Signs Of Signs And Of Silent Heart Attacks
Don't miss the subtle signs of a silent heart attack. Learn the atypical symptoms like unexplained fatigue, jaw pain, shortness of breath, and nausea that are often overlooked.

Written by Dr. J T Hema Pratima
Reviewed by Dr. Mohammed Kamran MBBS, FIDM
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
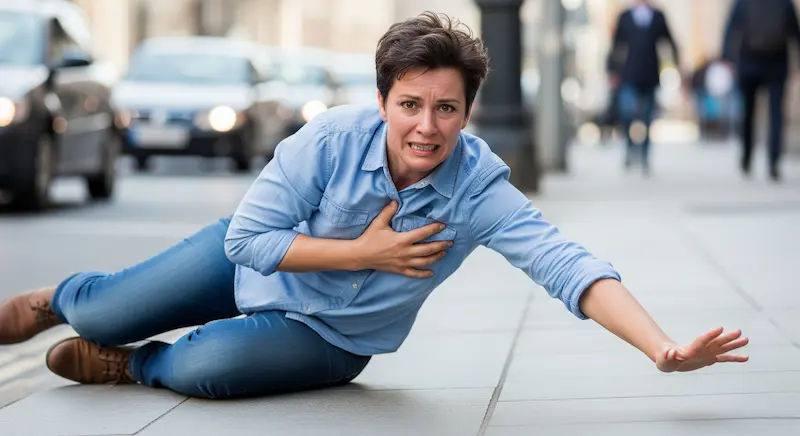
A heart attack doesn't always look like it does in the movies. There's not always a dramatic clutch to the chest followed by a collapse. In fact, a significant number of heart attacks are "silent"—they occur with minimal, vague, or no symptoms at all. These silent heart attacks are medically known as silent ischemia or silent myocardial infarction. The danger lies in their name: because they go unnoticed or are mistaken for less serious issues like indigestion or fatigue, they often go untreated. This lack of treatment can lead to lasting damage to the heart muscle and significantly increase the risk of a second, more severe heart attack. This article will guide you through the subtle, often-missed signs of a silent heart attack, explain who is most at risk, and outline the critical steps for prevention and diagnosis to protect your long-term heart health.
What Exactly is a Silent Heart Attack?
A silent heart attack is a myocardial infarction—a blockage in the coronary arteries that reduces or cuts off blood flow to the heart muscle—that occurs without the classic, intense symptoms. The damage is real and medically identical to a traditional heart attack; the only difference is how your body communicates the problem.
How It Differs From a Traditional Heart Attack?
A traditional heart attack typically presents with unmistakable warning signs:
Intense chest pain, pressure, or squeezing that may radiate to the arm, jaw, or back.
Severe shortness of breath.
Profuse sweating and a sense of impending doom.
In contrast, a silent heart attack may have symptoms so mild and brief that they are easily dismissed. You might attribute them to muscle strain, heartburn, the flu, or simply feeling run-down. The absence of crushing chest pain is the key differentiator, making it far more insidious.
Why "Silent" Doesn't Mean "Harmless"?
The term "silent" is dangerously misleading. The lack of dramatic symptoms does not equate to a lack of damage. When a coronary artery is blocked, heart muscle cells begin to die due to lack of oxygen. This scar tissue weakens the heart's ability to pump blood effectively, leading to complications like heart failure or arrhythmias later on. Because the event is not treated at the time, the underlying cause—such as coronary artery disease—remains unaddressed, setting the stage for future cardiac events.
Health Topic Carousel:
Doctor Speciality: General Physician
Text: Consult Top Specialists
The Subtle Signs: Listening to Your Body's Whispers
Recognizing a silent heart attack requires a heightened awareness of your body's more subtle signals. These are the "signs of the signs" that you should never ignore.
Unusual Fatigue and Profound Weakness
One of the most common symptoms of a silent heart attack is sudden, extreme fatigue without a clear cause. This isn't just feeling tired after a long day. It's a deep, overwhelming exhaustion that makes simple activities, like walking to the bathroom or making a meal, feel Herculean. This happens because your heart is struggling to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of your body.
Discomfort That Feels Like Indigestion or Heartburn
Many people who experience a silent myocardial infarction report a feeling of pressure, burning, or an upset stomach in the upper abdomen. It might seem like severe indigestion that doesn't go away with antacids. This discomfort can come and go, which further leads to the misconception that it's not serious.
Unexplained Shortness of Breath
If you find yourself becoming short of breath from activities you could previously handle easily—like climbing a short flight of stairs—it could be a red flag. This symptom, known as dyspnea, occurs if the heart is damaged and cannot pump enough blood to meet your body's needs, causing fluid to back up into the lungs.
Dizziness, Lightheadedness, or Cold Sweats
Feeling suddenly dizzy or breaking out in a cold sweat without physical exertion or a hot environment is a sign that your cardiovascular system is under stress. This can indicate a drop in blood pressure or an irregular heartbeat triggered by the heart attack.
Discomfort in the Jaw, Neck, Back, or Arm
Pain that radiates is a classic heart attack symptom, but in a silent heart attack, it might be the only symptom. You might feel a dull ache, tightness, or pressure in your jaw, between your shoulder blades, or down your left arm (or sometimes the right arm). This "referred pain" happens because nerves from the heart share pathways with nerves from these other areas.
Who is Most at Risk for a Silent Heart Attack?
While anyone with risk factors for heart disease can have a silent heart attack, certain groups are more vulnerable.
The Link with Diabetes and Nerve Damage
Individuals with diabetes, especially those with long-standing or poorly controlled blood sugar, are at a significantly higher risk. High blood glucose levels can damage the nerves throughout the body, a condition called diabetic neuropathy. When this affects the nerves that carry pain signals from the heart (cardiac autonomic neuropathy), a person may not feel the typical pain of a heart attack, making it more likely to be silent.
Gender Differences: Are Women More Susceptible?
Research shows that silent heart attacks are more common in women, particularly younger women. Women are more likely to experience non-traditional symptoms like the ones listed above. Unfortunately, these symptoms are often misattributed to anxiety or other conditions, leading to delays in diagnosis and treatment. Both men and women are at risk, but women and their doctors must be especially vigilant about these atypical presentations.
How is a Silent Heart Attack Diagnosed?
Often, a silent heart attack is discovered weeks, months, or even years after it happens during a routine medical check-up.
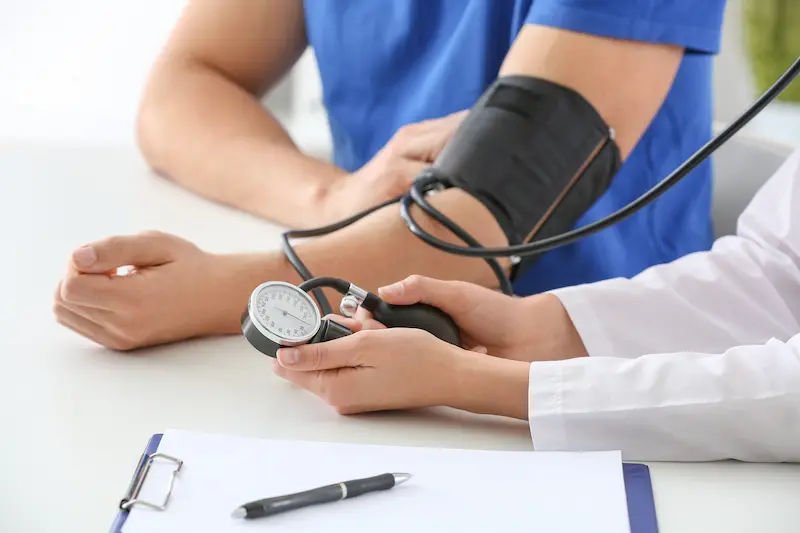
The Role of Routine EKGs and Blood Tests
The most common way it's found is through an electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). An EKG records the heart's electrical activity and can show patterns indicative of old, scarred heart tissue from a past heart attack. Blood tests that measure cardiac enzymes like troponin, which are released when the heart muscle is damaged, can also provide clues, though these levels return to normal after a short period. If you have risk factors, your doctor may recommend these tests as part of a preventive screening. Apollo24|7 offers a convenient home collection for tests like the Cardiac Risk Markers package, which can help assess your heart health from the comfort of your home.
The Long-Term Consequences of an Undiagnosed Event
The major danger of a silent heart attack is that the damage goes untreated. The scar tissue left behind weakens the heart, increasing the risk of:
Heart Failure: The damaged heart can't pump blood efficiently.
Arrhythmias: Scar tissue can disrupt the heart's electrical system, causing abnormal rhythms.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest: The risk of a fatal cardiac event is higher after any heart attack, including a silent one.
Knowing you've had one allows you and your doctor to take aggressive preventive measures to protect your heart from further damage.
Prevention: Your Best Defense Against Silent Heart Attacks
The strategy for preventing a silent heart attack is the same as for any cardiovascular disease: managing risk factors.
Lifestyle Changes for a Healthier Heart
Diet: Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit saturated fats, salt, and sugar.
Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Smoking: Quit smoking. It's one of the most significant risk factors.
Weight: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on your heart.
The Critical Importance of Regular Health Screenings
If you have risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes, regular monitoring is non-negotiable. If your blood pressure readings are consistently high or you experience any of the subtle symptoms mentioned, consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for further evaluation. Early intervention is key to preventing a heart attack, silent or otherwise.
Conclusion
A silent heart attack is a stealthy threat to your health, emphasizing that the absence of dramatic pain does not mean the absence of danger. By learning to recognize the subtle signs—the unusual fatigue, the mysterious indigestion, the unexplained shortness of breath—you empower yourself to seek help before significant damage occurs. Your heart often sends whispers before it screams. The key is to listen carefully. Prioritize your cardiovascular health by understanding your personal risk factors, committing to a heart-healthy lifestyle, and attending regular check-ups. Taking these steps today is your most powerful defense against the silent dangers of tomorrow. If you have any concerns about your heart health, especially if you fall into a high-risk category, do not hesitate to speak with a healthcare professional.
Health Topic Carousel:
Doctor Speciality: General Physician
Text: Consult Top Specialists
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can you have a heart attack and not know it?
A. Yes, absolutely. This is the definition of a silent heart attack (silent MI). Studies suggest that as many as 20-50% of all heart attacks may be silent, meaning many people have them without realizing it until much later.
2. What does silent heart attack pain feel like?
A. The pain is often not a sharp, stabbing sensation. It's more commonly described as a mild pressure, tightness, burning (like heartburn), or a dull ache in the chest, jaw, back, or arms. For many, the "pain" is so minor it's dismissed as indigestion or muscle soreness.
3. How long can a silent heart attack last?
A. Symptoms can be fleeting, lasting only a few minutes, or they may come and go over several hours. The brevity of the symptoms is a major reason why people don't seek medical attention.
4. What is the survival rate of a silent heart attack?
A. The initial survival rate is high precisely because the event is not severe enough to cause immediate collapse. However, the long-term prognosis is serious. Without treatment, individuals who have had a silent heart attack have a significantly higher risk of complications and death from future cardiac events compared to those who never had one.
5. How is a silent heart attack treated after it's discovered?
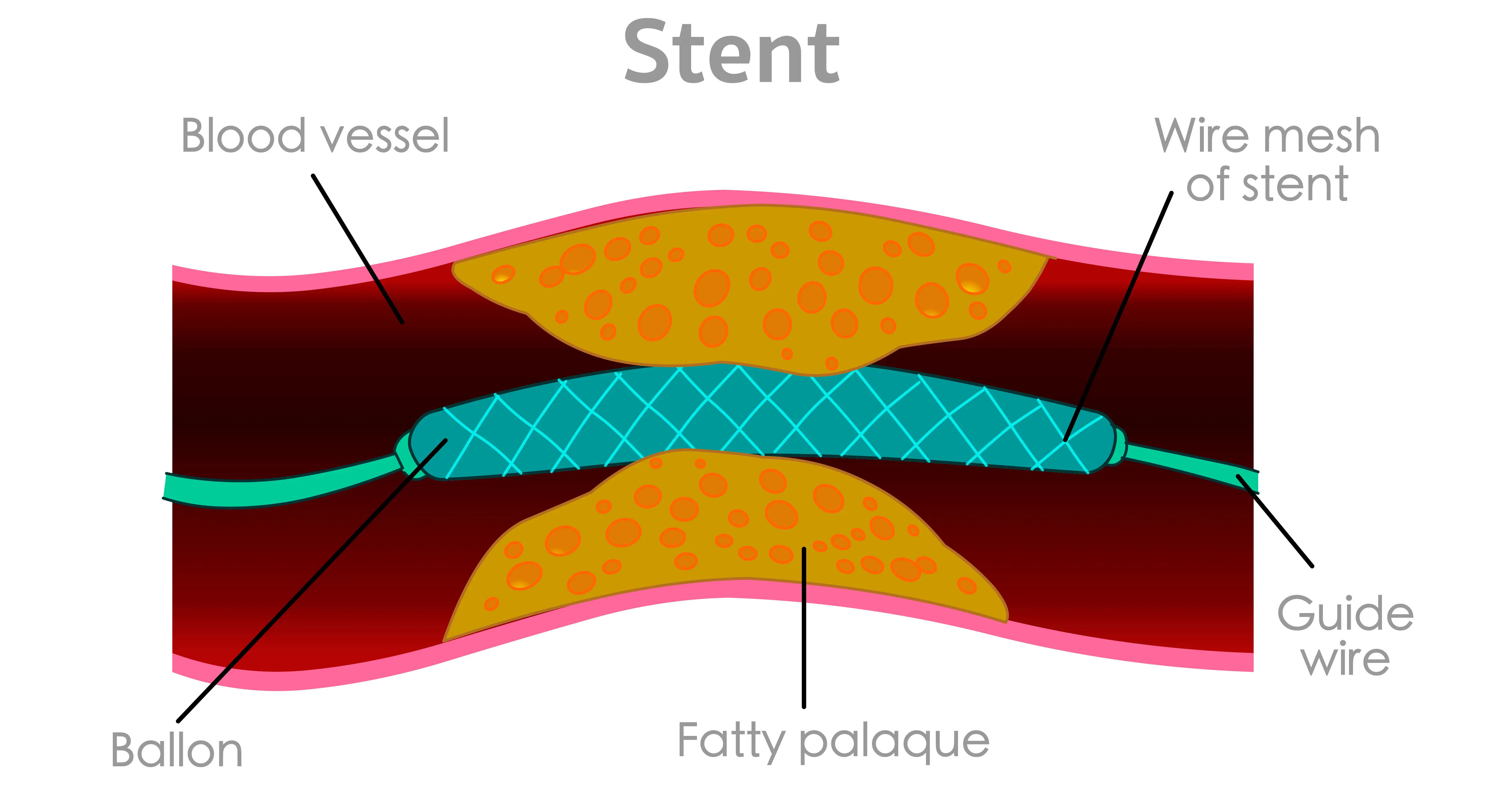
A. Treatment focuses on preventing another heart attack. This includes medications like aspirin, beta-blockers, statins (to lower cholesterol), and ACE inhibitors. Lifestyle changes are paramount, and sometimes procedures like angioplasty or stenting are needed to open blocked arteries.
Consult Top Specialists for Personalised Tips

Dr. Rajib Ghose
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
25 Years • MBBS
East Midnapore
VIVEKANANDA SEBA SADAN, East Midnapore

Dr. Ashmitha Padma
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS, MD Internal Medicine
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Jayanagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Aakash Garg
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DrNB (Gastroentrology).
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(150+ Patients)

Dr P Jagadeesha Chandra
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
37 Years • MBBS, MD
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Jayanagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Vijayalakshmi S
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
17 Years • MBBS, MDRC, PGDHS
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru
Consult Top Specialists

Dr. Rajib Ghose
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
25 Years • MBBS
East Midnapore
VIVEKANANDA SEBA SADAN, East Midnapore

Dr. Ashmitha Padma
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS, MD Internal Medicine
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Jayanagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Aakash Garg
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DrNB (Gastroentrology).
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(150+ Patients)

Dr P Jagadeesha Chandra
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
37 Years • MBBS, MD
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Jayanagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Vijayalakshmi S
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
17 Years • MBBS, MDRC, PGDHS
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru