Guide to Category/cardiology
Learn about cardiology and the role of cardiologists in maintaining heart health. Explore common heart conditions, treatments, and preventive care tips.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. Vasanthasree Nair MBBS
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Your heart is the tireless engine that powers your entire body. It beats roughly 100,000 times a day, pumping blood to every cell. The medical field dedicated to keeping this vital organ healthy is cardiology. But what does that really mean for you? This guide demystifies the world of cardiology, explaining what cardiologists do, the conditions they treat, and the critical signs that mean it's time to pay attention to your heart health. Whether you're proactively managing your well-being or seeking answers to specific concerns, understanding cardiology is the first step toward a longer, healthier life. We'll explore everything from common heart diseases like coronary artery disease and arrhythmias to the advanced diagnostic tools doctors use. More importantly, we'll highlight the power of preventive care and how lifestyle choices today can dramatically reduce your risk of heart problems tomorrow. Consider this your comprehensive roadmap to navigating heart health with confidence.
What is Cardiology? The Science of Your Heart and Blood Vessels
At its core, cardiology is the branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the blood vessels (the cardiovascular system). A doctor who specialises in this field is called a cardiologist. These specialists are not cardiac surgeons (who perform open-heart operations) but are experts in diagnosing, treating, and preventing medical conditions related to the heart. They are the master detectives of heart health, piecing together clues from symptoms, family history, and sophisticated tests to create a personalised treatment plan.
The Vital Role of Your Cardiovascular System
Think of your cardiovascular system as your body's delivery network. The heart is the central pump, and the blood vessels are the intricate highways. This system delivers oxygen and essential nutrients to your organs and muscles while carting away waste products like carbon dioxide. When this system is compromised by disease, it can affect everything from your brain function to your ability to walk up a flight of stairs. Cardiologists work to ensure this network remains open, efficient, and strong, addressing any blockages, leaks, or electrical faults that may occur.
Consult a Cardiologist for the best advice
Common Heart Conditions a Cardiologist Treats
Cardiologists manage a wide spectrum of conditions. Understanding these is key to recognising potential problems. Some of the most prevalent include:
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) and Atherosclerosis
This is the most common type of heart disease. CAD occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle itself, become narrowed or blocked by a buildup of cholesterol-rich plaque, a process called atherosclerosis. This can reduce blood flow to the heart, causing chest pain (angina). If a plaque ruptures and completely blocks an artery, it can lead to a heart attack. Cardiologists are experts in managing coronary artery disease through medication, lifestyle changes, and procedures to open blocked arteries.
Heart Arrhythmias (Irregular Heartbeats)
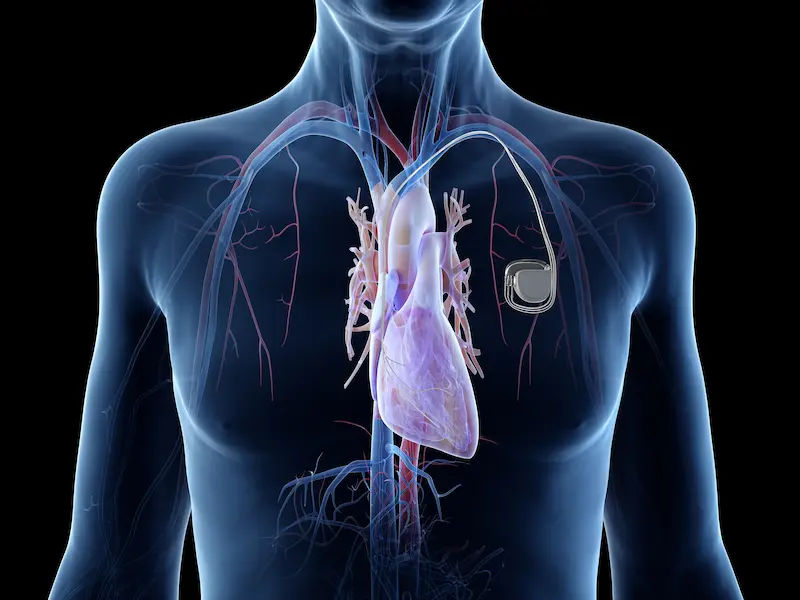
An arrhythmia is an abnormality in the heart's rhythm. It can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregularly. While some arrhythmias are harmless, others can be serious, causing dizziness, fainting, or increasing the risk of stroke. Conditions like atrial fibrillation (AFib) are a major focus for cardiologists, who use medications, pacemakers, or ablation procedures to restore a normal rhythm.
Heart Failure: A Problem of Pumping Power
Heart failure doesn't mean the heart has stopped beating. Rather, it means the heart muscle has become weakened or stiff and can't pump blood as effectively as it should. This can lead to fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs. It's a chronic condition that cardiologists manage with a combination of medications, device therapy, and careful monitoring to improve quality of life and longevity.
Valvular Heart Disease
Your heart has four valves that act as one-way gates to ensure blood flows in the correct direction. Valvular heart disease occurs when these valves become leaky (regurgitation) or narrowed (stenosis). This forces the heart to work harder. Cardiologists monitor valve function and can often repair or replace damaged valves using minimally invasive techniques.
Warning Signs: When Should You See a Cardiologist?
Knowing when to see a cardiologist can be life-saving. Don't ignore these symptoms:
- Chest Pain, Pressure, or Discomfort (Angina): This is a classic sign, but it's not always dramatic. It might feel like squeezing, fullness, or burning.
- Shortness of Breath: Especially if it occurs with minimal exertion or when lying flat.
- Heart Palpitations: The feeling that your heart is fluttering, pounding, or skipping beats.
- Dizziness or Fainting Spells (Syncope): This can indicate a problem with blood flow or heart rhythm.
- Swelling in Legs, Ankles, or Feet: This can be a sign of heart failure.
- Extreme Fatigue: Unusual, persistent tiredness can sometimes point to a heart issue.
Additionally, if you have risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, a family history of heart disease, or if you are a smoker, a proactive visit to a cardiologist for a risk assessment is a wise decision. If you experience sudden, severe chest pain, pain radiating to your arm or jaw, or extreme shortness of breath, seek emergency medical attention immediately.
The Cardiologist's Toolkit: Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Cardiologists have an impressive array of tools to look inside your heart without major surgery.
Non-Invasive Tests: EKG, Echocardiogram, and Stress Tests
- Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG): This simple, painless test records the heart's electrical activity and can detect
arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other problems. - Echocardiogram (Echo): Essentially an ultrasound of the heart, this test uses sound waves to create moving pictures of the heart's chambers and valves, assessing its structure and function.
- Stress Test: You'll walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike while your heart rate and EKG are monitored. This shows how your heart performs under physical exertion.
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Cardiac Catheterisation and Angioplasty
For a closer look, a cardiologist might perform a cardiac catheterisation. A thin tube (catheter) is threaded through a blood vessel in the groin or wrist to the heart. This allows them to inject dye to see blockages on an X-ray (angiogram). If a significant blockage is found, they can often treat it immediately with a procedure called angioplasty, where a tiny balloon is inflated to squash the plaque and a mesh tube (stent) is placed to keep the artery open.
Beyond Treatment: The Power of Preventive Cardiology
The most advanced field in cardiology today is prevention. The goal is to identify and manage risk factors before they lead to disease. This includes:
- Managing Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: These are silent killers that can be controlled with diet, exercise, and medication.
- Diabetes Management: High blood sugar damages blood vessels over time.
- Smoking Cessation: This is the single most important change a smoker can make for their heart health.
- Healthy Diet and Regular Exercise: A heart-healthy lifestyle is the cornerstone of prevention.
If you have risk factors like high blood pressure or a family history of heart disease, consulting a doctor online with Apollo24|7 can help you create a personalised prevention plan. Regular monitoring is key; for convenience, Apollo24|7 offers home collection for tests like cholesterol panels and HbA1c to track your progress.
Subspecialties in Cardiology: Finding the Right Expert
Just as heart conditions vary, so do cardiologists' expertise. Key subspecialties include:
- Interventional Cardiology: Experts in catheter-based procedures like angioplasty and stenting.
- Electrophysiology: Focuses on the heart's electrical system and complex arrhythmias, often implanting devices like pacemakers.
- Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology: Manages advanced heart failure and patients requiring mechanical support or transplant.
- Preventive Cardiology: Dedicated to reducing cardiovascular risk through lifestyle and medication.
Conclusion
Your heart health is a lifelong journey, and understanding cardiology empowers you to be an active participant in that journey. From recognising the early symptoms of heart problems to leveraging the advanced diagnostic and treatment options available today, you have more control than ever before. Remember, heart disease is often preventable. By embracing a heart-healthy lifestyle, managing your risk factors, and knowing when to seek expert advice, you can significantly improve your chances of a long and vibrant life. Don't wait for a crisis to think about your heart. Take the first step today, whether it's scheduling a check-up, making a dietary change, or simply going for a walk. Your heart is your most precious asset; invest in its care wisely.
Consult a Cardiologist for the best advice
Consult a Cardiologist for the best advice

Dr. Prashant Adeppa
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD General Medicine, DM Cardiology (Armed Forces Medical College)
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Bannerghatta Road, Bengaluru

Dr.ashwin Tumkur
Cardiologist
18 Years • MBBS, MGM Medical College, Aurangabad DNB (Pediatrics): Princess Durru Shehvar hospital, Hyderabad. DNB (Cardiology): Durgabai Deshmukh hospital, AMS, Hyderabad.
Hyderguda
Apollo Hospitals Hyderguda, Hyderguda

Dr. Poorna Pushkala Natarajan
Cardiologist
5 Years • MBBS, AB (INT MED), AB (CARDIOLOGY), AB (HEART FAILURE/TRANSPLANT CARDIOLOGY)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(50+ Patients)

Dr Gautam Naik
Cardiologist
12 Years • Senior ConsultMBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Cardiology), Interventional Cardiology Fellowship (Royal Papworth Hospital, Cambridge, UK), Structural Heart Intervention Fellowship (Barts Heart Centre, St Bartholomew's Hospital, London)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Praveen Subbanna
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS, M.D. (JIPMER. PONDICHERRY), DM (cardiology, SMS MEDICAL COLLEGE, JAIPUR)
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Bannerghatta Road, Bengaluru
Consult a Cardiologist for the best advice

Dr. Prashant Adeppa
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD General Medicine, DM Cardiology (Armed Forces Medical College)
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Bannerghatta Road, Bengaluru

Dr.ashwin Tumkur
Cardiologist
18 Years • MBBS, MGM Medical College, Aurangabad DNB (Pediatrics): Princess Durru Shehvar hospital, Hyderabad. DNB (Cardiology): Durgabai Deshmukh hospital, AMS, Hyderabad.
Hyderguda
Apollo Hospitals Hyderguda, Hyderguda

Dr. Poorna Pushkala Natarajan
Cardiologist
5 Years • MBBS, AB (INT MED), AB (CARDIOLOGY), AB (HEART FAILURE/TRANSPLANT CARDIOLOGY)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(50+ Patients)

Dr Gautam Naik
Cardiologist
12 Years • Senior ConsultMBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Cardiology), Interventional Cardiology Fellowship (Royal Papworth Hospital, Cambridge, UK), Structural Heart Intervention Fellowship (Barts Heart Centre, St Bartholomew's Hospital, London)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Praveen Subbanna
Cardiologist
10 Years • MBBS, M.D. (JIPMER. PONDICHERRY), DM (cardiology, SMS MEDICAL COLLEGE, JAIPUR)
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Bannerghatta Road, Bengaluru
More articles from Heart disease
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between a cardiologist and a cardiac surgeon?
A cardiologist is a medical doctor who diagnoses and treats heart disease using medications, lifestyle recommendations, and non-surgical procedures. A cardiac surgeon performs open-heart surgeries, such as bypass operations or valve replacements.
2. What kind of tests are done for chest pain to rule out a heart problem?
Initially, a doctor will typically perform an EKG to check the heart's rhythm and a blood test to look for markers of heart muscle damage. This is often followed by a stress test or an echocardiogram to assess heart function under strain.
3. Can heart disease be reversed?
While advanced damage like scarring from a heart attack cannot be reversed, the progression of coronary artery disease can often be halted and even partially reversed through aggressive lifestyle changes (very low-fat diet, exercise) and cholesterol-lowering medications under a doctor's supervision.
4. At what age should I start seeing a cardiologist?
There's no set age. You should consider a visit if you have symptoms, strong risk factors (like family history), or if you are over 40 and starting a new, intense exercise program. A proactive assessment in your 30s or 40s can establish a valuable baseline.
5. Is it normal to feel your heart beat irregularly sometimes?
Occasional, brief palpitations (like a skipped beat) can be normal and are often triggered by stress, caffeine, or lack of sleep. However, if you experience frequent, prolonged, or concerning heart arrhythmias, especially with dizziness or chest pain, you should see a doctor.