What Leads to Signs of Rosacea: Causes and Triggers
Uncover the complex causes and common triggers of rosacea. Learn about the role of genetics, inflammation, and lifestyle factors in this chronic skin condition and how to manage it.

Written by Dr. Mohammed Kamran
Reviewed by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula MBBS
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026

That sudden, unexplained flush across your cheeks or the persistent redness that just won’t fade—it might be more than just sensitive skin. You could be experiencing signs of rosacea, a common but often misunderstood chronic skin condition that affects millions. Characterized by flare-ups and periods of remission, rosacea primarily targets the face, leading to redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes small, pus-filled bumps. But what actually kickstarts this frustrating process? This article dives deep into the complex world of rosacea, moving beyond the surface symptoms to explore the underlying causes, from genetics and immune system quirks to microscopic mites. We’ll also decode the everyday triggers—from your morning coffee to a stressful work meeting—that can turn up the heat on your complexion. Understanding what leads to these signs of rosacea is the first, most powerful step toward effectively managing it and reclaiming your skin’s comfort.
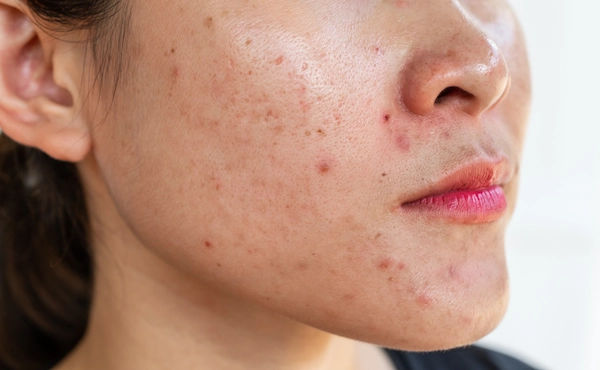
What is Rosacea? More Than Just a Red Face
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects the central face—the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. It's often misdiagnosed as acne, eczema, or simply a natural tendency to blush easily. However, it's a distinct disorder with its own set of characteristics. It typically begins after age 30 and often involves cycles of flare-ups and periods where symptoms are less noticeable. While there is no cure for rosacea, its signs and symptoms can be effectively controlled with medical treatment and lifestyle changes. The condition can vary significantly from person to person, which is why experts have categorized it into subtypes. Understanding these subtypes is key to identifying your specific facial redness and seeking the right treatment.
The Four Main Types of Rosacea
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): This subtype is characterized by persistent facial redness (erythema) and visible, spidery blood vessels known as telangiectasia. People with ETR often experience flushing and blushing that lasts longer than normal and may report a stinging or burning sensation, especially when applying skincare products.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Often mistaken for acne, this subtype presents with redness, swelling, and breakouts that resemble acne pimples. These acne-like breakouts can come and go, and they typically occur on the central face. It's crucial to distinguish this from acne vulgaris, as the treatment approaches differ.
- Phymatous Rosacea: This less common but more severe subtype leads to the skin thickening and developing a bumpy texture. The most well-known form is rhinophyma, an enlargement of the nose caused by thickening skin and sebaceous glands. It occurs more frequently in men and is often associated with untreated rosacea over many years.
- Ocular Rosacea: As the name suggests, this affects the eyes. Symptoms can include bloodshot, watery, or gritty-feeling eyes, burning or stinging, dryness, light sensitivity, and blurred vision. Ocular rosacea can occur before, after, or simultaneously with skin symptoms and requires attention from an ophthalmologist.
The Root Causes: What's Going on Beneath the Skin?
While the exact cause of rosacea remains unknown, research has pinpointed several strong contributing factors that work in combination. It's unlikely that a single factor is to blame; rather, it's a perfect storm of these elements that leads to the signs of rosacea.
Genetics and Family History
Studies and patient histories consistently show that rosacea often runs in families. If you have a close relative with the condition, your risk of developing it increases significantly. This genetic predisposition suggests that some people are born with a higher likelihood of developing the vascular and inflammatory responses characteristic of rosacea.
The Role of the Immune System and Inflammation
An abnormal innate immune response is a central player in rosacea. Research has shown that people with rosacea have higher levels of certain antimicrobial peptides in their skin, such as cathelicidin. These peptides, which are part of the body's natural defense system, can trigger a cascade of inflammation that leads to redness, swelling, and the acne-like breakouts seen in papulopustular rosacea. This has led some to question, "is rosacea an autoimmune disease?" While it involves immune dysfunction, it is not currently classified as a classic autoimmune disorder.
Demodex Mites: Unwanted Guests on Your Skin
Everyone has tiny mites called Demodex folliculorum living harmlessly in their hair follicles. However, studies have found that people with rosacea tend to have a significantly higher number of these mites. It's theorized that these excess mites, or the bacteria they carry, may trigger the inflammatory immune response that leads to symptoms. They may also contribute to the papules and pustules of rosacea.
Blood Vessel Abnormalities
Problems with facial blood vessels are a hallmark of rosacea. Abnormalities in the blood vessels can cause them to dilate (widen) too easily and remain dilated, leading to persistent redness and flushing. This vascular instability is why common triggers like heat and spice directly cause rosacea flare-ups.
Consult Top Skin Specialists
Common Rosacea Triggers: What Turns Up the Heat?
While the root causes create the underlying condition, everyday triggers are what spark the flare-ups. Identifying and avoiding your personal triggers is one of the most effective ways to manage the signs of rosacea. Triggers are highly individual, but some are commonly reported.
Environmental and Weather-Related Triggers
- Sun exposure: The number one trigger for most people.
- Extreme temperatures: Both hot weather and cold, windy conditions.
- Humidity and wind.
- Strenuous exercise: Particularly in hot environments.
Food and Drink Triggers
- Alcohol: Especially red wine.
- Hot beverages: Like coffee and tea.
- Spicy foods: Those containing capsaicin.
- Histamine-rich foods: Aged cheeses, processed meats, fermented foods.
- Cinnamaldehyde-containing foods: Chocolate, tomatoes, citrus.
Lifestyle and Emotional Triggers
- Emotional stress: A major trigger for many, which is why "can stress cause rosacea" is a common search query. The answer is yes, it can significantly exacerbate it.
- Certain skincare products: Those containing alcohol, fragrance, witch hazel, or harsh exfoliants.
- Medications: Particularly vasodilators like some blood pressure drugs.
- Physical exertion.
Who is Most at Risk? Understanding Rosacea Demographics
Rosacea doesn't affect everyone equally. Certain demographics are statistically more likely to develop it. It is most frequently diagnosed in:
- Fair-skinned individuals of Celtic or Northern European ancestry.
- Women, although men often develop more severe forms, like phymatous rosacea.
- Adults between the ages of 30 and 50.
- People with a family history of rosacea or severe acne.
- Those who smoke.
Diagnosis: Why Seeing a Doctor is Crucial
There is no specific medical test for rosacea. A doctor, usually a dermatologist, will diagnose it by examining your skin and taking a detailed medical history. They will rule out other conditions like lupus, psoriasis, or allergic reactions. It is vital to get a professional diagnosis because self-treating with standard acne medication can often worsen rosacea on cheeks and nose. If your persistent redness or acne-like bumps don't improve with over-the-counter methods, consult a dermatologist online with Apollo24|7 for an initial evaluation and guidance.
Managing and Treating Rosacea Signs
Management is a two-pronged approach: medical intervention to control inflammation and lifestyle changes to avoid triggers.
Medical Treatments and Prescriptions
A dermatologist may prescribe:
- Topical medications: To reduce redness and inflammation (e.g., ivermectin, azelaic acid, brimonidine).
- Oral antibiotics: For their anti-inflammatory properties, not to fight infection (e.g., doxycycline).
- Laser therapy: To reduce visible blood vessels and extensive redness.
- For ocular rosacea: Antibiotic eye drops and eyelid cleansers.
Lifestyle Modifications and Skincare
- Identify and avoid your triggers. Keep a diary to track flare-ups.
- Protect your skin from the sun daily. Use a gentle, mineral-based broad-spectrum SPF 30+.
- Adopt a gentle skincare routine. Use pH-balanced, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers.
- Manage stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
Quick Takeaways: Key Points to Remember
- Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition causing facial redness, bumps, and visible vessels.
- The exact cause is unknown but involves a combo of genetics, immune system overreaction, Demodex mites, and vascular issues.
- Common triggers include sun, heat, spicy food, alcohol, and stress.
- It is most common in fair-skinned women aged 30-50.
- There are four subtypes, each with distinct symptoms.
- There is no cure, but symptoms can be effectively managed with prescription treatments and trigger avoidance.
- Professional diagnosis is essential to rule out other conditions and get the right treatment.
Conclusion
Living with the signs of rosacea can be a frustrating and confusing journey, but it is far from a hopeless one. By understanding that this condition is rooted in a complex interplay of genetics, immune response, and environmental factors, you can move from feeling like a victim of your skin to becoming an empowered manager of it. The key lies in a proactive approach: partnering with a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan, while meticulously identifying and avoiding your personal triggers through a detailed diary. Remember, what leads to signs of rosacea is multifaceted, so your management strategy should be too. Embrace a gentle skincare routine, become a diligent sun protector, and prioritize stress management. While rosacea may be a lifelong companion, it doesn't have to define you. With knowledge and careful management, you can achieve calmer, more comfortable skin and significantly reduce the impact of flare-ups on your daily life. If your condition is severe or not improving with lifestyle changes, consider booking a physical visit to a dermatologist with Apollo 24|7 for advanced treatment options.
Consult Top Skin Specialists
Consult Top Skin Specialists

Dr. Sonal Jain
Dermatologist
9 Years • MBBS, MD Dermatology, Venerology & Leprosy
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata
(25+ Patients)
Dr. Kavitha Killaparthy
Dermatologist
23 Years • MBBS,DIPLOMA(DERMATOLOGY,VENEREOLOGY,LEPROSY)
Hyderabad
JDS Skin & Hair Clinic, Hyderabad
Dr. Mayuri Jain
Dermatologist
11 Years • MBBS, MD Dermatology , Venereology & Leprosy
Delhi
Dr Mayuri Jain Clinic, Delhi

Dr. Ashwini T
Dermatologist
8 Years • MBBS, MD ( DERMATOLOGY )
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
Dr.j Girishma
Dermatologist
6 Years • MBBS MD DERMATOLOGY
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru
Consult Top Skin Specialists

Dr. Sonal Jain
Dermatologist
9 Years • MBBS, MD Dermatology, Venerology & Leprosy
Kolkata
MCR SUPER SPECIALITY POLY CLINIC & PATHOLOGY, Kolkata
(25+ Patients)
Dr. Kavitha Killaparthy
Dermatologist
23 Years • MBBS,DIPLOMA(DERMATOLOGY,VENEREOLOGY,LEPROSY)
Hyderabad
JDS Skin & Hair Clinic, Hyderabad
Dr. Mayuri Jain
Dermatologist
11 Years • MBBS, MD Dermatology , Venereology & Leprosy
Delhi
Dr Mayuri Jain Clinic, Delhi

Dr. Ashwini T
Dermatologist
8 Years • MBBS, MD ( DERMATOLOGY )
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru
Dr.j Girishma
Dermatologist
6 Years • MBBS MD DERMATOLOGY
Bengaluru
Apollo Medical Center, Marathahalli, Bengaluru
More articles from rosacea
Frequently Asked Questions
Can rosacea be cured?
No, there is currently no cure for rosacea. However, it is a highly treatable condition. With the right medical therapy and lifestyle changes, most people can effectively control their symptoms and prevent significant flare-ups, allowing them to live comfortably.
What is the difference between rosacea and acne?
While both can cause red bumps and pustules, they are different. Acne vulgaris is often linked to clogged pores by oil and dead skin cells and is common in teenagers. Rosacea typically occurs in adults, involves persistent facial redness and flushing, and lacks the blackheads and whiteheads (comedones) seen in acne.
Are there any natural remedies for rosacea?
Some people find relief with soothing ingredients like green tea extract, licorice, niacinamide, and oatmeal. However, 'natural' doesn't always mean gentle. It's crucial to patch test any new product and consult with a dermatologist before starting any natural regimen, as many botanical ingredients can be irritating.
Can diet really cause rosacea flare-ups?
Yes, diet is a very common trigger. Hot drinks, alcohol (especially red wine), spicy foods, and foods high in histamines are frequent culprits. Keeping a food diary can help you identify your specific foods to avoid with rosacea.
Is rosacea contagious?
No, rosacea is not contagious. You cannot catch it from or spread it to another person through any form of contact. It is an inflammatory condition believed to be influenced by genetics and internal bodily functions.