All About Heart Disease Treatment!
Explore heart disease treatments, including lifestyle changes, medications, and surgeries. Early diagnosis and proper care improve heart health and quality of life effectively. Learn more about managing heart disease.

Written by Dr Shreya Sarkar
Last updated on 3rd Jul, 2025
Heart disease refers to various conditions that impact the heart's function. These include coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, congenital heart defects, heart muscle diseases, and valve disorders. When the heart doesn't function properly, it struggles to supply the body with adequate blood, nutrients, and oxygen, which can disrupt the functioning of other systems. Fortunately, many heart diseases are manageable with appropriate and timely treatments. Continue reading to explore the available options for treating heart disease.
Types of Heart Disease
Heart disease encompasses various conditions that impact the heart and blood vessels differently. Below are some of the common types:
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
This is the most prevalent form of heart disease. It occurs when plaque, composed of cholesterol and other substances, builds up in the arteries supplying blood to the heart. This buildup causes the arteries to harden and narrow, restricting blood flow and reducing the heart's supply of oxygen and essential nutrients.
Heart Valve Disease
Heart valve disease includes conditions that impair the proper functioning of one or more heart valves. When untreated, this condition can reduce blood flow and force the heart to work harder, which may lead to life-threatening complications.
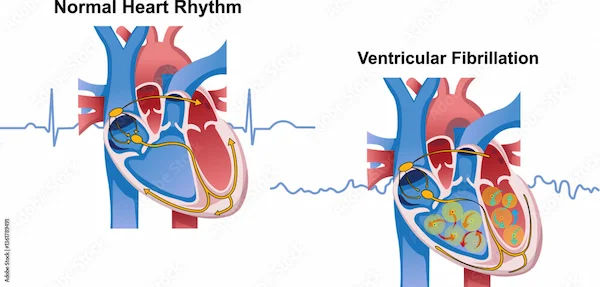
Heart Rhythm Disorders
Also known as arrhythmias, these disorders arise when the electrical signals regulating the heartbeat malfunction. This can cause the heart to beat irregularly- too slow, too fast, or erratically. While some arrhythmias are harmless and may not require treatment, others can lead to serious, potentially life-threatening health issues.
Heart Failure
Heart failure is a chronic condition where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively to meet the needs of the baby. Although the heart continues to function, it struggles to manage the required blood flow, leading to a buildup of blood in other parts of the body.
Symptoms of Heart Disease
The symptoms of heart disease can vary depending on the underlying condition. Common signs may include:
Excessive sweating
A racing or pounding heartbeat (palpitations)
Feeling lightheaded
Dizziness or fainting spells
Shortness of breath
Pain, heaviness, pressure, or discomfort in the chest or upper body
Symptoms resembling indigestion or heartburn
Discomfort in the neck
Swelling in the lower extremities
Nausea or vomiting
Persistent fatigue
Difficulty tolerating physical activity
Trouble sleeping
Fever
Diagnosis of Heart Disease
Healthcare providers diagnose heart disease through a combination of:
Conducting a physical examination.
Evaluating your symptoms.
Reviewing your personal and family medical history.
Performing diagnostic tests.
Common tests used to identify heart conditions include:
Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG): Measures the heart’s electrical activity.
Ambulatory Monitors: Tracks heart rhythms over time.
Echocardiogram (Echo): Uses ultrasound to visualize heart structure and function.
Cardiac CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the heart and blood vessels.
Heart MRI: Offers a detailed view of heart tissues.
Blood Tests: Assesses cholesterol levels and other markers.
Stress Test: Evaluates heart performance under physical stress.
Cardiac Catheterisation: Examines blood flow and identifies blockages
Lifestyle Modifications for Treating Heart Disease
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits is crucial for both preventing and managing heart disease. Key recommendations include:
Avoid Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease.
Follow a Balanced Diet: Include plenty of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains while reducing salt, sugar, and saturated fats.
Stay Active: Regular exercise supports heart health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days of the week.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight raises the risk of heart-related complications.
Manage Stress Effectively: Reduce emotional stress through activities like exercising, practising breathing exercises, or meditation.
Prioritise Quality Sleep: Poor sleep can heighten the risk of heart disease. Adults should aim for 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night.
Medications for Heart Disease
Various medications are available to manage different types of heart disease, often used in combination to improve outcomes. A commonly prescribed category includes:
Anti-Platelet Drugs
These medications help prevent blood clots by stopping platelets from clumping together. They are often prescribed for individuals who have experienced a heart attack, ischemic strokes, unstable angina, or transient ischemic attacks (TIA). They can also be used as a preventive measure when plaque buildup is present but has not yet caused significant arterial blockage. Common examples include aspirin, clopidogrel, prasugrel, dipyridamole, and ticagrelor.
Beta-blockers
Beta blockers are medications that reduce the heart rate and the force of its contractions, leading to lower blood pressure. They are commonly prescribed for managing certain heart conditions, including high blood pressure, heart attacks, and chest pain (angina) caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Additionally, they are used to treat some abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) and help prevent future heart attacks in individuals with a history of heart attack.
ACE Inhibitors
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors help lower blood pressure by relaxing and widening blood vessels, reducing the heart's workload. They are commonly used to manage cardiovascular conditions such as heart failure and high blood pressure. Additionally, they offer significant health benefits for individuals recovering from a heart attack.
Statins
Statins may be prescribed if you have high cholesterol or a history of heart attack. While not used for treating heart failure, these medications are effective in managing other conditions. They work by preventing plaque formation in the arteries, thereby lowering the risk of stroke and heart attack.
Surgical and Non-Surgical Procedures
Doctors may sometimes also recommend a surgical or non-surgical medical procedure to treat your heart condition. Some common procedures employed include:
Angioplasty and Stent Placement
Coronary angioplasty is a procedure performed to widen narrowed or blocked coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. A small balloon is used to stretch open the artery, and in most cases, a wire mesh tube called a stent is inserted. The stent remains in place permanently, ensuring improved blood flow through the artery.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
This is a surgical procedure used to manage coronary heart disease. It improves blood flow and oxygen supply to the heart by redirecting blood around narrowed or blocked arteries. This is achieved by taking a blood vessel from one part of the body, such as the leg, chest, or arm, and attaching it to the coronary artery below and above the affected area.
Pacemaker and Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD)
For severe arrhythmias, a cardiac pacemaker or an ICD may be required. These devices are implanted in the chest or abdomen. A pacemaker regulates abnormal heart rhythms by sending electrical pulses to maintain a normal heart rate. An ICD continuously monitors heart rhythms and delivers shocks when it detects dangerous irregularities, a process known as defibrillation.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Cardiac rehabilitation is a comprehensive recovery program designed for individuals who have undergone cardiac surgery or treatment for heart conditions like a heart attack. It aims to help patients regain strength and improve overall heart health. The program involves guidance from a team of healthcare providers, including exercise and nutrition specialists, and usually spans at least three months. Key components include heart health education, exercise training, dietary counselling, lifestyle and risk factor modifications, and emotional support.
Conclusion
Heart disease, a complex and multifaceted condition, poses significant challenges to individuals and healthcare systems alike. However, advancements in medical science and an increased emphasis on preventive care have made managing and treating heart disease more effective than ever. From lifestyle modifications and medications to surgical interventions and cardiac rehabilitation, there are numerous options available to improve heart health and quality of life. Early diagnosis, adherence to prescribed treatments, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle are pivotal steps in combating heart disease.
Consult Top Cardiologists
Check Your Risk For Heart Disease
₹800(₹2000)60% off
Consult Top Cardiologists

Dr. Amit. A. Bharadiya
Cardiologist
12 Years • MBBS, MD General Medicine, DNB Cardiology, FSCAI
Maharashtra
Surabhi Hospital, Maharashtra, Maharashtra

Dr. Mangesh Danej
Cardiologist
8 Years • MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DNB (Cardiology)
Pune
Dr Danej clinic, Pune
(375+ Patients)
Dr. Dixit Garg
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS , DNB (General medicine) , DNB (cardiology)
Gurugram
Smiles & Hearts, Gurugram
Dr. Pinaki Nath
Cardiologist
8 Years • MBBS, MD General Medicine, DM Cardiology
Barasat
Diab-Eat-Ease, Barasat
Dr. Sibashankar Kar
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS, DNB
Bhubaneswar
Hi-Tech Medical College & Hospital, Bhubaneswar
Consult top Cardiologists

Dr. Amit. A. Bharadiya
Cardiologist
12 Years • MBBS, MD General Medicine, DNB Cardiology, FSCAI
Maharashtra
Surabhi Hospital, Maharashtra, Maharashtra

Dr. Mangesh Danej
Cardiologist
8 Years • MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DNB (Cardiology)
Pune
Dr Danej clinic, Pune
(375+ Patients)
Dr. Dixit Garg
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS , DNB (General medicine) , DNB (cardiology)
Gurugram
Smiles & Hearts, Gurugram

Dr. Pinaki Nath
Cardiologist
8 Years • MBBS, MD General Medicine, DM Cardiology
Barasat
Diab-Eat-Ease, Barasat
Dr. Sibashankar Kar
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS, DNB
Bhubaneswar
Hi-Tech Medical College & Hospital, Bhubaneswar