Infertility Myths and Facts: A Clear Guide for Your Journey
Know about the infertility, myths & facts associated with the infertility and the way forward.

Written by
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
The journey to parenthood can be filled with excitement, but for many, it also brings unexpected challenges and a flood of conflicting advice. Infertility, defined as the inability to conceive after one year of unprotected intercourse (or six months for women over 35), affects millions of couples worldwide. Unfortunately, it's a topic shrouded in misconceptions that can lead to unnecessary guilt, stress, and delays in seeking proper care. This guide aims to cut through the noise by separating common myths and facts about infertility. We will tackle pervasive falsehoods about age, gender, lifestyle, and treatment, replacing them with evidence-based information. Our goal is to empower you with knowledge, reduce the stigma, and guide you toward the most effective path forward. Understanding the reality of fertility is the first step in taking control of your reproductive health.
Consult a Top Gynaecologist for Personalised Advice
Myth 1: Infertility is Primarily a "Woman's Problem"
This is one of the most persistent and damaging myths. For generations, the burden of conception has been unfairly placed on women. The reality is far more balanced.
The Fact About Male Factor Infertility
According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), infertility issues are attributed to the female factor in about one-third of cases and the male factor in another third. The remaining cases are due to a combination of both partners' issues or are unexplained. This means male factor infertility is just as common as female factor. Causes can range from low sperm count or poor sperm motility to structural abnormalities or hormonal imbalances. Therefore, a comprehensive fertility evaluation always involves assessing both partners.
Why This Myth is Harmful
Believing this myth can lead to women undergoing unnecessary and stressful tests and treatments first, while a potential male factor goes unaddressed. It can also create a significant emotional strain within a relationship, with one partner bearing the weight of blame. Approaching infertility as a shared challenge, rather than an individual's "problem," is crucial for both medical effectiveness and emotional well-being.
Myth 2: You Can't Get Pregnant After 35
The "biological clock" is a real concept, but the idea that fertility falls off a cliff at age 35 is an oversimplification. It creates undue panic for many women.
Understanding Age and Ovarian Reserve
Female fertility indeed declines with age, primarily due to a decrease in the quantity and quality of eggs (a factor known as ovarian reserve). This decline becomes more significant after age 35 and accelerates after 40. However, it is not an on/off switch. Many women in their late 30s and early 40s conceive naturally. The key is probability; the chances of conceiving in any given month are lower for a 38-year-old than for a 28-year-old. This is why doctors recommend seeking help sooner—after 6 months of trying—for women over 35.
The Role of Male Age in Fertility
While often overlooked, male age also impacts fertility. Sperm quality, including DNA fragmentation, can decline with age, potentially affecting embryo development and increasing the risk of miscarriage. This reinforces the need for a couple-focused approach.
Infertility is All About Stress and "Just Relaxing"
How many times has someone struggling with infertility been told, "Just stop trying so hard and relax, it will happen"? While well-intentioned, this advice is medically inaccurate and can be deeply frustrating.
The Difference Between Correlation and Causation
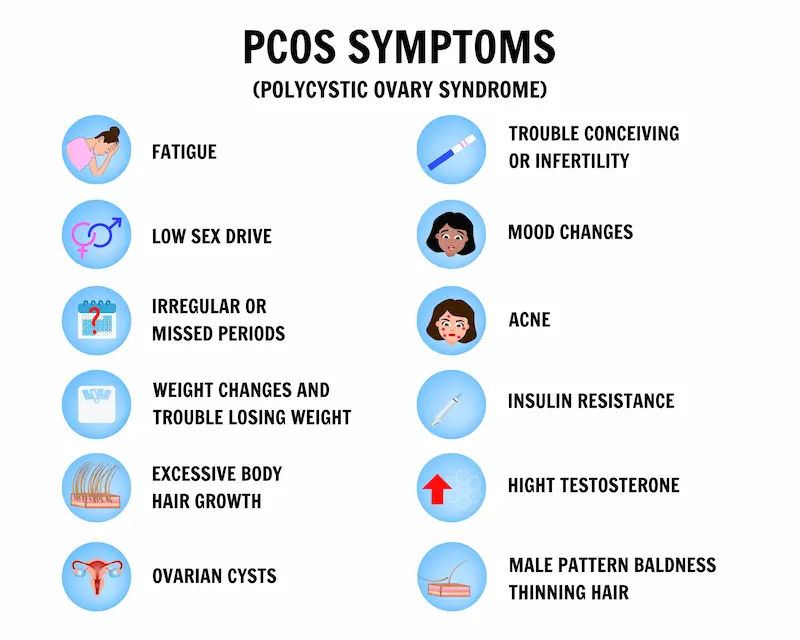
Extreme stress can sometimes affect hormone levels and ovulation, but it is rarely the sole cause of infertility. The relationship is often reversed: the experience of infertility causes tremendous stress, anxiety, and depression. Telling someone to "relax" implies they are to blame for their medical condition. Infertility is a disease of the reproductive system, with physiological causes like blocked fallopian tubes, endometriosis, PCOS, or low sperm count. These require medical intervention, not just a relaxing vacation. While stress management is important for overall health and coping, it is not a cure for the underlying causes of infertility.
Myth 4: Lifestyle Doesn't Impact Fertility That Much
On the opposite end of the spectrum from the stress myth is the belief that lifestyle has no impact. While not the primary cause for everyone, lifestyle factors play a significant supporting role.
The Real Impact of Weight, Smoking, and Alcohol
Weight: Being significantly underweight or overweight can disrupt hormonal balance, affecting ovulation in women and sperm production in men.
Smoking: This is profoundly damaging to fertility for both partners, accelerating egg loss in women and reducing sperm count and motility in men.
Alcohol: Heavy consumption can impair fertility. Most experts recommend limiting alcohol intake when trying to conceive.
Positive Lifestyle Changes You Can Make
The good news is that modifying these factors can improve your natural ways to improve fertility. Achieving a healthy weight through diet and exercise, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol can create a more favourable environment for conception. If you're struggling to make these changes, consulting a doctor or nutritionist can be a great first step. Apollo24|7 offers convenient consultations with nutritionists who can help you create a personalised plan.
Myth 5: If You Already Have a Child, You Can't Be Infertile
This myth leads to a condition known as secondary infertility, which is the inability to conceive or carry a pregnancy to term after previously having a child. It is surprisingly common, accounting for about 50% of infertility cases.
Understanding Secondary Infertility
The causes of secondary infertility are the same as those for primary infertility: age-related factors, new medical conditions (like uterine fibroids or pelvic inflammatory disease), changes in sperm quality, or complications from a previous pregnancy or surgery. The emotional impact can be unique, as couples often feel their struggle is invalidated because they already have a child. It's essential to recognise that secondary infertility is a real medical issue that warrants the same level of investigation and care as primary infertility.
Myth 6: Infertility Treatments Like IVF Guarantee a Baby
In-Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) is a powerful assisted reproductive technology, but it is not a magic bullet. Media portrayals often sensationalise success, leading to unrealistic expectations.
Setting Realistic Expectations for Fertility Treatments
Success rates of IVF are highly dependent on the woman's age, the cause of infertility, and the clinic's expertise. For example, according to SART (Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology), the live birth rate per IVF cycle for a woman under 35 is around 55%, but this drops significantly for women over 40. Treatments like IVF are a journey that may require multiple cycles, and even then, success is not guaranteed. Understanding the statistics and potential emotional and financial investment is crucial before beginning treatment.
The Path Forward: From Myths to Medical Facts
Once the myths are cleared away, the focus can shift to actionable, evidence-based steps.
When Should You Seek Help? Recognising the Signs
The general guideline is to consult a healthcare provider if you haven't conceived after one year of regular, unprotected intercourse if you're under 35, or after six months if you're 35 or older. You should seek help immediately if you have known issues like irregular periods, pelvic pain, a history of miscarriages, or prior cancer treatment.
What to Expect During a Fertility Evaluation
A basic fertility evaluation is straightforward and systematic. It typically involves:
For the woman: Assessing ovulation through blood tests (e.g., progesterone levels) and an ultrasound to examine the ovaries and uterus. A test called an HSG may be done to check if the fallopian tubes are open. Apollo24|7 offers convenient home collection for these initial blood tests.
For the man: A semen analysis to evaluate sperm count, motility, and morphology.
This initial workup helps identify the cause about 85% of the time and guides the next steps, which may include medications like Clomid, procedures like IUI, or more advanced options like IVF.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of infertility is challenging enough without the added burden of misinformation. By debunking these common myths, we hope to empower you with clarity and confidence. Remember, infertility is a medical condition, not a personal failure. Understanding the facts that it affects men and women equally, that age is a factor but not an absolute barrier, and that effective medical pathways exist is your most powerful tool. If you are on this journey, know that you are not alone. The most important step you can take is to seek accurate information and professional guidance from a qualified healthcare provider. They can help you create a personalised plan based on your unique situation, moving you from a place of uncertainty to one of empowered action. Take that first step today by starting a conversation with a medical expert.
Consult a Top Gynaecologist for Personalised Advice
Consult a Top Gynaecologist for Personalised Advice

Dr. Senthamil Selvi
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
23 Years • MBBS, DNB (OBGYN)
Chennai
Apollo Women Hospitals Thousand Lights, Chennai
(75+ Patients)

Dr. Swetha P
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
11 Years • MBBS, MS(OBGY)
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
(50+ Patients)

Dr. K Sandhya
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
18 Years • MBBS, DNB (OBGYN)
Chennai
Apollo First Med Hospitals P H Road, Chennai

Dr Shravya Manohar
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
9 Years • MB,MS OBGYN ,MRCOG (Lon),FMAS
Chennai
Apollo Women Hospitals Thousand Lights, Chennai
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Swati Shah
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • DNB Surgical Oncology, certified Robotic Cancer Surgeon
Ahmedabad
Apollo Hospitals Gandhinagar, Ahmedabad
(25+ Patients)
More articles from Infertility
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the most common signs of infertility in women?
The most common signs include irregular or absent menstrual periods, painful periods, known conditions like PCOS or endometriosis, and a history of multiple miscarriages. However, many women with infertility have no obvious symptoms.
2. How can a man know if he is infertile?
Often, there are no outward signs of male factor infertility. The only way to know is through a semen analysis, a simple test that evaluates sperm health. Risk factors include a history of testicular injury, infection, or certain lifestyle habits.
3. Is infertility always permanent?
No, not always. 'Sterility' means a zero chance of conception, while 'infertility' means a reduced ability to conceive. Many causes of infertility, such as ovulation disorders or hormonal imbalances, are treatable.
4. What is the difference between infertility and sterility?
Infertility implies a reduced capacity to conceive, often requiring medical assistance. Sterility is a complete inability to conceive naturally because of an irreversible physical condition, such as the absence of reproductive organs.
5. How much does fertility treatment typically cost?
The cost of fertility treatments varies widely depending on the type of treatment and location. Basic medications may cost a few thousand rupees, while a single cycle of IVF can cost significantly more. It's important to discuss financial options with your clinic.