The “Healthy” Snacker: Why Men in Their 30s Still Need Glucose Fasting and PP Tests
Even "healthy" men in their 30s can be at risk for hidden blood sugar issues. Learn why glucose fasting and PP tests are vital for early detection of pre-diabetes and insulin resistance.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. Md Yusuf Shareef MBBS
Last updated on 7th Aug, 2025

Men in their 30s who appear physically fit and follow health-conscious eating habits may believe they are not at risk for metabolic conditions. However, many processed or high-carbohydrate foods such as energy bars, packaged fruit juices and large portions of grains can contribute to rising blood sugar levels over time.
Regular glucose tests for men 30 plus, including both fasting and postprandial (PP) blood sugar assessments, are important tools for early diabetes detection. These tests identify subtle imbalances in glucose metabolism before symptoms arise and help support proactive steps for long-term health and disease prevention.
Why Blood Sugar Management Matters for Men in Their 30s?
You might be thinking, "I'm active, I eat well, why do I need to worry about blood sugar now?" However, this stage of life often brings subtle changes in metabolism and lifestyle that can increase the risk of blood sugar imbalances. Understanding how these shifts affect long-term health is essential.
Dietary Habits Can Be Deceptive: Foods marketed as healthy, such as protein bars, smoothies and packaged snacks, often contain high levels of sugar and refined carbohydrates. These can lead to frequent spikes in blood glucose and gradually reduce insulin sensitivity.
Type 2 Diabetes Is Appearing Earlier: Once considered a condition of older adults, type 2 diabetes is now being diagnosed in younger individuals. Men in their 30s are increasingly affected, often without noticeable symptoms. Early screening can help prevent complications.
- Energy and Focus May Be Impacted: Blood sugar fluctuations can cause fatigue, reduced concentration and inconsistent physical performance. These effects can interfere with daily productivity and overall well-being.
- Long-Term Health Risks Accumulate: Elevated blood sugar, even at prediabetic levels, can damage blood vessels and organs over time. This increases the likelihood of heart disease, kidney problems and nerve damage later in life.
- Genetics Play a Role: A family history of diabetes significantly raises the risk. Men with diabetic parents or siblings should be especially proactive about monitoring their blood sugar and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Common Challenges in Blood Sugar Control for Men in Their 30s
Even active men can face unique challenges with blood sugar control:
- High-Carb "Healthy" Foods: As mentioned, many foods marketed as healthy or energy-boosting (e.g., granola, sports drinks, large fruit servings) are high in carbohydrates, which turn into sugar
- .Stress and Work Demands: High-pressure jobs and busy schedules can lead to irregular eating habits, increased reliance on quick snacks, and chronic stress, all of which can negatively impact blood sugar.
- Less Obvious Symptoms: In the early stages, symptoms of high blood sugar might be subtle or mistaken for other issues, such as general fatigue or stress. This makes testing even more important for early diabetes detection.
- Ignoring Risk Factors: A perceived high fitness level can sometimes lead to overlooking other risk factors like family history or dietary patterns.
Key Tests for Blood Sugar Monitoring - To get a clear picture of your blood sugar control, especially your morning levels, several tests are commonly used. These tests are vital for a comprehensive glucose test for men 30 plus.
Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Test:
- What it is: This test measures your blood sugar after an overnight fast (8-12 hours).
- What it reveals: It shows your baseline blood sugar level before food influences it. For men in their 30s without diabetes, a normal fasting blood sugar level is typically less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L). Levels between 100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L) suggest pre-diabetes. A reading of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests usually indicates diabetes.
Post-Prandial Blood Sugar (PPBS) Test:
- What it is: This test measures blood sugar levels usually two hours after you have eaten a meal. This is your post meal sugar test.
- What it reveals: It shows how your body handles sugar after food. For most healthy men in their 30s, a 2-hour post-meal blood sugar should be less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L).
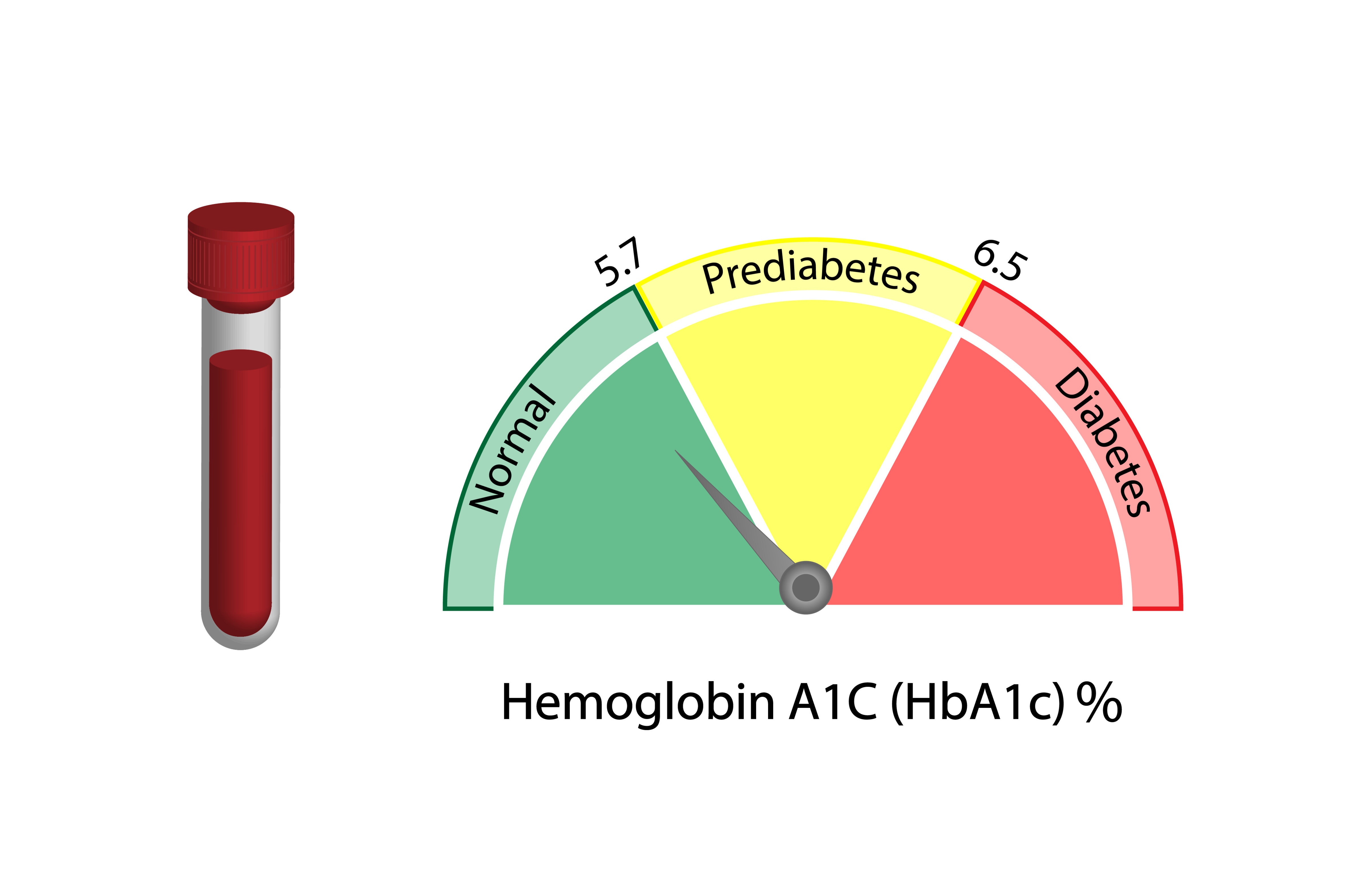
HbA1c Test (Glycated Haemoglobin Test):
- What it is: This test gives an average of your blood sugar levels over the past 2 to 3 months. It does not require fasting.
- What it reveals: The HbA1c provides a long-term view of your blood sugar control. For men in their 30s without diabetes, a normal HbA1c is typically below 5.7% (39 mmol/mol). Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% (39-46 mmol/mol) indicate pre-diabetes. A reading of 6.5% (48 mmol/mol) or higher suggests diabetes. For men with diabetes, the target HbA1c is often below 7% (53 mmol/mol), but this can vary based on individual health. Your doctor will set a personal target for you.
Your doctor will use a combination of these tests, along with your symptoms and medical history, to make an accurate diagnosis and tailor your health management plan.
Smart Blood Sugar Habits for Men in Their 30s
Staying on top of your blood sugar isn’t just for people with diabetes. For men in their 30s, it’s about protecting energy, performance and long-term health. Here are practical, everyday habits that can help:
- Rethink Your “Healthy” Carbs: Foods like fruit smoothies, protein bars and large grain portions may seem nutritious, but can be high in sugar or refined carbs. Choose whole fruits with nuts, and go for smaller portions of complex carbs like quinoa or brown rice.
- Build Balanced Plates: Combine lean protein, healthy fats and fibre-rich vegetables with your carbs. This slows digestion and helps prevent sharp spikes in blood sugar.
- Move Regularly: Exercise improves how your body uses insulin. Aim for a mix of cardio and strength training each week to support glucose control and overall fitness.
- Sleep Well: Poor sleep can throw off hormones that regulate blood sugar. Try to get 7 to 9 hours of restful sleep each night.
- Keep Stress in Check: Ongoing stress can raise blood sugar levels. Find what works for you, whether it’s walking, journaling, meditation or time with friends.
- Get Routine Screenings: You don’t need symptoms to justify a check-up. Regular blood sugar tests can catch issues early and help you make informed decisions about your health.
Key Tests for Blood Sugar Monitoring
To get a clear picture of your blood sugar control, especially your morning levels, several tests are commonly used. These tests are vital for a comprehensive glucose test for men 50 plus.
Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Test:
- What it is: This test measures your blood sugar after an overnight fast (8-12 hours).
- What it reveals: It shows your baseline blood sugar level before food influences it. For men over 50 without diabetes, a normal fasting blood sugar level is typically less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L). Levels between 100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L) suggest pre-diabetes. A reading of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests usually indicates diabetes.
Book Post-Prandial Blood Sugar (PPBS) Test
Post-Prandial Blood Sugar (PPBS) Test:
- What it is: This test measures blood sugar levels usually two hours after you have eaten a meal. This is your post meal sugar test.
- What it reveals: It shows how your body handles sugar after food. For most healthy men over 50, a 2-hour post-meal blood sugar should be less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L).
Book Post-Prandial Blood Sugar (PPBS) Test
HbA1c Test (Glycated Haemoglobin Test):
- What it is: This test gives an average of your blood sugar levels over the past 2 to 3 months. It does not require fasting.
- What it reveals: The HbA1c provides a long-term view of your blood sugar control. For men over 50 without diabetes, a normal HbA1c is typically below 5.7% (39 mmol/mol). Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% (39-46 mmol/mol) indicate pre-diabetes. A reading of 6.5% (48 mmol/mol) or higher suggests diabetes. For men over 50 with diabetes, the target HbA1c is often below 7% (53 mmol/mol), but this can vary based on your overall health and other medical conditions. Your doctor will set a personal target for you.
Your doctor will use a combination of these tests, along with your symptoms and medical history, to make an accurate diagnosis and tailor your diabetes management plan.
Where Senior Men Can Get Reliable Glucose Testing?
For senior men managing diabetes, keeping track of fasting blood sugar levels is key to controlling morning glucose and overall health. Apollo 24|7 offers convenient and trustworthy glucose testing services designed to support the needs of elderly patients.
Apollo 24|7 provides essential tests such as:
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Test: Measures blood sugar levels after fasting, providing a baseline reading
- Post-Prandial Blood Sugar (PPBS) Test: Measures blood sugar levels after a meal, helpful for monitoring how the body processes glucose.
HbA1c Test: Gives an average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months and usually does not require fasting.
Along with individual tests, Apollo 24|7 also offers various health check-up packages that include glucose tests as part of a broader assessment. You can explore their "Diabetes" or "Full Body Checkup" categories on the Apollo 24|7 website to find suitable options. With easy online booking and home sample collection options, Apollo 24|7 makes it simple and comfortable for senior men to stay on top of their blood sugar control.
Get Your Health Assessed Here
Conclusion
For men over 50, understanding and actively managing blood sugar levels is a crucial part of living well, whether you have diabetes or are at risk. The glucose test for men 50 plus, including both fasting and post meal sugar test readings, provides vital information. However, it's important to manage your diet, medication, and lifestyle to truly make a difference.
By staying in regular touch with your doctor, you can manage your blood sugar more effectively, which helps you feel more energetic and healthy overall. With the added support of trusted