Understanding Kidney Stone Removal Methods
Understanding kidney stone removal methods: Learn about various procedures, from non-invasive to surgical options. Find the best approach for you.

Written by
Last updated on 3rd Jul, 2025
Introduction
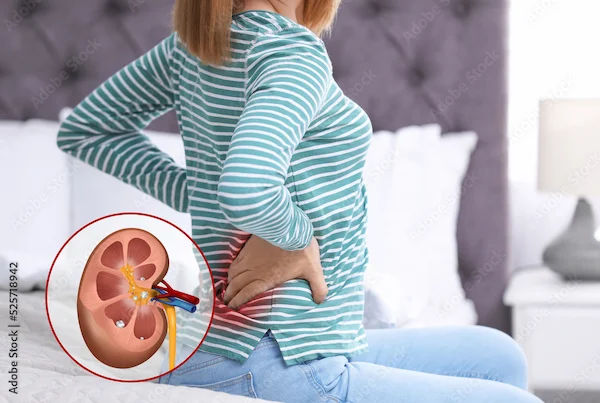
Kidney stones are hard, crystalline deposits that form in the kidneys. They can be painful, disruptive, and challenging to deal with, especially when they grow large enough to cause blockages. While some kidney stones can pass naturally through the urinary system with enough hydration and time, others require medical intervention to remove. In this article, we will explore the various methods of kidney stone removal, from non-invasive options to surgical procedures. Understanding the available treatments can help patients make informed decisions about their care and recovery.
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. They develop when substances in your urine, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, become too concentrated and crystallise. These crystals can grow over time, forming stones that vary in size, from small grains to large stones that can be as big as a golf ball. Kidney stones can form anywhere in the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. While small stones might pass without causing major issues, larger ones can be painful and may obstruct the urinary flow, leading to discomfort and complications.
Causes of Kidney Stones
Several factors contribute to the development of kidney stones:
Dehydration: Not drinking enough water leads to concentrated urine, which can make it easier for minerals to crystallise.
Diet: A diet high in salt, animal protein, and oxalate-rich foods (such as spinach, nuts, and chocolate) can increase the risk of kidney stones.
Medical Conditions: Health conditions like hyperparathyroidism, gout, and chronic urinary tract infections can promote stone formation.
Genetics: A family history of kidney stones increases the likelihood of developing them.
Medications: Certain medications can alter the composition of urine, making it more conducive to stone formation.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
The symptoms of kidney stones can vary depending on their size and location. Common signs include:
Severe Pain: Often felt in the back, side, lower abdomen, or groin, the pain can be sudden and intense, especially when the stone moves.
Blood in Urine: Hematuria, or blood in the urine, is a common symptom.
Frequent Urination: An increased urge to urinate, often with discomfort or burning.
Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can occur as the body reacts to severe pain.
Fever and Chills: A fever may indicate an infection and requires immediate medical attention.
Consult Top Urologists
Kidney Stone Removal Methods
Several treatments are available to remove kidney stones, ranging from non-invasive methods to more advanced surgical procedures. The best method depends on factors like the stone's size, location, and the patient's overall health.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
ESWL is one of the most common non-invasive treatments for kidney stones. It uses shock waves to break the stone into smaller fragments that can be passed more easily through the urinary tract. Here's how it works:
Procedure: The patient lies on a table or sits in a water bath while a machine generates shock waves. These waves are precisely directed at the kidney stone, breaking it into smaller pieces.
Effectiveness: ESWL is typically effective for stones that are less than 2 cm in diameter. Success rates can vary depending on the stone's composition and location.
Recovery: Most patients experience only mild discomfort and can return to normal activities within a few days. However, passing the stone fragments can cause some pain and discomfort.
Complications: Potential side effects include bruising, bleeding, or discomfort. Occasionally, additional treatments may be needed if stone fragments remain.
Ureteroscopic Lithotripsy
For stones located in the ureter or kidney, ureteroscopic lithotripsy is an effective, minimally invasive option. This method involves using a thin, flexible tube called a ureteroscope, which is inserted through the urethra and bladder to reach the stone. Once located, the stone is broken into smaller pieces using a laser or another device.
Procedure: A small, flexible tube (ureteroscope) is inserted through the urethra into the urinary tract. The stone is broken down with a laser, and fragments are either removed or allowed to pass naturally.
Effectiveness: Ureteroscopic lithotripsy is effective for stones in the lower urinary tract and can also treat larger stones that are unsuitable for ESWL.
Recovery: Most patients can return to normal activities in a few days, although temporary discomfort, blood in the urine, and mild pain during the passage of fragments are common.
Complications: Possible side effects include infection, injury to the ureter, or the need for additional procedures if fragments remain.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
PCNL is typically used for large stones or those located in a difficult-to-reach part of the kidney. This minimally invasive surgery involves making a small incision in the back to access the kidney directly. It is considered the gold standard for stones larger than 2 cm.
Procedure: A small incision is made in the patient's back, allowing a nephroscope to locate and remove the stone. Ultrasound or laser technology may be used to break up the stone if necessary.
Effectiveness: PCNL is highly effective for large or complex stones, with a high success rate in treating kidney stones.
Recovery: Recovery time is typically longer than for other methods. Most patients can return to regular activities within 1-2 weeks. Hospitalisation for 1-2 days is usually required.
Complications: Potential complications include bleeding, infection, and injury to surrounding organs or tissues.
Medication-Based Treatment
For smaller stones (usually less than 5 mm), medications may be used to facilitate the stone's natural passage. Alpha-blockers, like tamsulosin, relax the muscles in the ureter, making it easier for the stone to pass. Pain relievers can also help manage discomfort during this process.
Procedure: Medications are prescribed to relax the urinary tract and ease the passage of smaller stones. Patients are advised to stay well-hydrated to help flush the stone out of the body.
Effectiveness: This approach is most effective for small stones that can pass naturally. Medication can help reduce the time it takes for the stone to pass and alleviate pain.
Recovery: Recovery typically involves self-care and medication. The stone usually passes within a few weeks.
Complications: Some side effects of medication include dizziness, nausea, and gastrointestinal upset.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention
Prevention is key to reducing the risk of kidney stones returning. Here are some lifestyle changes and dietary modifications to help lower the likelihood of future stone formation:
Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to ensure that urine remains diluted, reducing the likelihood of crystals forming.
Dietary Modifications: Reduce salt intake and avoid excessive animal protein and oxalate-rich foods like spinach and nuts. Include calcium-rich foods in your diet to help prevent the absorption of oxalate in the intestines.
Regular Exercise: Staying physically active can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of kidney stones.
Monitor Medications: Some medications can increase the risk of kidney stones, so it's important to discuss alternatives with your healthcare provider if necessary.
Manage Underlying Conditions: Addressing health conditions such as high blood pressure, gout, and diabetes can help lower the risk of kidney stones.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience symptoms such as unbearable pain, blood in your urine, or signs of infection (fever, chills, or cloudy urine), seek medical attention immediately. Prompt treatment can prevent complications and ensure the right course of action for your situation.
Severe Pain: Unrelenting or sudden pain may indicate a larger stone or blockage in the urinary tract that requires medical intervention.
Signs of Infection: Fever, chills, and foul-smelling or cloudy urine may indicate a urinary tract infection that requires antibiotics.
Inability to Urinate: Difficulty or inability to urinate may indicate a blockage that requires urgent medical care.
Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms don’t improve with home remedies or over-the-counter medications, consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
Conclusion
While kidney stones can be a painful and disruptive condition, there are several effective methods for removal, ranging from non-invasive options like Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) and ureteroscopic lithotripsy to more advanced procedures such as Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL). Each treatment option has its benefits, risks, and recovery timelines, so it is essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your specific situation. In addition to medical treatment, adopting lifestyle changes, such as staying well-hydrated and adjusting your diet, can help prevent the formation of future kidney stones and support your overall kidney health. If you suspect you have kidney stones or experience symptoms, do not hesitate to seek professional medical advice to ensure you receive the best care possible.
Consult Top Urologists
Consult Top Urologists

Dr. Pavan Kumar S K
Urologist
11 Years • MBBS, MS , Mch( Urology) DNB (Urology)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Prabir Basu
Urologist
19 Years • MBBS, MS General Surgery, DNB Genito-Urinary Surgery
Jodhpur Park
Dr. Prabir Basu urology clinic, Jodhpur Park
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Sudhakar G V
Urologist
25 Years • MBBS, MS(Gen.Surgery), DNB Urology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr Anupam Sharma
Urologist
18 Years • MBBS, MS(Gen Surgery), DNB (Urology)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
Dr. Deepak Bolbandi
Urologist
24 Years • MBBS, MS, DNB, MCh (Uro)
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Bannerghatta Road, Bengaluru
(350+ Patients)
Consult Top Urologists

Dr. Pavan Kumar S K
Urologist
11 Years • MBBS, MS , Mch( Urology) DNB (Urology)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Prabir Basu
Urologist
19 Years • MBBS, MS General Surgery, DNB Genito-Urinary Surgery
Jodhpur Park
Dr. Prabir Basu urology clinic, Jodhpur Park
(125+ Patients)

Dr. Sudhakar G V
Urologist
25 Years • MBBS, MS(Gen.Surgery), DNB Urology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr Anupam Sharma
Urologist
18 Years • MBBS, MS(Gen Surgery), DNB (Urology)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Deepak Bolbandi
Urologist
24 Years • MBBS, MS, DNB, MCh (Uro)
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Bannerghatta Road, Bengaluru
(350+ Patients)