Psoriasis Transmission
Understating what is Psoriasis and Learning about its causes and risk factors, myths regarding its spread, diagnosis and prevention strategies.

Written by Dr Sonia Bhatt
Last updated on 3rd Jul, 2025
What is psoriasis?
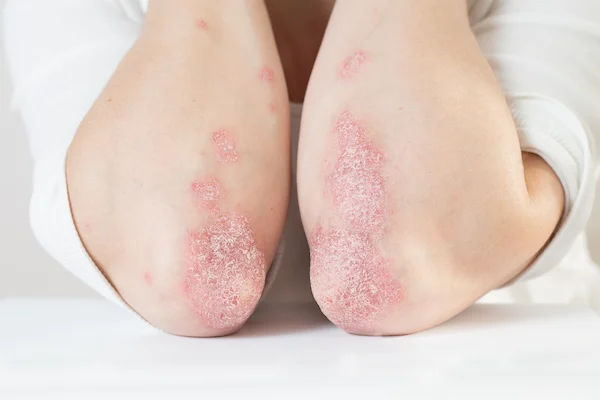
Psoriasis is a long-term autoimmune condition that causes inflammation of the skin. It leads to red, raised, and itchy patches covered with silvery or white scales that can flake off, resembling dandruff. The condition can affect various parts of the body, including the elbows, knees, torso, nails, and joints. Although psoriasis can be managed with treatment, it is not curable and may result in complications such as psoriatic arthritis, other autoimmune conditions, or metabolic syndrome.
What are the Causes of Psoriasis?
The primary cause of psoriasis is a dysfunction of immune cells, which mistakenly identify healthy skin cells as harmful invaders, such as bacteria or viruses. This immune response triggers inflammation and accelerates the production of skin cells, resulting in the accumulation of both new and old cells in thick plaques. This leads to the characteristic rash, known as psoriatic dermatitis, accompanied by shedding of the outer skin layers.
Several other factors can contribute to or trigger psoriasis, including:
Genetics: Around one in three individuals with psoriasis have a family history of the condition.
Environmental factors: Extreme weather conditions, bright sunlight, and insect bites may exacerbate symptoms.
Viral infections: Certain viruses, including rhinoviruses, HIV, human papillomavirus (HPV), and hepatitis C (HCV), can act as triggers.
Bacterial infections: Infections in the throat, such as those caused by streptococci, which can lead to sore throats or tonsillitis.
Inadequate sleep: Poor sleep can weaken the body’s defences and exacerbate psoriasis.
Stress: High stress levels can worsen symptoms.
Medications: Certain drugs, including beta-blockers and lithium, can trigger or worsen psoriasis.
Skin injuries: Trauma to the skin, including post-surgical contact dermatitis, may contribute to flare-ups.
Is Psoriasis Contagious?
Psoriasis is not contagious—you cannot catch it from another person. However, without treatment, it can spread to other areas of your body. Managing triggers and adhering to a treatment plan can help prevent symptoms from worsening.
Psoriasis is distinct from other skin conditions as it is not caused by bacteria or any form of infection, likely arising from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A family history of psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the condition, as certain genes associated with it may be inherited.
How does the Immune System play a Role in Psoriasis?
Psoriasis develops due to the interplay of your immune system and genetic factors. A key contributor is the dysfunction of T cells, a type of immune cell that normally protects the body by fighting off viruses and bacteria. In people with psoriasis, T cells mistakenly attack healthy skin cells, triggering an abnormal immune response. This response leads to the overproduction of skin cells, T cells, and other white blood cells.
Typically, new skin cells form over several weeks. However, in individuals with psoriasis, this process is accelerated, with new skin cells forming within days. The body cannot shed the excess cells quickly enough, causing them to build up on the outer layer of the skin. This results in the scaly patches characteristic of certain types of psoriasis.
What are the Risk Factors for Developing Psoriasis?
Psoriasis can be influenced by a combination of internal and external factors, which may increase the likelihood of developing the condition or triggering flare-ups in those who already have it.
Contributing Factors:
Genes: Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with a higher risk for those with a family history of psoriasis.
Skin trauma: Injuries such as cuts, scratches, or surgical wounds may trigger psoriasis lesions.
Infections: Viral infections (e.g., HIV or rhinovirus) and bacterial infections (e.g., streptococcal throat infections) can exacerbate or trigger symptoms.
Medications: Certain drugs, including beta-blockers and lithium, may contribute to flare-ups.
Obesity: Being overweight can worsen symptoms and increase the risk of developing psoriasis.
Other Triggers:
Temperature: Extreme weather conditions—both hot and cold—as well as changes in humidity, can aggravate psoriasis. Although sunlight is often recommended, prolonged exposure to intense heat or direct sunlight can worsen symptoms.
Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to flare-ups.
Stress: Chronic physical or emotional stress can facilitate the onset of psoriasis or worsen symptoms, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Smoking: Tobacco use is associated with a higher likelihood of developing psoriasis and can reduce the effectiveness of certain treatments, such as biologics.
What are Symptoms of Psoriasis?
The symptoms and severity of psoriasis vary depending on the type, affected areas, extent, size, distribution, and duration of the condition. Generally, the common signs and symptoms of psoriasis include:
Raised lesions: Patches with curved or wavy edges and flaking of the uppermost skin layers, while the deeper layers form a thick plaque.
Size variability: Lesions can range in size from as small as a water droplet to as large as the palm of a hand.
Skin discolouration: Lesions may present as purple rashes that peel, white scaly patches, or red or pink rashes with silver, peeling scales underneath.
Texture changes: Affected areas may become dry, cracked, itchy, or exhibit a burning sensation.
Bleeding: Scratching the lesions can tear the plaques, leading to bleeding
Consult Top Dermatologists
How to Diagnose Psoriasis?
In most cases psoriasis gets diagnosed through a physical examination of the skin. However, because psoriasis can resemble eczema and other skin conditions, diagnosis can sometimes be challenging. Dermatologists use a combination of methods to diagnose psoriasis, assess its severity, and determine the appropriate course of treatment. These methods include:
Medical history: Evaluating the onset of symptoms, recent illnesses, medications, family history, and potential triggers like stress or environmental factors.
Physical examination: Assessing the size, location, and appearance of affected areas on the skin, scalp, or nails.
Skin biopsy: A small skin sample is examined under a microscope to confirm the type of psoriasis or rule out other conditions.
For patients with symptoms of psoriatic arthritis, such as swollen or painful joints, additional tests may be required. Blood tests and X-rays can help rule out other types of arthritis.
What are Prevention and Management Strategies for psoriasis?
Psoriasis treatment aims to slow the rapid production of skin cells, and managing lifestyle factors can help prevent flare-ups. Key strategies include:
Diet: Eat a nutrient-dense diet.
Lifestyle: Avoid smoking, alcohol, and stress. Get sufficient sleep.
Skin care: Use moisturisers to keep skin hydrated, clean skin regularly, and protect it from injury or infection. Avoid dry, cold air.
Sunlight: Moderate sun exposure can be beneficial, but avoid excessive sun.
Medication: Review medications with your doctor, as some may trigger flare-ups.
While psoriasis cannot be completely prevented, maintaining overall skin health, managing stress, and avoiding known triggers can reduce the risk of developing or worsening the condition.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a long-term inflammatory skin condition that is manageable but not curable. Effective treatment requires patience and consistent effort. While the exact causes of psoriasis are not fully understood, its risk factors and triggers are well-established. You can reduce your risk by following your healthcare provider’s treatment plan, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, taking good care of your skin, and avoiding triggers that may provoke flare-ups.
Consult Top Dermatologists
Consult Top Dermatologists

Dr. Bhavya Swarnkar
Dermatologist
14 Years • MBBS, MD, DNB (Dermatology, Venereology & Leprosy) Former Senior Resident, Department of Dermatology- AIIMS, New Delhi. Associate Consultant - Dermatology.
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(225+ Patients)

Dr. Tejaswi Cherukuri
Dermatologist
11 Years • MBBS, MD (DVL), FAM, FAAD
Chennai
Apollo Speciality Hospitals OMR, Chennai
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Pranoti Deshpande
Dermatologist
5 Years • MBBS, MD (Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy)
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals D R D O kanchanbagh, Hyderabad
(150+ Patients)

Dr. Priyankar Mishra
Dermatologist
11 Years • MBBS, MD Dermatology , Venereology & Leprosy
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Parul Gohil
Dermatologist
5 Years • MBBS, MD(DERMATOLOGY,VENEREOLOGY & LEPROSY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
Consult Top Dermatologists

Dr. Bhavya Swarnkar
Dermatologist
14 Years • MBBS, MD, DNB (Dermatology, Venereology & Leprosy) Former Senior Resident, Department of Dermatology- AIIMS, New Delhi. Associate Consultant - Dermatology.
Bilaspur
Apollo Hospitals Seepat Road, Bilaspur
(225+ Patients)

Dr. Tejaswi Cherukuri
Dermatologist
11 Years • MBBS, MD (DVL), FAM, FAAD
Chennai
Apollo Speciality Hospitals OMR, Chennai
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Pranoti Deshpande
Dermatologist
5 Years • MBBS, MD (Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy)
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals D R D O kanchanbagh, Hyderabad
(150+ Patients)

Dr. Priyankar Mishra
Dermatologist
11 Years • MBBS, MD Dermatology , Venereology & Leprosy
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Parul Gohil
Dermatologist
5 Years • MBBS, MD(DERMATOLOGY,VENEREOLOGY & LEPROSY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru