Jaundice: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Jaundice: Understand its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Learn how to recognize and manage jaundice for improved health.

Written by Dr.Sonia Bhatt
Last updated on 3rd Jul, 2025
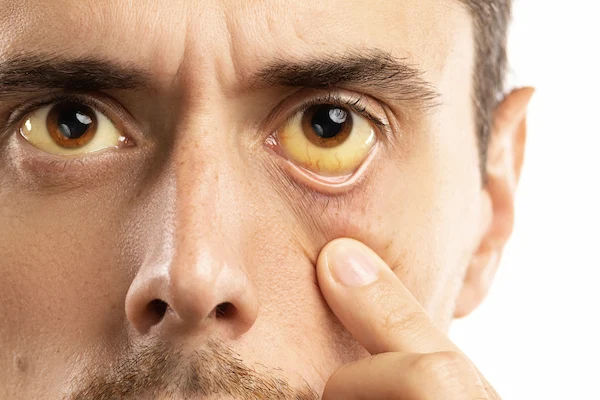
Jaundice is a medical condition commonly characterised by the yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. It occurs due to an excess buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment created when the body breaks down old red blood cells. While jaundice is often seen as a symptom rather than a disease itself, its presence can indicate serious underlying health issues. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial in managing jaundice and preventing complications. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for jaundice.
What is Jaundice?
Jaundice occurs when there is an excess of bilirubin in the bloodstream. Bilirubin is produced as a byproduct of the normal breakdown of red blood cells, a routine process in the body. Under normal conditions, the liver processes and removes bilirubin, but when the liver is overwhelmed or not functioning properly, bilirubin builds up in the blood, causing the yellow tint characteristic of jaundice.
In addition to the yellowing of the skin and eyes, jaundice can lead to darker urine and pale stools. While it can affect people of all ages, it is especially common among newborns. Jaundice in adults, however, often signals a more serious health condition that requires immediate attention.
Causes and Types of Jaundice
Jaundice can be caused by a variety of underlying conditions and is usually divided into three main types: pre-hepatic, hepatic, and post-hepatic, depending on where the problem originates in the body. Each type reflects a different mechanism that disrupts the normal processing and elimination of bilirubin from the body.
Pre-hepatic Jaundice
This type of jaundice occurs when there is an increased breakdown of red blood cells, leading to an excess of bilirubin that overwhelms the liver's ability to process it. Pre-hepatic jaundice is typically caused by:
Haemolytic Anaemia: Disorders such as sickle cell anaemia, thalassaemia, or autoimmune haemolytic anaemia cause the premature destruction of red blood cells, resulting in an excess of bilirubin in the bloodstream.
Infections: Certain infections, such as malaria, can lead to the destruction of red blood cells, contributing to the condition.
Inherited Blood Disorders: Genetic conditions, such as hereditary spherocytosis, also cause the premature breakdown of red blood cells.
Hepatic Jaundice
Hepatic jaundice occurs when the liver itself is damaged or diseased, impairing its ability to process bilirubin properly. This type is usually associated with liver dysfunction caused by:
Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver caused by viral infections (hepatitis A, B, or C), alcohol use, or autoimmune diseases.
Cirrhosis: Chronic liver disease, often due to alcohol abuse or viral hepatitis, leads to liver scarring, reducing its ability to process bilirubin.
Liver Cancer: Malignant growths in the liver disrupt its function, preventing it from processing bilirubin.
Fatty Liver Disease: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), where fat accumulates in liver cells, can also impair bilirubin processing.
Post-hepatic Jaundice
Post-hepatic jaundice, also known as obstructive jaundice, occurs when there is a blockage in the bile ducts, preventing bilirubin from being excreted from the liver. Common causes of post-hepatic jaundice include:
Gallstones: Stones formed in the gallbladder can obstruct the bile ducts, preventing the normal flow of bile, which carries bilirubin.
Bile Duct Tumours: Cancers in the bile ducts or pancreas can obstruct bile flow and cause jaundice.
Bile Duct Strictures: Scarring or narrowing of the bile ducts due to previous surgeries or injuries can prevent bilirubin from being eliminated properly.
Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas can cause bile duct obstructions, resulting in jaundice.
While these three categories—pre-hepatic, hepatic, and post-hepatic—cover the majority of jaundice cases, there are also rare conditions such as Gilbert’s syndrome and Dubin-Johnson syndrome, both of which involve genetic issues with bilirubin processing in the liver.
Symptoms of Jaundice
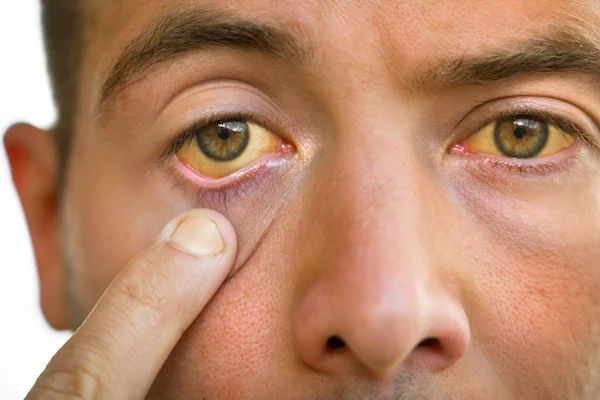
The primary symptom of jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes (sclerae). This can range from a mild yellowish tint to a deep, noticeable yellow colour. In addition to the yellowing, individuals with jaundice may experience:
Dark Urine: When bilirubin is unable to enter the digestive system, it may be excreted in the urine, giving it a dark amber or brown colour.
Pale Stools: Due to the lack of bile in the intestines, stools may become lighter or clay-coloured.
Itching (Pruritus): Bilirubin accumulation in the skin can cause discomfort and itching.
Fatigue and Weakness: Because jaundice often occurs alongside liver or blood disorders, individuals may feel unusually tired or weak.
Loss of Appetite: Many people with jaundice experience a diminished appetite due to underlying liver or blood disorders.
In severe cases, jaundice can be accompanied by more serious symptoms like abdominal swelling, mental confusion, and even bleeding.
Consult Top Hepatologists
Diagnosing Jaundice
Diagnosing jaundice involves a combination of physical examinations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Here are some common steps:
Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination can provide valuable clues about the underlying cause of jaundice. The healthcare provider will ask about recent infections, alcohol consumption, medication use, and family history of liver diseases.
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests are essential in diagnosing jaundice and include:
Complete Blood Count (CBC): Helps identify anaemia or signs of infection.
Liver Function Tests (LFTs): Measure levels of liver enzymes, bilirubin, and proteins to assess liver function.
Hepatitis Panel: Detects viral hepatitis infections.
Coagulation Tests: Evaluate the blood’s ability to clot, which can be affected by liver dysfunction.
Imaging Studies
Imaging techniques help visualise the liver, bile ducts, and surrounding structures. Common imaging studies include:
Ultrasound: A non-invasive technique that uses sound waves to create images of the liver and bile ducts.
CT Scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the liver and bile ducts.
MRI: Offers high-resolution images and can be used with contrast agents to enhance visualisation of bile ducts.
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): A procedure that combines endoscopy and X-rays to examine the bile ducts and pancreas.
Treatment of Jaundice
The treatment of jaundice depends on the underlying cause. Addressing the root cause of jaundice is crucial for effective management. Here are some common treatment approaches:
Pre-Hepatic Jaundice:
Treating Haemolytic Anaemia: Depending on the type of haemolytic anaemia, treatments may include blood transfusions, medications to suppress the immune system, or bone marrow transplants.
Managing Infections: Treating underlying infections, such as malaria or bacterial infections, can help reduce haemolysis and subsequent jaundice.
Hepatic Jaundice:
Hepatitis Treatment: Antiviral medications can be used to treat viral hepatitis, while lifestyle modifications, such as abstaining from alcohol, are crucial for alcoholic hepatitis. In some cases, corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be prescribed.
Cirrhosis Management: Managing cirrhosis involves treating the underlying cause (e.g., antiviral therapy for hepatitis), lifestyle changes, and medications to manage symptoms. In severe cases, liver transplantation may be necessary.
Genetic Disorders: While there is no cure for genetic conditions like Gilbert’s syndrome, symptoms can often be managed with lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medications.
Post-Hepatic Jaundice:
Removing Gallstones: Procedures like endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or surgery can remove gallstones and relieve bile duct obstruction.
Treating Tumours: Surgical resection, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy may be required to treat malignancies causing bile duct obstruction.
Managing Biliary Strictures: Depending on the cause, treatments may include surgical correction, stent placement, or balloon dilatation.
Supportive Care
For severe cases, especially in newborns, phototherapy can be used to help reduce bilirubin levels. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as a liver-friendly diet, avoiding alcohol, and weight management can help improve liver function and alleviate symptoms.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
While jaundice itself cannot always be prevented, some measures can reduce the risk of liver disease:
Vaccination: Vaccines for hepatitis A and B can prevent viral infections that may lead to liver disease.
Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and exercising regularly can reduce the risk of liver disease.
Early Detection: Regular check-ups, especially for those at high risk (e.g., heavy drinkers or individuals with a family history of liver disease), are important for catching liver problems early.
Conclusion
Jaundice is a noticeable and concerning symptom that can indicate a range of underlying health problems, from benign conditions to serious liver diseases. By recognising its causes, symptoms, and the importance of early diagnosis, individuals can seek timely treatment and potentially avoid severe complications. If you or someone you know exhibits signs of jaundice, it’s important to consult a doctor for a thorough evaluation and appropriate care.
Consult Top Hepatologists
Consult Top Hepatologists

Dr. Srinivasa Reddy
Hepatologist
12 Years • MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Hepatology),ASGE
Hyderabad
Myra Liver & Gastro Care, Hyderabad

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Sushith C
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Aakash Garg
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DrNB (Gastroentrology).
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Aswin S. Krishna
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine,MMC), DM (Hepatology, MMC), PDF(Fellowship in Liver Transplanatation)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(100+ Patients)
Consult Top Hepatologists

Dr. Srinivasa Reddy
Hepatologist
12 Years • MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DM (Hepatology),ASGE
Hyderabad
Myra Liver & Gastro Care, Hyderabad

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Sushith C
General Physician
2 Years • MBBS
Bengaluru
PRESTIGE SHANTHINIKETAN - SOCIETY CLINIC, Bengaluru

Dr. Aakash Garg
Gastroenterology/gi Medicine Specialist
12 Years • MBBS, DNB (Medicine), DrNB (Gastroentrology).
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Aswin S. Krishna
Hepatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine,MMC), DM (Hepatology, MMC), PDF(Fellowship in Liver Transplanatation)
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(100+ Patients)