Understanding Rupioid Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Learn about Rupioid Psoriasis, a rare form of psoriasis. Explore its symptoms, causes, and available treatment options to effectively manage this skin condition.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. J T Hema Pratima MBBS, Fellowship in Diabetes Mellitus
Last updated on 6th Mar, 2026

Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the skin, leading to the development of red, inflamed, and scaly patches. While many people are familiar with common types of psoriasis, such as plaque psoriasis, there are also rarer, more severe forms that deserve attention. One such form is rupioid psoriasis, a particularly challenging and aggressive variant. In this article, we'll explore what rupioid psoriasis is, its key symptoms, its underlying causes, and the treatment options available for managing the condition.
What is Rupioid Psoriasis?
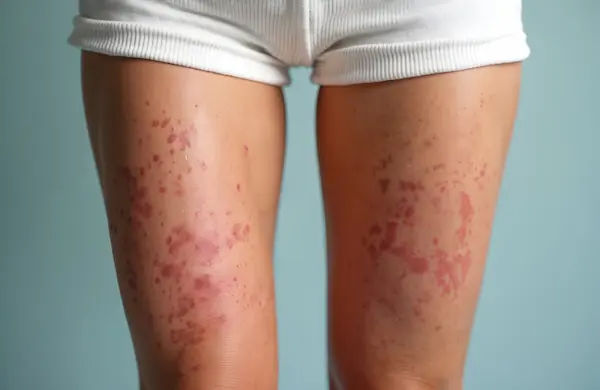
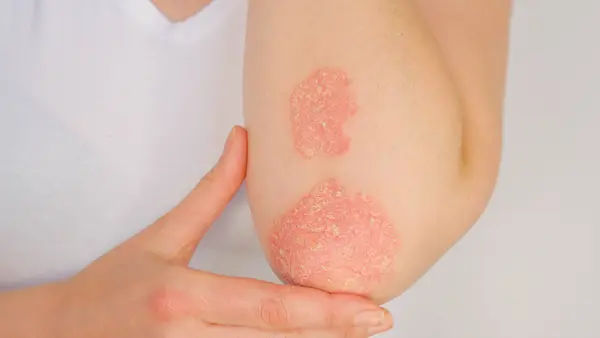
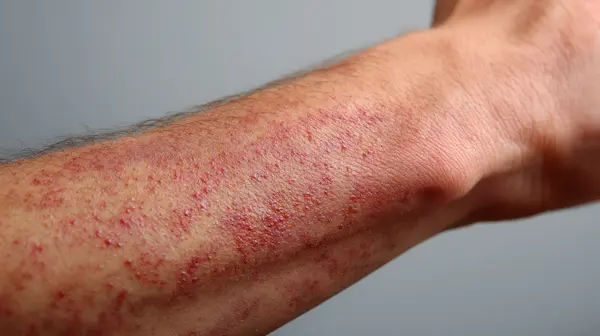
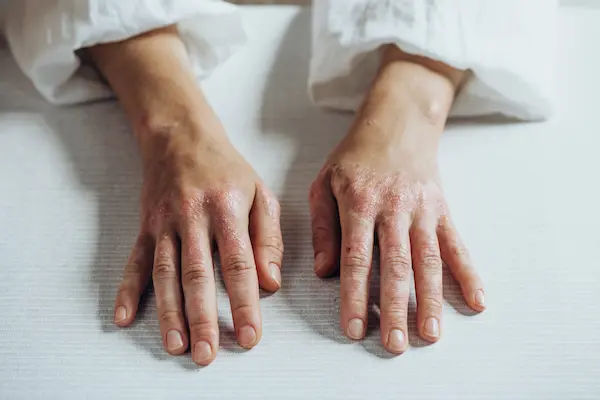
Rupioid psoriasis is a rare and severe form of psoriasis characterised by thick, crusted, cone-shaped lesions resembling limpet shells. Derived from the Greek word “rupia,” meaning shell, this subtype is particularly distinct due to its unique presentation. These lesions are typically small, with a 2-5 centimetres diameter, more pronounced and elevated compared to those seen in other forms of psoriasis, making them particularly noticeable and challenging to manage. While uncommon, it requires prompt medical attention to manage symptoms effectively and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Symptoms of Rupioid Psoriasis
Rupioid psoriasis is characterised by unique and distinct lesions that set it apart from other forms of psoriasis. Here are the key features:
Thick, Crusted Lesions: Rupioid lesions are notable for their thick, hard crusts that resemble oyster shells or cone-shaped, limpet-like structures. These crusts are often elevated and can be quite pronounced.
Conical Shape: The lesions typically have a conical, hyperkeratotic appearance, giving them a rough and uneven surface. This shape is a hallmark of rupioid psoriasis and can make the lesions more noticeable.
Raised and Elevated Patches: Unlike other forms of psoriasis that may present as flatter plaques, rupioid lesions are raised and elevated, making them more prominent and easier to distinguish.
Scaling and Flaking: The thick crusts of rupioid lesions are composed of layers of dead skin cells that build up and form scales. These scales can flake off, leading to a rough texture and potential discomfort.
Red or Purple Base: Beneath the thick crusts, the skin is typically inflamed and can appear red or purple. This inflammation is due to the underlying immune response and contributes to the characteristic appearance of the lesions.
Pain and Discomfort: The thick, crusted nature of the lesions can cause pain and discomfort, especially if the skin cracks or bleeds. Itching and soreness are also common symptoms associated with rupioid lesions.
Consult Top Doctors For Rupioid Psoriasis
Causes and Risk Factors of Rupioid Psoriasis
The development of rupioid psoriasis is influenced by a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. Understanding these elements is key to managing the condition effectively and minimising flare-ups.
1. Genetic Predisposition
A family history of psoriasis significantly increases the risk of developing rupioid psoriasis, indicating the important role of heredity in the condition's onset. Certain gene mutations related to immune regulation, such as PSORS1, HLA-C, and TNF-α, are associated with the condition. These genetic factors contribute to the abnormal immune response that drives inflammation and rapid skin cell turnover.
2. Autoimmune Mechanism
At its core, rupioid psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder. In this condition, the immune system mistakenly targets healthy skin cells, causing an accelerated skin cell turnover process. This results in the formation of thick, scaly plaques that are characteristic of the disease. Key immune system components, such as T-cells and cytokines, play a central role in this process. The overactive T-cells release cytokines, which trigger inflammation and the rapid production of new skin cells. This abnormal immune response leads to the persistent skin lesions that define rupioid psoriasis.
3. Environmental Triggers
In addition to genetic and immune factors, several environmental triggers can worsen or precipitate rupioid psoriasis flare-ups. These include:
Stress: Emotional and physical stress are well-known triggers for psoriasis and can cause flare-ups of rupioid psoriasis.
Infections: Certain infections, particularly streptococcal throat infections, can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms.
Medications: Drugs like beta-blockers, lithium, and anti-malarial drugs can cause flare-ups of rupioid psoriasis.
Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing rupioid psoriasis.
Climate and Skin Trauma: Cold weather, dry conditions, and skin injuries such as cuts or scrapes can provoke flare-ups, with the skin being particularly sensitive to trauma, a phenomenon known as the Koebner effect.
Diagnosing Rupioid Psoriasis
Diagnosing rupioid psoriasis typically involves a thorough clinical examination by a dermatologist. The doctor will assess the appearance of the skin lesions and ask about the patient’s medical history, family history, and lifestyle factors. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Rupioid Psoriasis
Rupioid psoriasis is a rare and challenging form of plaque psoriasis that requires tailored treatment approaches. Here are the main treatment options available:
1. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defence for managing rupioid psoriasis. These include:
Corticosteroids: Creams and ointments containing corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
Vitamin D Analogues: These medications, such as calcipotriene, slow down the growth of skin cells and can help flatten the plaques.
Calcineurin Inhibitors: Topical treatments like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus reduce inflammation and plaque buildup by suppressing the immune system.
2. Systemic Treatments
For more severe cases, systemic treatments that work throughout the body may be necessary:
Methotrexate: Suppresses immune response to slow skin cell turnover. Available as oral tablets or injections.
Cyclosporine: Inhibits the immune system for rapid relief, typically short-term. Available in capsules.
Acitretin: Reduces skin cell growth. Available as oral capsules.
Biologics (e.g., Adalimumab, Ustekinumab): Target specific immune components to reduce inflammation and plaques. Administered via injections or intravenous infusions.
3. Light Therapy
UV light therapies can treat moderate to severe cases and are administered under controlled medical supervision:
UVB Phototherapy: Slows skin cell production using ultraviolet B light.
PUVA Therapy: Combines UVA light and psoralen (a photosensitizing drug).
4. Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms of rupioid psoriasis and prevent flare-ups:
Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can help reduce stress, which is a common trigger for psoriasis.
Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can support overall skin health.
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding personal triggers, such as certain medications or infections, can help prevent flare-ups.
5. Supportive Care:
Moisturising: Regular emollients or moisturisers are essential for keeping the skin hydrated and preventing the plaques from becoming too dry or cracked.
Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or corticosteroid injections may be used to manage pain associated with the plaques.
Conclusion
Rupioid psoriasis is a rare and severe form of psoriasis that can be challenging to treat and manage. While the condition can be painful and cause significant distress, various treatment options are available to control symptoms and improve quality of life. Early diagnosis and a personalised treatment plan are essential for managing the condition effectively. By understanding the nature of this condition, patients can feel empowered to take the necessary steps toward managing their health and improving their skin condition. With the right treatment approach, people living with rupioid psoriasis can lead a fulfilling life.
If you suspect you have rupioid psoriasis or are experiencing unusual skin symptoms, consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Consult Top Dermatologist
Consult Top Dermatologist

Dr. Pranoti Deshpande
Dermatologist
5 Years • MBBS, MD (Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy)
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals D R D O kanchanbagh, Hyderabad
(175+ Patients)

Dr. Kaushiki Hajra
Dermatologist
5 Years • MBBS, MD Dermatology, Venerology & Leprosy
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Arisha Salam
Dermatologist
6 Years • MBBS, MD, DVL, Fellowship in Paediatric Dermatology (Singapore) Fellowship in Dermatosurgery Lasers and Aesthetics
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Sonal Jain
Dermatologist
9 Years • MBBS, MD Dermatology, Venerology & Leprosy
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Madhab Datta
Dermatologist
7 Years • MBBS, MD (DVL)
Kolkata
Dr. Madhab Datta's Clinic, Kolkata
Consult Top Doctors For Rupioid Psoriasis

Dr. Pranoti Deshpande
Dermatologist
5 Years • MBBS, MD (Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy)
Hyderabad
Apollo Hospitals D R D O kanchanbagh, Hyderabad
(175+ Patients)

Dr. Kaushiki Hajra
Dermatologist
5 Years • MBBS, MD Dermatology, Venerology & Leprosy
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata

Dr. Arisha Salam
Dermatologist
6 Years • MBBS, MD, DVL, Fellowship in Paediatric Dermatology (Singapore) Fellowship in Dermatosurgery Lasers and Aesthetics
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. Sonal Jain
Dermatologist
9 Years • MBBS, MD Dermatology, Venerology & Leprosy
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Madhab Datta
Dermatologist
7 Years • MBBS, MD (DVL)
Kolkata
Dr. Madhab Datta's Clinic, Kolkata