Skin Cancer Causes and Risk Factors

Written by Dr. Mohammed Kamran
Reviewed by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai MBBS
Last updated on 30th Jul, 2025
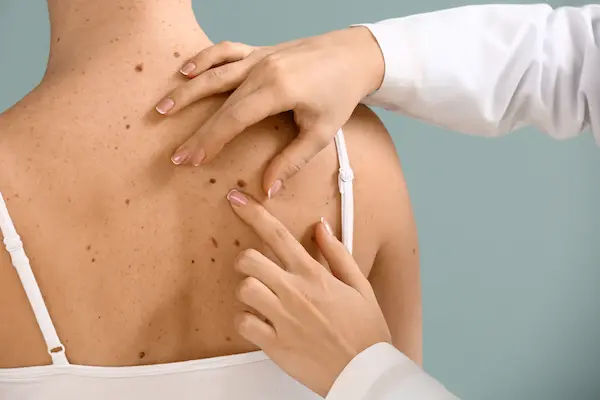
Introduction
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, but the good news is that it’s often preventable and treatable when detected early. Understanding the causes and risk factors can help you take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones.
What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer occurs when abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably, usually due to damage from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. The three main types are:
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) – The most common type, slow-growing, and rarely spreads.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) – More aggressive than BCC but still treatable if caught early.
3. Melanoma – The most dangerous form, as it can spread quickly to other organs if not treated early.
What Causes Skin Cancer?
The primary cause of skin cancer is UV radiation, which damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations and uncontrolled growth. Sources of UV exposure include:
- Sunlight – Prolonged or intense sun exposure, especially without protection.
- Tanning Beds – Artificial UV rays increase the risk significantly.
- Sunburns – Severe burns, especially in childhood, raise the risk of melanoma.
Other contributing factors include:
- Weakened Immune System – People with conditions like HIV or those taking immunosuppressive drugs are at higher risk.
- Certain Skin Conditions – Chronic wounds, scars, or inflammatory skin diseases can increase risk.
- Chemical Exposure – Some chemicals (e.g., arsenic, coal tar) may contribute to skin cancer.
Who Is at Risk?
While anyone can develop skin cancer, some people are at higher risk due to:
1. Fair Skin, Light Hair, and Light Eyes
People with less melanin (the pigment that protects skin from UV damage) have a higher risk.
2. History of Sunburns
Even one severe sunburn in childhood can increase the risk of melanoma later in life.
3. Excessive Sun Exposure
People who spend a lot of time outdoors (farmers, construction workers, athletes) without protection are more vulnerable.
4. Family or Personal History of Skin Cancer
If you or a close relative has had skin cancer, your risk is higher.
5. Moles (Atypical or Numerous Moles)
Having many moles or unusual-looking moles (asymmetrical, irregular borders) increases melanoma risk.
6. Age and Gender
- Older adults are more likely to develop skin cancer due to cumulative sun exposure.
- Men are more prone to melanoma than women.
7. Geographic Location
Living in sunny or high-altitude areas increases UV exposure.
How Can You Reduce Your Risk?
The good news is that most skin cancers are preventable with these simple steps:
1. Use Sun Protection Daily
- Sunscreen – Use a broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen, even on cloudy days. Reapply every 2 hours.
- Clothing – Wear long sleeves, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses.
- Seek Shade – Avoid direct sun between 10 AM – 4 PM when UV rays are strongest.
2. Avoid Tanning Beds
Artificial UV rays increase melanoma risk by 75% if used before age 35.
3. Check Your Skin Regularly
- Perform monthly self-checks for new or changing moles.
- Follow the ABCDE rule for melanoma detection:
- Asymmetry (one half doesn’t match the other)
- Border irregularity (edges are ragged or blurred)
- Color variation (multiple colors in one mole)
- Diameter (larger than 6mm, about the size of a pencil eraser)
- Evolving (changes in size, shape, or color)
4. Get Professional Skin Checks
If you’re at high risk, see a dermatologist annually for a full-body skin exam.
5. Boost Skin Health with Diet & Lifestyle
- Eat antioxidant-rich foods (berries, leafy greens, nuts) to help repair skin damage.
- Stay hydrated and avoid smoking, which can damage skin cells.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you notice any of the following, consult a dermatologist:
- A new mole or an existing mole that changes in size, shape, or color.
- A sore that doesn’t heal.
- A spot that itches, bleeds, or becomes painful.
Early detection saves lives! If you’re concerned about skin cancer, you can book a consultation with a dermatologist through Apollo 24|7 for expert advice and screening.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is largely preventable with sun-safe habits and regular skin checks. By understanding the risks and taking simple precautions, you can protect your skin and stay healthy. Remember—your skin is your body’s first defense; take care of it!
Stay sun-safe, stay vigilant, and don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if something seems unusual. Your health is worth it!
Book a Skin Check-Up Today (Link to Apollo 24|7 consultation page)