Oral Cavity Cancer: Signs, Causes, and Treatments in India
Learn to recognise early signs of oral cavity cancer, understand its causes, and explore effective treatments available in India for better prevention and care.

Written by Dr. J T Hema Pratima
Reviewed by Dr. Shaik Abdul Kalam MD (Physician)
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
Introduction
A persistent mouth ulcer. A white or red patch that doesn't heal. A painless lump on the cheek. While these might seem like minor annoyances, they can be the first whispers of a serious health concern: oral cavity cancer. In India, this type of cancer is particularly prevalent, accounting for a significant portion of all cancer cases, largely driven by widespread habits like tobacco and betel nut chewing. The good news is that when detected early, oral cavity cancer is highly treatable, with excellent outcomes. This comprehensive guide is designed to empower you with knowledge. We will walk you through the early warning signs you must not ignore, delve into the root causes, and explore the advanced treatment options available within India's leading healthcare institutions. Understanding this journey from cause to cure is the first step towards prevention and timely action.
What is Oral Cavity Cancer?
Oral cavity cancer, a subset of head and neck cancers, refers to the uncontrollable growth of cells that invade and cause damage to surrounding tissues in the mouth. It can occur in any part of the oral cavity, including the lips, gums, tongue, inner lining of the cheeks, the floor of the mouth, and the hard palate.
Defining the Oral Cavity
The oral cavity is the gateway to our digestive and respiratory systems. It starts at the lips and extends to the front two-thirds of the tongue, the gums, the buccal mucosa (inner cheeks), the floor of the mouth below the tongue, and the hard palate (the bony roof of the mouth). Cancers in this region are typically squamous cell carcinomas, meaning they begin in the thin, flat cells that line the inside of the mouth.
How Common is Oral Cancer in India?
India bears a disproportionately high burden of oral cancer, making it a major public health issue. According to the GLOBOCAN 2022 report, India accounts for nearly one-third of the world's oral cancer cases. This high incidence is directly linked to the consumption of tobacco in various forms—such as gutka, khaini, and betel quid—which are deeply embedded in the social and cultural fabric of many communities.
Consult an Oncologist for the best advice
Early Signs and Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
Early detection is the cornerstone of successful cancer treatment. Being aware of your body and recognising these signs can make a life-saving difference.
Visible Changes and Sores
Be alert to these visible changes in your mouth:
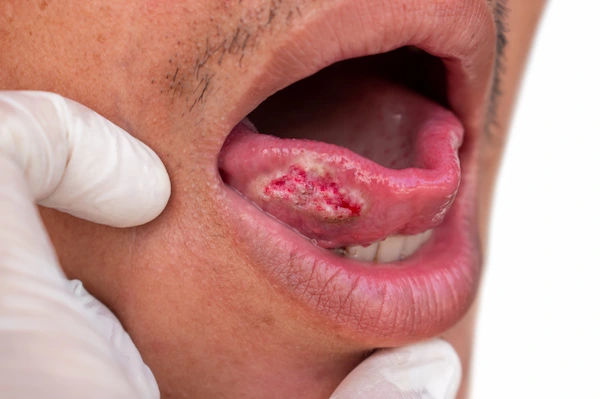
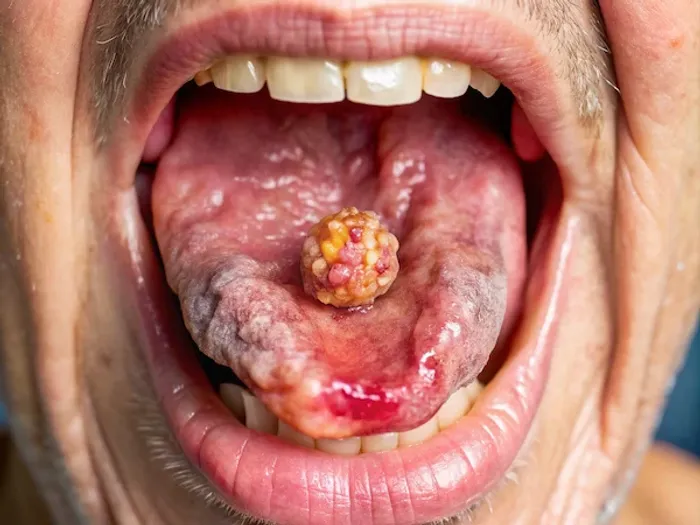
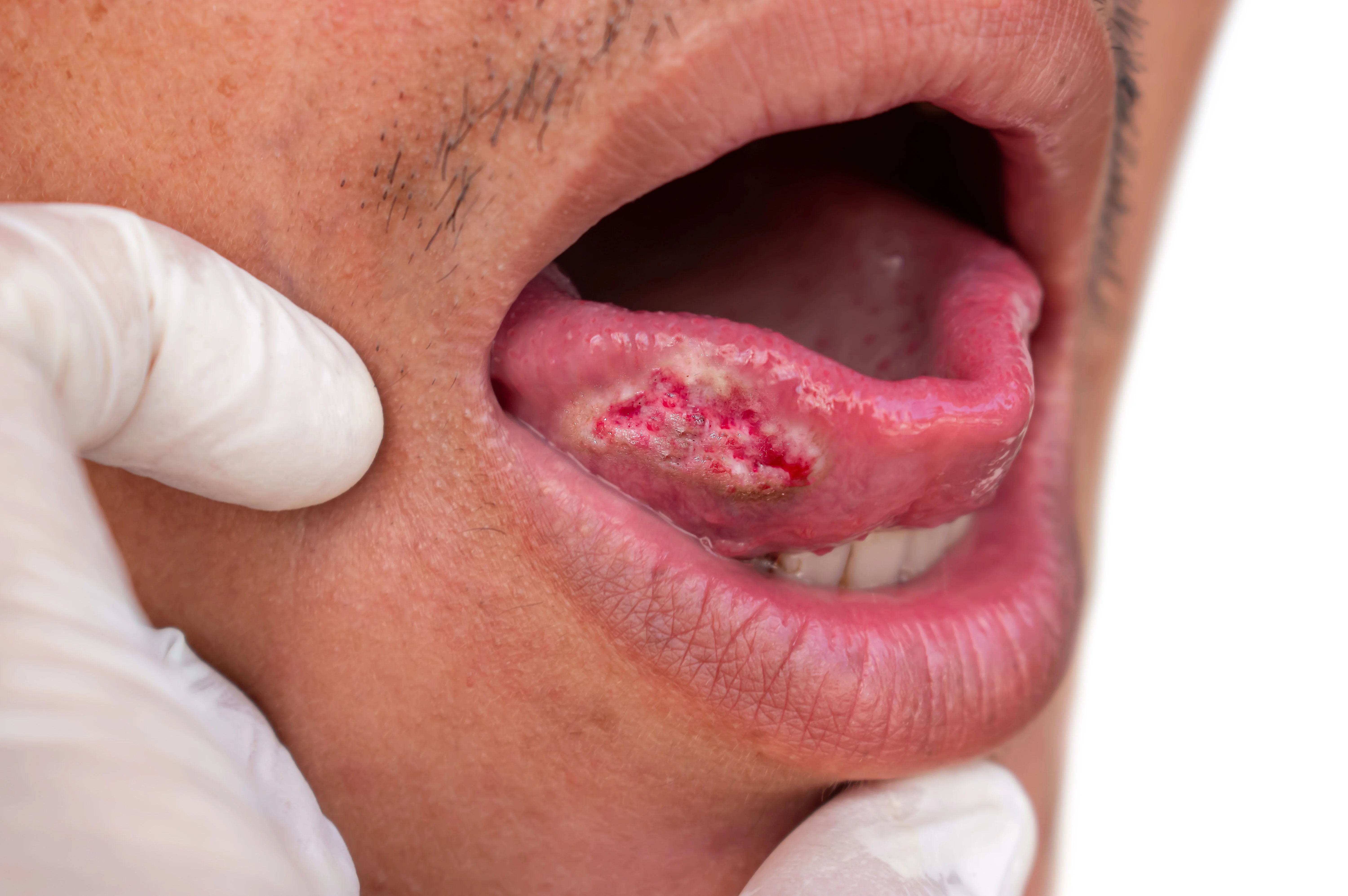
- Patches: A white patch (leukoplakia) or a red patch (erythroplakia) on the gums, tongue, tonsils, or lining of the mouth. Erythroplakia is of greater concern as it has a higher potential to become cancerous.
- Sores: A sore on the lip or in the mouth that does not heal within two weeks is a classic red flag.
- Lumps: A thickening, lump, or rough spot anywhere in the oral cavity.
Sensory Changes and Pain
Pay attention to these unusual changes in your mouth and throat:
- Pain: Unexplained pain, tenderness, or numbness in the mouth or on the lips.
- Difficulty: Trouble chewing, swallowing, speaking, or moving the jaw or tongue.
- Sensation: A feeling that something is caught in the back of the throat.
- Voice Change: A chronic sore throat or a change in your voice.
When to See a Doctor Immediately
If any of the above symptoms persist for more than two weeks, it is crucial to seek professional medical advice. Do not self-diagnose or dismiss them as a simple ulcer or infection. If symptoms persist beyond two weeks, consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for further evaluation. They can provide an initial assessment and guide you on the next steps.
The Primary Causes and Risk Factors of Oral Cancer
Understanding what leads to oral cavity cancer is key to prevention. Several factors can increase a person's risk.
Tobacco: The Single Biggest Culprit
Tobacco use in any form is the most significant risk factor. It contains over 60 known carcinogens that cause genetic mutations in the cells of the mouth.
- Smoked vs. Smokeless Tobacco in the Indian Context: While smoking cigarettes and bidis is harmful, the problem in India is particularly acute with smokeless tobacco products. Gutka, khaini, zarda, and betel quid with tobacco are extremely popular and are directly placed in the mouth, leading to prolonged exposure of the oral mucosa to carcinogens.
Alcohol and the Synergistic Effect
Heavy and regular alcohol consumption significantly increases the risk of oral cancer. When combined with tobacco, the risk isn't just additive; it's multiplicative. Alcohol acts as a solvent, helping the harmful chemicals in tobacco to penetrate the lining of the mouth more effectively.
The Role of HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
Infection with certain high-risk strains of HPV, particularly HPV-16, is a growing cause of oropharyngeal cancers (the back of the throat, including the base of the tongue and tonsils). While its link to oral cavity cancer (front of the mouth) is less direct than for oropharyngeal cancer, it remains a significant risk factor.
Other Contributing Factors
The other contributing factors include:
- Poor Nutrition: A diet low in fruits and vegetables may increase risk.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged sun exposure is linked to cancer of the lip.
- Age and Gender: The risk increases with age, and men are twice as likely to develop oral cancer as women.
Modern Treatment Options Available in India
India offers world-class treatment for oral cavity cancer, comparable to global standards. The choice of treatment depends on the cancer's location, stage, and the patient's overall health.
Surgery as the Primary Treatment
For early-stage cancers, surgery is often the first line of treatment. The goal is to remove the tumour along with a margin of healthy tissue.
Advanced Surgical Techniques: Laser and Robotic Surgery
Many top hospitals in India now employ minimally invasive techniques. Transoral robotic surgery (TORS) allows surgeons to remove tumours with greater precision, flexibility, and vision, leading to less pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Radiation Therapy: Targeting Cancer Cells Precisely
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. It can be used as a primary treatment, after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells, or in advanced cases to relieve symptoms. Techniques like IMRT (intensity-modulated radiation therapy) allow for highly precise targeting, sparing healthy tissues.
Chemotherapy and Targeted Drug Therapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body and is often combined with radiation therapy (chemoradiation) for advanced cancers. Targeted therapy drugs attack specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells (like the EGFR protein) with potentially fewer side effects than standard chemotherapy.
The Multi-Disciplinary Team (MDT) Approach
The best outcomes are achieved through a collaborative MDT approach. This team typically includes a surgical oncologist, a radiation oncologist, a medical oncologist, a pathologist, a radiologist, a reconstructive surgeon, a dietitian, and a speech therapist, all working together to create a personalised treatment plan.
Life After Treatment: Rehabilitation and Follow-up Care
Recovery doesn't end with the last treatment session. Rehabilitation is a critical part of the journey.
Speech and Swallowing Therapy
Surgery or radiation can affect the muscles used for speech and swallowing. Speech-language pathologists work with patients to regain these vital functions through specialised exercises.
Nutritional Support and Dental Care
A dietitian can help manage eating difficulties and ensure proper nutrition. Dental care is also crucial, as treatments can increase the risk of tooth decay and jaw problems. Regular follow-up visits for years after treatment are essential to monitor for recurrence and manage long-term side effects.
Prevention: Reducing Your Risk of Oral Cancer
The most effective way to combat oral cavity cancer is to prevent it from occurring.
Lifestyle Modifications (Quitting Tobacco, Limiting Alcohol)
The single most important step is to avoid all forms of tobacco and limit alcohol consumption. If your condition does not improve after trying these methods, book a physical visit to a doctor with Apollo24|7 for support and cessation programs.
The HPV Vaccine and Its Potential Role
The HPV vaccine, recommended for both boys and girls, protects against the HPV strains most commonly linked to cancer. While its primary aim is cervical cancer, it also significantly reduces the risk of HPV-related oral cancers.
Importance of Regular Self-Exams and Dental Check-ups
Perform a monthly self-exam in a well-lit mirror, checking all areas of your mouth for any changes. Additionally, regular dental check-ups are vital, as dentists are often the first to spot potential signs of oral cancer.
Conclusion
The journey through understanding oral cavity cancer—from its initial signs to the advanced treatments available in India—highlights a powerful message: knowledge is protection. While the statistics in India are sobering, the path forward is clear. By recognising the early warning signals, such as a non-healing ulcer or a suspicious patch, and understanding the profound risks associated with tobacco and alcohol, we can take proactive control of our health. The Indian medical landscape is well-equipped with sophisticated technology and expert multi-disciplinary teams to provide compassionate and effective care. Ultimately, the goal is to shift the narrative from treatment to prevention. By making informed lifestyle choices and prioritising regular check-ups, we can significantly reduce the burden of this disease. Your oral health is a window to your overall well-being; give it the attention it deserves.
Consult an Oncologist for the best advice
Consult an Oncologist for the best advice

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Anindita Ray
Oncologist
7 Years • MBBS, MD ( Radiation Oncology )
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr Gowshikk Rajkumar
Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB in Radiation oncology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Prashant Chandra Das
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • MBBS (MKCG Medical college) MCh (Surgical Oncology, Kidwai memorial institute of Oncology, Bangalore) MS (General Surgery, BHU Varanasi) Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery ( FMAS). ESSO Course On Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy & Gastrectomy (UMC, Utrecht, Netherlands). Trained in Robotic and Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery.
Bhubaneswar
Apollo Hospitals Old Sainik School Road, Bhubaneswar
(25+ Patients)
Consult an Oncologist for the best advice

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Anindita Ray
Oncologist
7 Years • MBBS, MD ( Radiation Oncology )
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr Gowshikk Rajkumar
Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB in Radiation oncology
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Prashant Chandra Das
Surgical Oncologist
15 Years • MBBS (MKCG Medical college) MCh (Surgical Oncology, Kidwai memorial institute of Oncology, Bangalore) MS (General Surgery, BHU Varanasi) Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery ( FMAS). ESSO Course On Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy & Gastrectomy (UMC, Utrecht, Netherlands). Trained in Robotic and Laparoscopic Cancer Surgery.
Bhubaneswar
Apollo Hospitals Old Sainik School Road, Bhubaneswar
(25+ Patients)
More articles from Oral Cancer
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a white patch in the mouth always a sign of cancer?
Not always. A white patch (leukoplakia) can be benign, often caused by friction or irritation. However, because some leukoplakia can show early cancerous changes, any persistent white or red patch must be evaluated by a doctor to rule out oral cavity cancer.
What is the survival rate for oral cancer?
The survival rate depends heavily on the stage at diagnosis. For oral cancer detected at an early, localised stage, the 5-year survival rate can be as high as 80-90%. This drops significantly if the cancer has spread, underscoring the critical importance of early detection.
Are there any new or emerging treatments for advanced oral cancer?
Yes, beyond standard treatments, immunotherapy is a promising new area. It uses drugs to help a patient's own immune system recognise and destroy cancer cells more effectively. It is currently used for some cases of recurrent or metastatic cancer.
How can I perform a self-exam for oral cancer at home?
In a well-lit room, use a mirror and a bright light. Look and feel inside your lips and cheeks, examine your gums, the roof and floor of your mouth, and all sides of your tongue. Check for sores, lumps, patches, or any changes in colour or texture.
Does getting dental X-rays increase the risk of oral cancer?
No. The amount of radiation exposure from modern dental X-rays is extremely low and is not considered a risk factor for oral cancer. The benefits of detecting dental problems far outweigh the minimal risks.

.webp)
_0.webp)