Oral Cavity Cancer: 10 Early Signs You Shouldn't Ignore
Discover the 10 early warning signs of oral cavity cancer. Learn key risk factors, prevention tips, and when to seek medical help for better outcomes.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. M L Ezhilarasan MBBS
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Your mouth is a window to your overall health, and changes within it can sometimes signal something more serious. Oral cavity cancer, which includes cancers of the lips, cheeks, tongue, and floor of the mouth, is a significant health concern worldwide. The key to successfully combating this disease lies in its early detection. Recognising the early signs of oral cancer can dramatically improve treatment outcomes and survival rates. This article will guide you through the ten most critical warning signs, explain the key risk factors, and emphasise the importance of prompt medical consultation. Whether you're concerned about a persistent sore or simply want to be proactive about your health, understanding these symptoms is a powerful first step. If you notice any oral cavity cancer signs that persist beyond two weeks, it is crucial to seek professional evaluation.
What is Oral Cavity Cancer?
Oral cavity cancer refers to the uncontrolled growth of cells that invades and causes damage to surrounding tissues in the mouth. Over 90% of these cancers are squamous cell carcinomas, meaning they begin in the flat, thin cells (squamous cells) that line the oral cavity.
Oral Cavity vs. Oropharyngeal Cancer
It's important to distinguish between oral cavity cancer and oropharyngeal cancer. The oral cavity includes everything you can see when you open your mouth: your lips, the inside of your lips and cheeks, your teeth, gums, the front two-thirds of your tongue, the floor of your mouth under your tongue, and the hard palate. Oropharyngeal cancer affects the back of the throat, including the base of the tongue, the tonsils, and the soft palate. While they share some risk factors and symptoms, they are classified differently.
Consult a Specialist for the best advice
The Top 10 Early Warning Signs of Oral Cancer
Early symptoms of mouth cancer can be subtle and easy to dismiss. However, any of the following signs that last for more than two weeks warrant a professional examination.
Visual Signs: Sores, Patches, and Lumps
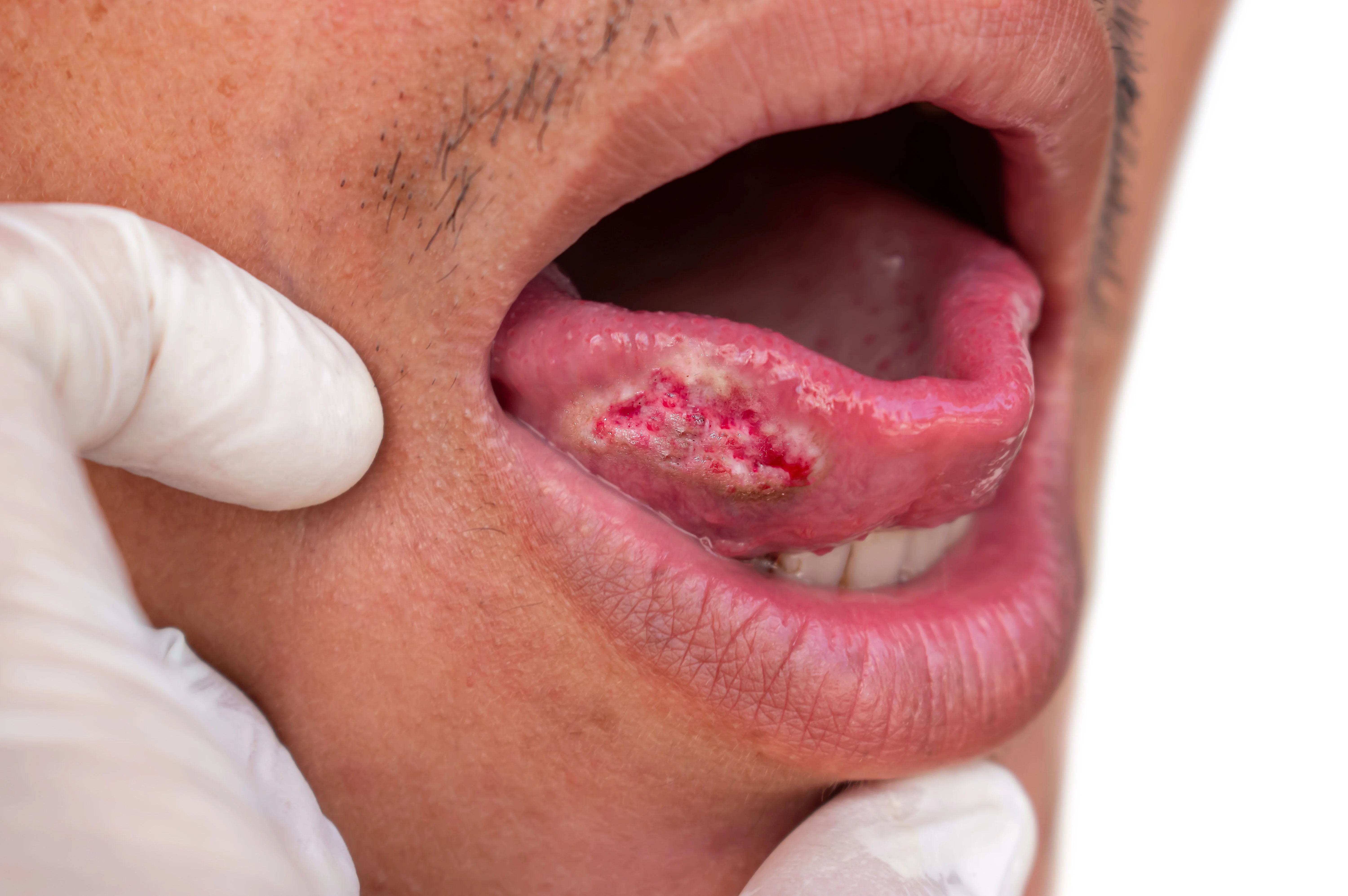
Non-Healing Ulcers
The most common early sign is an ulcer or sore on the lip or inside the mouth that does not heal. Unlike a common canker sore, which typically resolves within 10-14 days, a cancerous ulcer will remain and may even grow larger.
Red or White Patches (Erythroplakia/Leukoplakia)
Persistent red (erythroplakia), white (leukoplakia), or mixed patches on the gums, tongue, tonsils, or lining of the mouth are a major red flag. While not all patches are cancerous, erythroplakia has a higher potential to become malignant. A white patch in the mouth that won't go away should always be investigated by a dentist or doctor.
Unusual Lumps or Thickening
A lump, bump, rough spot, or area of thickened tissue in the oral cavity can indicate a tumor. You might feel this with your tongue, or notice a change in the fit of your dentures.
Sensory and Functional Changes
Persistent Pain or Tenderness
Unexplained and persistent pain or tenderness in any area of the mouth, lip, or tongue is a significant symptom. This pain in your mouth without reason is a signal from your body that something is wrong.
Numbness or Loss of Feeling
A loss of sensation, numbness, or pain in any area of the face, mouth, or neck can occur if a tumor is affecting a nerve.
Difficulty Chewing and Swallowing
Cancer can make it difficult or painful to chew, swallow, or move your jaw or tongue. You might feel like food is getting stuck in your throat.
Other Key Symptoms
Chronic Sore Throat and Hoarseness
A persistent sore throat, the feeling of something stuck in the throat (globus sensation), or a change in your voice, such as hoarseness, can be related to cancers at the back of the tongue or throat.
Ear Pain
Pain in one ear without any signs of infection can be "referred pain" from a tumor located in the oral cavity or throat.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant and unintended weight loss is a common symptom of many cancers, as the disease alters the body's metabolism.
Major Risk Factors for Oral Cavity Cancer
Understanding what increases your risk can help in prevention and early detection.
Lifestyle Factors: Tobacco and Alcohol
Tobacco use in any form—cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco, and snuff—is the single largest risk factor. Alcohol consumption, especially heavy use, significantly increases risk. The combination of tobacco and alcohol creates a synergistic effect, multiplying the risk far more than either alone.
The HPV Connection
Infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly HPV type 16, is a rapidly growing cause of oropharyngeal cancers. It's important to note that HPV and mouth cancer are linked, and this often presents with different symptoms, like a lump in the neck.
Other Contributing Factors
These include prolonged sun exposure (leading to lip cancer), a weakened immune system, a diet low in fruits and vegetables, and genetic predisposition.
How is Oral Cancer Diagnosed?
The Importance of a Dental Check-Up
Often, the first professional to spot signs of oral cancer is a dentist. During a routine check-up, they examine your entire oral cavity for abnormalities. This highlights the critical importance of regular dental visits.
The Biopsy: Confirming a Diagnosis
If a suspicious area is found, the only definitive way to diagnose cancer is through a biopsy, where a small sample of tissue is removed and sent to a lab for analysis. Imaging tests like CT or MRI scans may then be used to determine the stage (extent) of the cancer.
Prevention and Early Detection is Key
Regular Self-Examinations
You can perform a monthly self-check for oral cancer at home. Using a bright light and mirror, look and feel for any lumps, sores, or patches of color change. Check your lips, gums, cheeks, tongue (top, bottom, and sides), roof, and floor of your mouth.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Risk
The best prevention is to avoid tobacco, limit alcohol consumption, protect your lips from the sun with UV-blocking lip balm, maintain a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, and get vaccinated against HPV.
Conclusion
Oral cavity cancer is a serious but highly treatable disease when caught in its early stages. The signs are often visible and tangible, making awareness your most powerful tool. By familiarising yourself with the ten warning signs outlined here—from non-healing ulcers to unexplained ear pain—you empower yourself to take charge of your health. Remember, these symptoms are often caused by less serious conditions, but it is never a risk worth taking to assume that. If you notice any persistent changes in your mouth, do not hesitate. If symptoms persist beyond two weeks, consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for a preliminary evaluation or to book a physical visit with a specialist. Your vigilance could make all the difference.
Consult a Specialist for the best advice
Consult a Specialist for the best advice

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Anindita Ray
Oncologist
7 Years • MBBS, MD ( Radiation Oncology )
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr Gowshikk Rajkumar
Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB in Radiation oncology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Prashant Chandra Das
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • MBBS (MKCG Medical college) MCh (Surgical Oncology, Kidwai memorial institute of Oncology, Bangalore) MS (General Surgery, BHU Varanasi) Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery ( FMAS). ESSO Course On Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy & Gastrectomy (UMC, Utrecht, Netherlands). Trained in Robotic and Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery.
Bhubaneswar
Apollo Hospitals Old Sainik School Road, Bhubaneswar
(25+ Patients)
Consult a Specialist for the best advice

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Anindita Ray
Oncologist
7 Years • MBBS, MD ( Radiation Oncology )
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr Gowshikk Rajkumar
Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB in Radiation oncology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Prashant Chandra Das
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • MBBS (MKCG Medical college) MCh (Surgical Oncology, Kidwai memorial institute of Oncology, Bangalore) MS (General Surgery, BHU Varanasi) Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery ( FMAS). ESSO Course On Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy & Gastrectomy (UMC, Utrecht, Netherlands). Trained in Robotic and Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery.
Bhubaneswar
Apollo Hospitals Old Sainik School Road, Bhubaneswar
(25+ Patients)
More articles from Oral Cancer
Frequently Asked Questions
Is leukoplakia always cancerous?
No, not all leukoplakia is cancerous. However, it is considered a precancerous condition, meaning it has an increased potential to develop into cancer. Any persistent white patch must be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine if a biopsy is needed.
What is the difference between a canker sore and oral cancer?
Canker sores are painful but typically heal completely within 10-14 days. Oral cancer sores do not heal, persist for weeks, and may be accompanied by other symptoms like lumps, numbness, or red/white patches.
How can I check for oral cancer at home?
In a well-lit area, use a mirror to look at your lips, gums, cheeks, roof, and floor of your mouth. Feel for any lumps or rough spots. Examine your tongue, including the sides and underside. Look for any color changes, sores, or patches that are new or won't go away.
What is the survival rate for early-stage mouth cancer?
The survival rate is significantly higher when detected early. For localised oral cavity cancer (cancer that hasn't spread), the 5-year relative survival rate is around 85%. This underscores the critical importance of early detection.
Does HPV cause oral cancer?
Yes, the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), especially HPV16, is a leading cause of oropharyngeal cancers (affecting the tonsils and base of the tongue). It is distinct from cancers caused by tobacco and alcohol.

.webp)