Signs of Ovarian Cancer: Recognising the Subtle Warnings
Know about ovarian cancer, common signs, symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment options and more.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. Mohammed Kamran MBBS, FIDM
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Ovarian cancer has long been labelled a "silent killer," a term that reflects the challenge of its early detection. Unlike some cancers that announce themselves with clear, unmistakable signs in their initial stages, ovarian cancer often whispers. Its symptoms are frequently subtle, easily mistaken for common digestive or menstrual issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or persistent bloating. This ambiguity can lead to critical delays in diagnosis. However, growing research confirms that women do experience symptoms, even in the early stages of the disease.. This article will guide you through the common signs of ovarian cancer, explain what makes them distinctive, and outline the risk factors and diagnostic steps. If you experience symptoms that are persistent and a change from your norm, consulting a doctor online with Apollo24|7 can be a convenient first step for a professional evaluation.
The Most Common Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Awareness of the specific symptoms is the first line of defense. They are often related to the location of the ovaries in the pelvis and the way a growing tumour can affect surrounding organs.
Health topic carousel:
Doctor speciality: Oncologist
Text: Consult a Top Oncologist for Personalised Advice
The Key Quartet: Bloating, Pain, Fullness, and Urgency
This group of symptoms is considered the most characteristic, especially when they occur together and persistently.
Bloating (Abdominal Distension): This isn't the typical bloating that comes and goes with your menstrual cycle. It's a persistent feeling of fullness, pressure, or swelling in the abdomen that doesn't resolve. Your clothes may feel tighter around your waist.
Abdominal or Pelvic Pain: A constant or recurring ache, discomfort, or feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or even the lower back. It’s important to note what ovarian cancer pain feels like—it's often described as a dull, heavy sensation rather than a sharp, acute pain.
Difficulty Eating or Feeling Full Quickly (Early Satiety): You might find that you feel full after eating only a small amount of food. This can be accompanied by a loss of appetite.
Urinary Symptoms: An increased urgency to urinate (needing to go immediately) or frequency (needing to go more often than usual). This happens because a tumour can press on the bladder.
Other Important Symptoms to Note
Beyond the main quartet, several other signs can be associated with ovarian cancer:
Unexplained fatigue and low energy.
Indigestion, heartburn, or nausea.
Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhoea.
Pain during sexual intercourse.
Unexplained weight loss or, in some cases, weight gain primarily due to fluid buildup (ascites).
What Makes These Symptoms Different? Persistence is Key
The most critical factor distinguishing potential early warning signs of ovarian cancer from common ailments is their persistence and pattern. Occasional bloating or a stomach bug is normal. The red flags for ovarian cancer are symptoms that:
They represent a change from your normal: They represent a new pattern of discomfort you haven't experienced before.
They are persistent: They don't come and go but are present most of the time.
Occur frequently: A good rule of thumb is if they happen on more than 12 days per month.
If you experience these symptoms consistently for two to three weeks, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. Keeping a symptom diary can be incredibly helpful for your doctor.
Who is at Risk? Understanding Ovarian Cancer Risk Factors
While any woman can develop ovarian cancer, certain factors increase the risk. Understanding these can help you and your doctor assess your personal situation.
Genetic and Familial Factors (BRCA Gene)
A significant risk factor is a family history of ovarian, breast, or certain other cancers. Inherited mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 dramatically increase the lifetime risk of developing ovarian cancer. If you have a close relative (mother, sister, daughter) who has had ovarian or breast cancer, discussing genetic counselling with a doctor from Apollo24|7 is highly recommended.
Age, Reproductive History, and Lifestyle
Age: The risk increases with age, with most cases diagnosed in postmenopausal women.
Reproductive History: Starting periods at a young age, late menopause, or never having given birth (nulliparity) can slightly increase risk. Conversely, having carried pregnancies to term and breastfeeding are associated with a reduced risk.
Endometriosis: This condition is linked to an increased risk of certain types of ovarian cancer.
Obesity: Being obese in early adulthood is linked to a higher risk.
Diagnosis: What to Expect if You See a Doctor
If you report symptoms suggestive of ovarian cancer, your doctor will likely follow a series of steps to investigate.
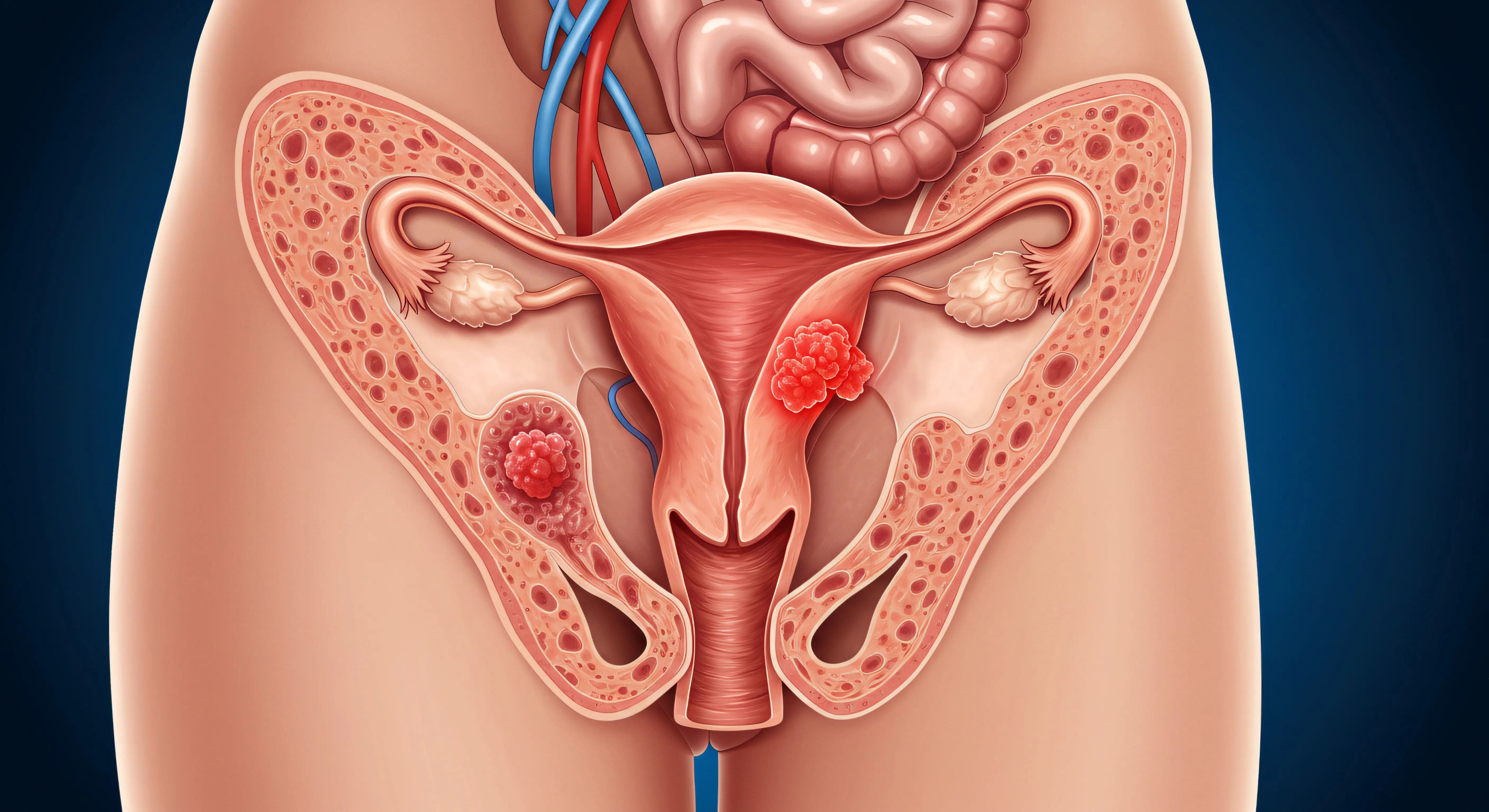
The Pelvic Exam and Imaging Tests
The first step is often a pelvic exam, where the doctor feels the ovaries and uterus for any lumps or changes in size or shape. This is usually followed by a transvaginal ultrasound, which uses sound waves to create a detailed image of the ovaries and can reveal the presence, size, and structure of a mass (whether it's fluid-filled or solid).
The CA-125 Blood Test and Its Role
A CA-125 test measures the level of a protein in the blood that can be elevated in women with ovarian cancer. However, it's not a definitive screening test for the general public because high levels can also be caused by non-cancerous conditions like endometriosis, fibroids, or even menstruation. Its primary value is in conjunction with other tests and for monitoring women already diagnosed with the disease.
If these tests suggest a potential concern, the only way to confirm a diagnosis is through surgery (a biopsy) to remove the suspicious tissue for analysis.
Health topic carousel:
Lab test: Ultrasound, CA 125 Blood Test
Text: Get Your Symptoms Assessed
The Critical Importance of Early Detection
The survival rate for ovarian cancer is significantly higher when it is diagnosed and treated at an early stage, while the cancer is still confined to the ovary. For Stage 1 ovarian cancer, the 5-year survival rate can be over 90%. Unfortunately, due to the lack of specific early symptoms and no reliable routine screening test, only about 20% of cases are found at this early stage. This stark reality underscores the immense power of personal awareness. Knowing your body and advocating for further investigation when something feels persistently wrong can truly be life-saving.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer may be subtle, but it is not entirely silent. By familiarising yourself with its common signs—particularly persistent bloating, pelvic pain, feeling full quickly, and urinary changes—you equip yourself with crucial knowledge. Remember the key differentiator: symptoms that represent a persistent change from your normal baseline. While understanding risk factors for ovarian cancer is important, every woman should be vigilant. If you have concerns, do not hesitate to seek medical advice. Early detection saves lives. If your symptoms persist beyond two weeks, consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for further evaluation and to discuss the next appropriate steps.
Health topic carousel:
Doctor speciality: Oncologist
Text: Consult a Top Oncologist for Personalised Advice
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can a Pap smear detect ovarian cancer?
A.No, a Pap smear is designed to screen for cervical cancer, not ovarian cancer. It collects cells from the cervix and cannot detect abnormalities in the ovaries.
2. What is the difference between an ovarian cyst and ovarian cancer?
A.Most ovarian cysts are harmless (benign), fluid-filled sacs that form during the menstrual cycle and often go away on their own. Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumour. While cysts are common, complex cysts or those that persist and grow, especially in postmenopausal women, need closer evaluation to rule out cancer.
3. Are there any early detection tests for ovarian cancer for the general public?
A.Currently, there is no recommended screening test for ovarian cancer for women at average risk. The transvaginal ultrasound and CA-125 blood test are used as diagnostic tools when symptoms are present, but they are not foolproof for early detection in asymptomatic women due to the risk of false positives.
4. What are the survival rates for ovarian cancer?
A.Survival rates vary greatly by stage. The 5-year relative survival rate for localised ovarian cancer (confined to the ovary) is over 90%. However, for all stages combined, it is around 50%, highlighting the need for earlier diagnosis.
5. If I have a family history, what should I do?
A.If you have a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer, speak with your doctor or a genetic counsellor. They can assess your risk and discuss options, which may include genetic testing for BRCA mutations and considering risk-reducing strategies.
Consult Top Specialists for Personalised Tips

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Prashant Upadhyay
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
16 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB, FUICC
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
Dr. B Shravanthi Reddy
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
8 Years • MBBS, DNB(Radiation Oncology)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir

Dr. Satyesh Nadella
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
Consult Top Specialists

Dr.sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
Dr. Sanchayan Mandal Oncology Clinic, Kolkata

Dr. Sanchayan Mandal
Medical Oncologist
17 Years • MBBS, DrNB( MEDICAL ONCOLOGY), DNB (RADIOTHERAPY),ECMO. PDCR. ASCO
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Prashant Upadhyay
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
16 Years • MBBS, DMRT, DNB, FUICC
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad
Dr. B Shravanthi Reddy
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
8 Years • MBBS, DNB(Radiation Oncology)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir

Dr. Satyesh Nadella
Radiation Specialist Oncologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad