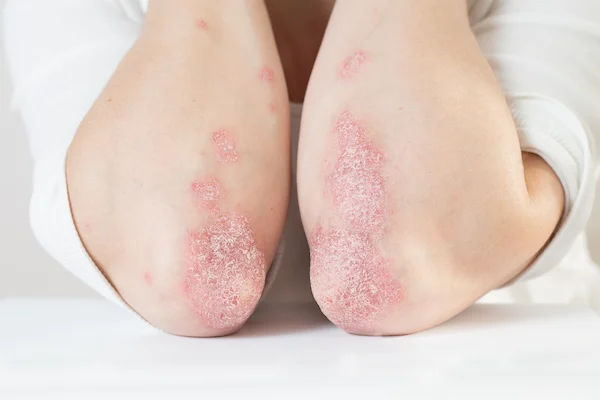
Is Psoriasis Dangerous? Understanding The Risks And How To Manage The Condition
Understand the risks associated with psoriasis and explore effective strategies to manage the condition for a healthier life.

Written by Dr Sonia Bhatt
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes skin cells to multiply too quickly, leading to thick, scaly patches of skin. While the visible symptoms of psoriasis, such as red, inflamed areas covered with silvery-white scales, may seem uncomfortable or unsightly, many people often wonder if psoriasis is truly dangerous. In this article, we’ll address whether psoriasis can be dangerous, the potential risks and complications associated with the condition, and how it can be managed effectively.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing them to reproduce at an accelerated rate. This rapid turnover results in thick patches of skin that often appear on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back, though it can affect any part of the body. Psoriasis is considered a lifelong condition with periods of flare-ups and remission.
There are different types of psoriasis, including:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, characterised by raised, red patches covered with silvery scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Small, drop-shaped spots on the torso, arms, or legs.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Red, smooth patches found in skin folds such as underarms, groin, or beneath the breasts.
- Pustular Psoriasis: White pustules (blisters of noninfectious pus) surrounded by red skin.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare and severe form that causes widespread redness and shedding of the skin.
Is Psoriasis Dangerous? Understanding the Risks
While psoriasis is not typically life-threatening, it can lead to various complications that can be dangerous if not managed properly. Let’s explore the key risks and complications associated with psoriasis:
1. Psoriatic Arthritis
One of the primary dangers of psoriasis is the development of psoriatic arthritis (PsA), a type of inflammatory arthritis that affects people with psoriasis. Psoriatic arthritis can lead to joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. Over time, untreated psoriatic arthritis can cause irreversible joint damage, leading to disability. If you experience joint pain or swelling alongside your psoriasis, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to address both skin and joint symptoms.
2. Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
For those with moderate to severe psoriasis, there is a heightened risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Studies have shown that the chronic inflammation linked to psoriasis can contribute to an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and high blood pressure. Psoriasis is dangerous for heart health, especially if the condition is not well-managed. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising, and following a heart-healthy diet, are essential for managing both psoriasis and reducing cardiovascular risk.
3. Mental Health Impact: Psoriasis and Depression
Living with psoriasis can be emotionally challenging. The visible symptoms of the condition can cause significant self-esteem issues, leading to anxiety and depression. Many people with psoriasis experience social isolation due to the stigma associated with the appearance of their skin. The emotional toll can be just as debilitating as the physical symptoms, and it’s important to seek support through therapy or counselling if you're struggling with your mental health.
4. Increased Risk of Infections
Psoriasis can compromise the skin’s natural barrier, making it more susceptible to infections. The cracks and fissures in psoriasis plaques can provide an entry point for bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Individuals with psoriasis are more prone to developing skin infections like cellulitis, a serious bacterial infection. Additionally, some treatments for psoriasis, such as biologic drugs, may suppress the immune system, further increasing the risk of infections. So, is psoriasis dangerous when it comes to infections? Yes, especially if the skin becomes damaged or if you’re using immune-suppressing medications.
5. Cancer Risk
Recent studies suggest a potential link between psoriasis and an increased risk of certain types of cancer, including lymphoma (a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system) and skin cancer. While the overall risk is still under investigation, individuals with severe psoriasis, especially those who use immunosuppressive medications, should remain vigilant about any changes in their skin and undergo regular dermatological check-ups.
6. Erythrodermic Psoriasis
In rare cases, erythrodermic psoriasis can occur. This severe form of psoriasis causes the skin to become red, inflamed, and shed rapidly. It can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and other life-threatening complications like sepsis. Erythrodermic psoriasis requires immediate medical attention, often necessitating hospitalisation for stabilisation and treatment.
How Can Psoriasis Be Managed to Reduce Its Risks?
Although psoriasis can have serious health implications, it can typically be managed with the right treatment plan. Here are some common approaches to managing the condition:
1. Topical Treatments
For mild cases, topical treatments such as corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, and coal tar preparations can help reduce inflammation and control skin cell turnover. Regular moisturising is also essential to keep the skin hydrated and prevent flare-ups.
2. Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light to slow the rapid production of skin cells. This treatment is often effective for people with more widespread or persistent psoriasis.
3. Systemic Treatments
Systemic treatments that affect the entire body may be necessary for moderate to severe cases of psoriasis. These include medications like methotrexate, oral biologics, and immunosuppressive drugs. These treatments target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation and skin cell turnover.
4. Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of psoriasis flare-ups. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, managing stress, and avoiding known triggers such as smoking, alcohol, and certain medications.
5. Psychological Support
Given the mental health challenges associated with psoriasis, seeking psychological support is essential. Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT), mindfulness techniques, and joining psoriasis support groups can help patients manage the emotional toll of living with the condition.
Consult Top Dermatologists To Manage Psoriasis
Living with Psoriasis
While psoriasis may not be permanently cured, many individuals can manage their symptoms effectively and even experience extended periods of remission. If you are living with psoriasis, it is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to create a personalised treatment plan. Whether through topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic therapies, or lifestyle adjustments, there are many ways to reduce symptoms, control flare-ups, and improve your quality of life.
A consistent skincare routine, including regular moisturising and using mild soaps, helps reduce scaling and irritation. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle—balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management—also plays a key role in symptom control.
Psoriasis can impact mental health, so emotional support through therapy or support groups is important. Identifying and avoiding triggers like smoking, alcohol, and stress can help prevent flare-ups. Finally, practising self-compassion and accepting your condition can improve both emotional and physical well-being.
By taking these steps, individuals with psoriasis can improve their quality of life and manage their symptoms effectively.
Conclusion
While psoriasis itself is not typically life-threatening, it can lead to serious complications if left untreated. So in certain cases—especially when it leads to psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, or infections. It's also important to manage the emotional and psychological effects of the disease. The good news is that with proper treatment, psoriasis can be effectively controlled, reducing the risk of complications and improving quality of life.
If you or someone you know is living with psoriasis, it’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs. Early intervention and appropriate management can help minimise the risks associated with this condition and improve overall health outcomes.
Consult Top Dermatologists To Manage Psoriasis

Dr. S Madhuri
Dermatologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD. DVL, DNB, Fellow (Dermatosurgery & Lasers)
Secunderabad
Apollo Hospitals Secunderabad, Secunderabad
(450+ Patients)

Dr. Asad Ansari
Dermatologist
14 Years • MBBS, DDVL
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata
Dr. Kavitha Killaparthy
Dermatologist
23 Years • MBBS,DIPLOMA(DERMATOLOGY,VENEREOLOGY,LEPROSY)
Hyderabad
JDS Skin & Hair Clinic, Hyderabad
Dr. Syeda Sarwath Saniya
Dermatologist
5 Years • MBBS,DVD
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru

Dr. Parul Gohil
Dermatologist
5 Years • MBBS, MD(DERMATOLOGY,VENEREOLOGY & LEPROSY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru