • MBBS, DNB (Otorhinolaryngology)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(50+ Patients)

Dr. Sushma Patil
Ent Specialist
20 Years • MBBS, DLO (Diploma in Laryngology & otology) ENT
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
Consult an ENT Specialist for the best advice

Dr. Ravi Y L
Ent Specialist
15 Years • MBBS, MS (ENT)
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
(175+ Patients)

Dr. Sreeram Valluri
Ent Specialist
15 Years • MBBS, MS ENT, HEAD & NECK SURGERY
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad

Dr. Sreeram Valluri
Ent Specialist
15 Years • MBBS, MS ENT
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir

Dr. Ashwani Kumar
Ent Specialist
11 Years • MBBS, DNB (Otorhinolaryngology)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(50+ Patients)

Dr. Sushma Patil
Ent Specialist
20 Years • MBBS, DLO (Diploma in Laryngology & otology) ENT
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
More articles from Hearing Loss
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the success rate of cochlear implant surgery?
The surgery itself has a very high success rate (>97%) with a low complication rate. The success in terms of hearing outcomes is also very high, with the vast majority of users experiencing significant improvement in their ability to hear and understand speech, especially when committed to rehabilitation.
2. Can you hear normally with a cochlear implant?
It does not restore 'normal' hearing. The brain receives a digital representation of sound, which is initially heard as beeps or robotic noises. Over time, the brain learns to interpret these signals as meaningful sound, like speech and environmental noises. For most, it becomes their new 'normal' and a vast improvement over their hearing pre-implant.
3. Is cochlear implant surgery risky?
As with any surgery, there are risks, including infection, bleeding, dizziness, tinnitus, changes in taste, and very rarely, injury to the facial nerve. However, it is considered a very safe and routine procedure when performed by an experienced surgeon.
4. Can you get an MRI if you have a cochlear implant?
Most modern cochlear implants are MRI-compatible up to a certain strength (typically 1.5 Tesla or 3.0 Tesla). It is crucial to inform your radiologist and MRI technician about your implant brand and model, as they may need to use a special head wrap or take specific precautions.
5. What are the best cochlear implant brands?
The three leading global brands are Cochlear™, MED-EL®, and Advanced Bionics (AB). There is no single 'best' brand; the ideal choice depends on individual anatomy, lifestyle needs, technological preferences, and the recommendation of your surgical and audiology team.