Pneumonia: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Learn about pneumonia, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, to recognise the condition early and manage it effectively.

Written by Dr. Vasanthasree Nair
Reviewed by Dr. D Bhanu Prakash MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

Introduction
Pneumonia is a common yet potentially serious respiratory infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. These sacs may fill with fluid or pus, leading to a phlegmy cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. While anyone can get pneumonia, it can be particularly dangerous for infants, young children, older adults, and those with weakened immune systems. Understanding this condition is your first step toward prevention and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about pneumonia, from spotting the early signs and understanding its causes to exploring modern treatment options and robust prevention strategies. Whether you're seeking information for yourself or a loved one, our goal is to provide clear, actionable advice to help you navigate this illness with confidence.
What is Pneumonia?
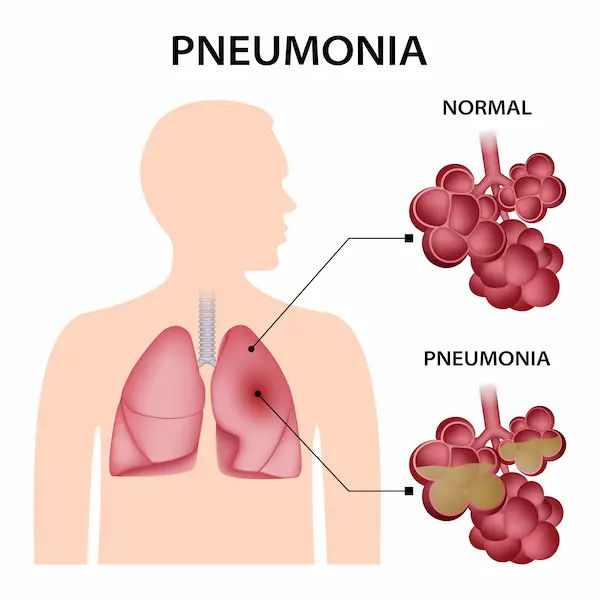
At its core, pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation in the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in your lungs. Normally, these sacs fill with air when you breathe, allowing oxygen to enter your bloodstream. When you have pneumonia, they become filled with pus and other liquid, which makes breathing painful and limits oxygen intake. This can lead to feelings of being short of breath, even while resting. It's not a single disease but rather a term that covers a wide range of infections caused by different organisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The severity can range from mild, often called "walking pneumonia," to life-threatening, especially if it spreads throughout the lungs or enters the bloodstream.
How Pneumonia Affects Your Lungs
Imagine your lungs as an upside-down tree. The trachea (windpipe) is the trunk, which branches into smaller tubes called bronchi and then even smaller bronchioles. At the end of these tiny branches are clusters of alveoli, which look like bunches of grapes. These delicate structures are where the vital gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide happens. When an infectious agent enters, your immune system sends cells to attack it. The battle between your immune cells and the invaders causes the alveoli to become inflamed and fill with fluid, disrupting this essential process and causing the classic symptoms of pneumonia.
Consult a Pulmonologist for the best advice
Recognising the Symptoms of Pneumonia
Symptoms can vary from mild to severe, depending on the type of germ causing the infection, your age, and your overall health. It's important not to dismiss them as just a bad cold or flu.
Common Symptoms in Adults
Adults may exhibit symptoms like:
Cough: Often producing phlegm (sputum) that may be green, yellow, or even rusty-colored due to blood.
Fever: Which can be high and accompanied by sweating and chills.
Shortness of breath: Especially during physical activities or even while resting in severe cases.
Chest pain: Sharp or stabbing pain that worsens when you breathe deeply or cough.
Fatigue: Extreme tiredness and a general feeling of being unwell.
Confusion: Particularly noticeable in older adults.
Symptoms in Children and Infants
Children may exhibit the same symptoms as adults, but infants can be harder to diagnose. Look for:
Cough, fever, and fatigue.
Vomiting or lack of energy.
Difficulty breathing: Watch for grunting sounds, flaring nostrils, or the skin between the ribs pulling in with each breath (retractions).
Irritability and feeding difficulties.
Walking Pneumonia: The Stealthier Variant
Often caused by the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae, "walking pneumonia" is a milder form. People with it often feel well enough to go about their daily activities, hence the name. Symptoms are often similar to a persistent bad cold: a dry, lingering cough, low-grade fever, headache, and fatigue that can last for weeks. Because it's less dramatic, it can be easily overlooked, allowing the infection to spread.
What Causes Pneumonia? The Key Culprits
Pneumonia is categorised based on the type of germ that causes it and where the infection was acquired.
Bacterial Pneumonia
The most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia in adults is Streptococcus pneumoniae. It can occur on its own or after a cold or flu. Bacterial pneumonia is often more severe and is typically treated with antibiotics for pneumonia.
Viral Pneumonia
Respiratory viruses, including influenza (flu), RSV, and SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19), are frequent causes of pneumonia, especially in young children. Viral pneumonia is usually less severe than bacterial forms but can create a pathway for a secondary bacterial infection. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, as antibiotics are ineffective against viruses.
Fungal Pneumonia
This type is less common and primarily affects people with chronic health problems or weakened immune systems. Fungal pneumonia is often acquired by inhaling fungal spores from the environment.
Are You at Risk? Understanding Pneumonia Risk Factors
Certain groups are more vulnerable to developing severe pneumonia:
Age: Children under 2 and adults over 65.
Chronic diseases: Asthma, COPD, heart disease, diabetes.
Weakened immune system: Due to HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy, organ transplants, or long-term steroid use.
Smoking: Damages your lungs' natural defenses.
Hospitalisation: Being on a ventilator, especially in an ICU, increases the risk of hospital-acquired pneumonia.
How is Pneumonia Diagnosed?
If a doctor suspects pneumonia, they will first listen to your lungs with a stethoscope for crackling, bubbling, or rumbling sounds. Key diagnostic tests include:
Chest X-ray: To confirm the presence and location of the infection.
Blood tests: To identify the type of organism causing the infection and assess your white blood cell count.
Sputum test: Analyzing a sample of your phlegm can help pinpoint the specific bacterium.
Pulse oximetry: Measures the oxygen level in your blood.
Get Your Health Assessed
When to See a Doctor
It's crucial to seek medical advice if you have difficulty breathing, chest pain, a persistent fever above 102°F (39°C), or a persistent cough, especially if you are coughing up pus. If your condition does not improve after trying over-the-counter methods, consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Pneumonia Treatment: The Road to Recovery
Treatment depends entirely on the cause and severity of your pneumonia.
Treating Bacterial vs. Viral Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia requires a course of antibiotics. It's vital to take the entire prescription, even if you start feeling better. Viral pneumonia does not respond to antibiotics; treatment involves rest, fluids, and medications to manage fever and pain. In some cases, antiviral drugs may be prescribed.
Home Remedies and Supportive Care
Most people can recover at home with:
Ample rest to allow your body to fight the infection.
Staying hydrated to loosen phlegm and reduce fever.
Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen for fever and pain.
Using a humidifier to ease coughing.
Hospitalisation for Severe Cases
Hospital care may be necessary for high-risk individuals or those with severe symptoms. Treatment there may include intravenous antibiotics, respiratory therapy to deliver medications directly to the lungs, and oxygen therapy to maintain blood oxygen levels.
Potential Complications of Pneumonia
Even with proper treatment, some people experience complications, such as:
Bacteremia: Bacteria spreading into the bloodstream, potentially causing septic shock.
Pleural effusion: Fluid buildup around the lungs that may become infected and require drainage.
Lung abscess: A pus-filled cavity in the lung.
Respiratory failure: Requiring a ventilator to assist with breathing.
How to Prevent Pneumonia: Your Best Defense
Prevention is always better than cure.
The Importance of Vaccination
Vaccines are the most effective way to prevent certain types of pneumonia.
Pneumococcal vaccines: Protect against the most common bacterial cause.
Flu shot: Since the flu is a common cause of viral pneumonia, getting an annual vaccine is crucial.
COVID-19 vaccine: Protects against severe pneumonia caused by the coronavirus.
Consult your doctor about which vaccines are appropriate for you and your family.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly with soap and water.
Don't smoke: Smoking severely damages your lungs' defense mechanisms.
Keep your immune system strong: Get enough sleep, exercise regularly, and eat a healthy diet.
The Recovery Process: What to Expect
Recovery time varies. Young, healthy people may feel better in a week, while others may take a month or more to regain their energy. Fatigue and a lingering cough are common for several weeks. Gradually increasing your activity is key. Pushing too hard too soon can lead to a relapse. If you experience chest pain after pneumonia or your cough worsens, it's important to follow up with a doctor.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a significant health concern, but it is often preventable and treatable. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors, you can take proactive steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. Listening to your body and seeking timely medical advice is crucial for a smooth recovery. If you experience persistent respiratory symptoms, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. You can consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for a quick evaluation to determine if your symptoms align with pneumonia and what the best next steps are for your health. Remember, prioritising prevention through vaccines and healthy habits is your most powerful tool against this common infection.
Consult a Pulmonologist for the best advice
Consult a Pulmonologist for the best advice

Dr. P Sravani
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
3 Years • MBBS, MD
Visakhapatnam
Apollo Clinic Vizag, Visakhapatnam

Dr. Kohena Roy
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
8 Years • MBBS, MD Respiratory Medicine
Rajpur Sonarpur
SRL Diagnostics Pvt. Ltd, Rajpur Sonarpur
Dr. Ambuj Kumar
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (Pulmonary Medicine)
New Delhi
Smriti Gynaecology and Lung Centre, New Delhi

Dr Rakesh Bilagi
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS MD PULMONOLOGIST
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(175+ Patients)
More articles from Pneumonitis
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is pneumonia contagious?
Yes, the germs that cause pneumonia (both viral and bacterial) can be contagious. They are spread through airborne droplets from a cough or sneeze. However, catching the germ doesn't always mean you'll develop pneumonia.
2. What is the best antibiotic for pneumonia?
There is no single 'best' antibiotic. The choice depends on the specific bacterium causing the infection, your age, health, and local antibiotic resistance patterns. A doctor will prescribe the most appropriate one.
3. How long does pneumonia last?
The recovery timeline varies. You may start feeling better after a week of antibiotics, but fatigue and a cough can linger for a month or longer, especially in older adults.
4. What’s the difference between pneumonia and bronchitis?
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (airways), while pneumonia is an infection deeper in the lungs (air sacs). Pneumonia is generally more severe and is more likely to cause a high fever and shortness of breath.
5. Can you get pneumonia from being cold?
No, going out in the cold with wet hair does not directly cause pneumonia. You must be exposed to a germ that causes it. However, cold weather can weaken your immune response and keep people indoors in close contact, facilitating the spread of germs.