Feeling Chest Tightness? These Tests Can Help Rule Out Risks
Discover which diagnostic tests, ECG, stress test, troponin, and lipid profile are essential when experiencing chest tightness. Learn how combining these tools can help promptly identify or rule out serious heart conditions.

Written by
Last updated on 21st Jul, 2025
.webp?tr=q-80,f-webp,w-350,dpr-2,c-at_max 700w)
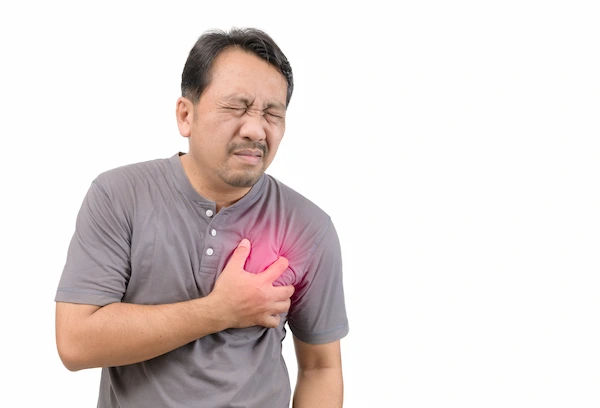
A feeling of tightness or pressure in your chest can be alarming. While it might sometimes be due to less serious issues like indigestion or muscle strain, for many adults, especially those over 40 and smokers, it's a symptom that demands immediate attention. Chest tightness can be a warning sign of serious heart conditions, and understanding what might be causing it is crucial for your health.
Understanding Chest Tightness and Associated Risks
Chest tightness can feel different for everyone. It might be described as a squeezing, pressure, fullness, or a burning sensation in the chest. Sometimes it spreads to your arms, neck, jaw, or back. While many things can cause chest tightness, the most concerning are those related to your heart.
Cardiac (Heart-Related) Causes like Angina, Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction) or Other Heart Conditions can cause chest tightness.
Non-Cardiac Causes like Digestive Issues, Muscle or Bone Problems, Lung Conditions, Anxiety or Panic Attacks can also cause chest tightness.
Who is at Higher Risk?
For adults over 40, and especially those who smoke, the risk of chest tightness being related to a heart condition is significantly higher. Other important risk factors include:
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and increases heart disease risk.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) strains the heart and arteries.
- High Cholesterol: Contributes to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Diabetes increases the risk of nerve and blood vessel damage.
- Family History: Having close relatives with early heart disease.
- Obesity and Lack of Physical Activity Contribute to heart disease.
Given these risks, it's vital to investigate chest tightness promptly, particularly if you fall into these higher-risk groups.
Important Tests to Help Rule Out Risks
When you experience chest tightness, your doctor will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms and medical history. They will then likely recommend specific diagnostic tests to understand if your heart is involved and to rule out serious conditions.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
The Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is often the first test done when chest tightness is a concern. It's a quick, painless, and non-invasive test that records the electrical signals of your heart.
What it reveals: An ECG provides a snapshot of your heart's electrical activity at that moment. It can show:
- Heart Rhythm: If your heart is beating too fast, too slow, or irregularly.
- Signs of Heart Attack: It can reveal if you are having a heart attack or if you've had one in the past.
- Blood Flow Problems (Ischemia): Changes in the ECG pattern can suggest that parts of your heart muscle are not getting enough blood.
- Heart Muscle Thickness: It can sometimes indicate if the walls of your heart chambers are thicker than normal.
Normal Range and What it Means: A normal ECG shows a steady heart rhythm, usually between 60 and 100 beats per minute, with specific wave patterns that indicate healthy electrical signals. Any changes from these normal patterns might suggest a problem that needs further investigation.
Book an Electrocardiogram test
Treadmill Test (TMT) / Stress ECG
If your resting ECG is normal but your doctor still suspects a heart problem, especially if your chest tightness occurs during physical activity, a Treadmill Test (TMT), also known as a Stress ECG, might be recommended. This test helps assess how your heart performs under stress.
Why it matters for chest tightness: Some heart problems, like narrowed arteries, might not show up on a resting ECG but become apparent when your heart needs to work harder. The TMT helps to:
- Provoke Symptoms: See if exercise brings on your chest tightness.
- Detect Blockages: Identify if there are blockages in your heart arteries that limit blood flow during exertion.
- Assess Heart's Response: Check how your heart rate and blood pressure respond to physical activity.
What it Reveals: An abnormal TMT can indicate that your heart muscle is not getting enough blood during exercise, suggesting coronary artery disease.
Book Treadmill Test / Stress ECG test now
Troponin I (Cardiac Marker)
If your chest tightness is severe, sudden, or accompanied by symptoms like sweating, shortness of breath, or pain radiating to your arm, your doctor will immediately consider a heart attack. In such cases, a blood test for cardiac markers, especially Troponin I, is critical.
Why it's relevant: Troponin I is a protein found in the heart muscle. When the heart muscle is damaged, such as during a heart attack, Troponin I is released into the bloodstream.
Normal Range and What it Means: In healthy individuals, Troponin I levels are very low or undetectable.
- Elevated Troponin I levels indicate heart muscle injury or damage. The higher the level, and the more it rises over time, the more likely it is that a heart attack has occurred.
This test is vital for quickly diagnosing a heart attack and guiding urgent medical treatment.
Lipid Profile
High cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart disease, which can lead to chest tightness. A Lipid Profile is a blood test that measures the different types of fats (lipids) in your blood.
Why it's relevant: High levels of certain lipids can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in your arteries, narrowing them and restricting blood flow to your heart. This is a common cause of angina and can lead to heart attacks.
What it measures: A Lipid Profile typically includes:
- Total Cholesterol: The total amount of cholesterol in your blood.
- HDL Cholesterol (High-Density Lipoprotein): Often called "good" cholesterol because it helps remove excess cholesterol from your arteries. Higher levels are better.
- LDL Cholesterol (Low-Density Lipoprotein): Often called "bad" cholesterol because high levels contribute to plaque buildup in arteries. Lower levels are better.
- Triglycerides: Another type of fat in your blood. High levels can increase heart disease risk.
Normal Ranges and What They Mean: Optimal levels generally are:
- Total Cholesterol: Below mg/dL (5.2 mmol/L)
- HDL Cholesterol: 40 mg/dL (1.0 mmol/L) or higher (for men), 50 mg/dL (1.3 mmol/L) or higher (for women)
- LDL Cholesterol: Below 100 mg/dL (2.6 mmol/L) (lower for high-risk individuals)
- Triglycerides: Below 150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L)
Abnormal levels, especially high LDL or triglycerides, indicate an increased risk of heart disease and are crucial to manage to prevent chest tightness and other cardiac events.
Get These Tests To Get A Yourself Checked up
Other Important Tests Your Doctor Might Consider
Depending on your symptoms and initial test results, your doctor might also recommend:
- Echocardiogram
- Blood Pressure Monitoring
- Blood Sugar Tests (FBS, HbA1c)
Who Should Get These Tests?
If you are experiencing chest tightness, it's always best to talk to a healthcare professional. These tests are particularly important for:
- Adults aged 40 and above
- Smokers
- Individuals with persistent, recurrent, or worsening chest tightness
- Those with risk factors
Getting an early diagnosis is key to managing any heart problems effectively and preventing serious complications.
Why Choose Apollo 24|7 for Your Tests?
When you need diagnostic tests, especially for something as important as chest tightness, you want a service that is reliable, accurate, and convenient. Apollo 24|7 offers all of this and more. They make it easy to get tested with home sample collection for many blood tests, which is very helpful for those who might find it difficult to visit a lab. As part of the trusted Apollo Hospitals group, they ensure high-quality, accurate results using advanced lab equipment. They provide a wide range of tests and comprehensive health packages, including those focused on heart health, helping you get a complete picture of your well-being.
Conclusion
Chest tightness is a symptom that should never be ignored, especially for adults over 40 and smokers. It can be a crucial sign of underlying heart conditions. Diagnostic tests like the Electrocardiogram (ECG), Treadmill Test (TMT), Troponin I blood test, and Lipid Profile are essential tools to help your doctor understand the cause and rule out serious risks. By taking proactive steps and undergoing these recommended tests through trusted providers like Apollo 24/7, you gain valuable insights into your heart health. Early detection and appropriate management can significantly improve your health outcomes and help you lead a healthier, more confident life. Prioritising these investigations is a vital step towards protecting your heart.