Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
Know about tuberculosis, what its common symptoms, causes, diagnosis and tips for managing TB.

Written by Dr. Mohammed Kamran
Reviewed by Dr. Rohinipriyanka Pondugula MBBS
Last updated on 28th Aug, 2025

Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious but treatable bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs. Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications and stop the spread of the disease. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms or has been exposed to TB, getting tested is essential.
In this article, we’ll explain how TB is diagnosed, the different tests available, and what steps you can take if you
suspect an infection.
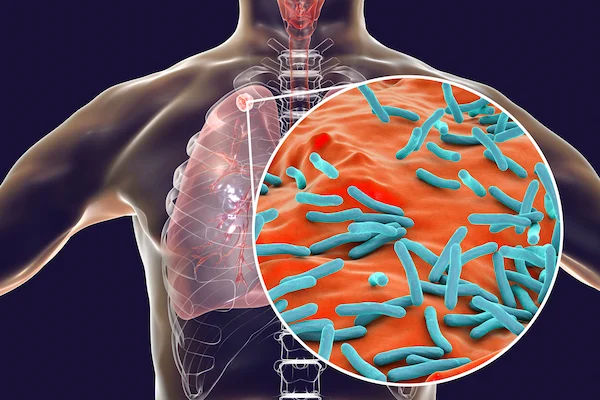
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?
TB is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It spreads through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. While TB mostly affects the lungs, it can also impact other organs like the kidneys, spine, or brain.
There are two types of TB:
- Latent TB – The bacteria are present but inactive, meaning you don’t have symptoms and can’t spread it.
- Active TB – The bacteria are active, causing symptoms and making the disease contagious.
Early diagnosis helps in effective treatment and prevents severe health risks.
Common Symptoms of TB
If you have active TB, you may experience:
- Persistent cough (lasting 3 weeks or more)
- Coughing up blood or mucus
- Chest pain
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever and night sweats
- Unintended weight loss
- Loss of appetite
If you notice these symptoms, consult a doctor immediately.
Consult a Pulmonologist for Personalised Advice
How is TB Diagnosed?
Doctors use different tests to confirm TB. Here’s what you can expect:
1. Medical History and Physical Exam
- Your doctor will ask about symptoms, exposure to TB, and overall health. They may also check for swollen lymph
nodes or abnormal lung sounds.
2. Tuberculin Skin Test (TST or Mantoux Test)
- A small amount of fluid (PPD) is injected under your skin.
- After 48–72 hours, a healthcare provider checks for swelling at the injection site.
- A positive result means you’ve been exposed to TB, but further tests are needed to confirm active infection.
3. Blood Tests (IGRA – Interferon-Gamma Release Assay)
- Blood tests like QuantiFERON-TB Gold or T-SPOT.TB detect TB infection.
- These tests are more accurate than skin tests and don’t require a second visit.
4. Chest X-ray
- If your skin or blood test is positive, a chest X-ray helps detect lung damage caused by active TB.
5. Sputum Test
- If TB is suspected, you may be asked to cough up sputum (mucus) for lab testing.
- The sample is checked under a microscope and cultured to confirm TB bacteria.
6. Molecular Tests (GeneXpert MTB/RIF)
- A rapid test that detects TB DNA and checks for drug resistance.
- Results are available within hours, helping start treatment early.
What Happens After Diagnosis?
If you’re diagnosed with latent TB, your doctor may recommend preventive treatment to stop it from becoming active.
For active TB, you’ll need a course of antibiotics (usually 6–9 months). It’s crucial to complete the treatment even if you feel better, as stopping early can lead to drug-resistant TB.
Tips for Managing TB
It includes:
- Take Medications as Prescribed – Missing doses can make TB harder to treat.
- Eat a Nutritious Diet – A balanced diet with proteins, vitamins, and minerals helps recovery.
- Avoid Close Contact – Cover your mouth when coughing and wear a mask to protect others.
- Stay Hygienic – Wash hands frequently and ensure good ventilation at home.
- Follow Up with Your Doctor – Regular check-ups ensure the treatment is working.
When to See a Doctor?
If you have:
- A persistent cough (3+ weeks)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats and fever
- Close contact with a TB patient
Final Thoughts
TB is a serious but curable disease. The key is early detection and proper treatment. If you or someone you know shows symptoms, don’t ignore them. Get tested and take the necessary steps to stay healthy.
Consult a Pulmonologist for Personalised Advice
Consult a Pulmonologist for Personalised Advice

Dr. P Sravani
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
3 Years • MBBS, MD
Visakhapatnam
Apollo Clinic Vizag, Visakhapatnam

Dr. Hyder
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS, MD (PULMONOLOGY)
Guntur
Kalam chest and multi-speciality clinic, Guntur

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(125+ Patients)

Dr. K Prasanna Kumar Reddy
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
16 Years • MBBS, DTCD (TB&CHEST), DNB (PULM MED), FCCP
Hyderabad
Apollo Medical Centre Kondapur, Hyderabad

Dr. R. Nithiyanandan
Pulmonology/critical Care Specialist
6 Years • MBBS, MD Internal Medicine , DM Pulmonary and critical care medicine
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(25+ Patients)
Consult a Pulmonologist for Personalised Advice

Dr. P Sravani
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
3 Years • MBBS, MD
Visakhapatnam
Apollo Clinic Vizag, Visakhapatnam

Dr. Hyder
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
5 Years • MBBS, MD (PULMONOLOGY)
Guntur
Kalam chest and multi-speciality clinic, Guntur

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(125+ Patients)

Dr. K Prasanna Kumar Reddy
Pulmonology Respiratory Medicine Specialist
16 Years • MBBS, DTCD (TB&CHEST), DNB (PULM MED), FCCP
Hyderabad
Apollo Medical Centre Kondapur, Hyderabad

Dr. R. Nithiyanandan
Pulmonology/critical Care Specialist
6 Years • MBBS, MD Internal Medicine , DM Pulmonary and critical care medicine
Chennai
Apollo Hospitals Greams Road, Chennai
(25+ Patients)