How to Reduce Calcium Oxalate in Urine: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn effective strategies to reduce calcium oxalate in urine through dietary changes, proper hydration, and lifestyle modifications. Discover the causes, symptoms and implications for kidney stone management and prevention.


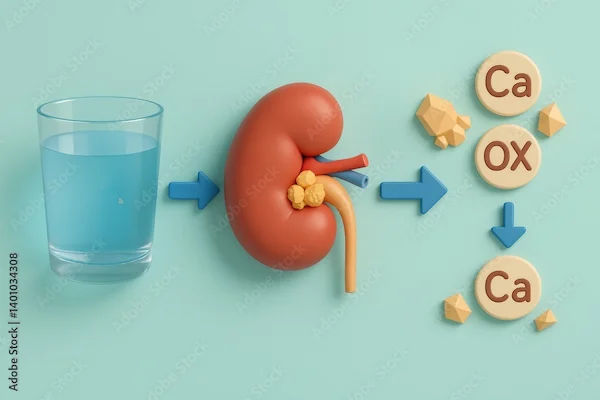
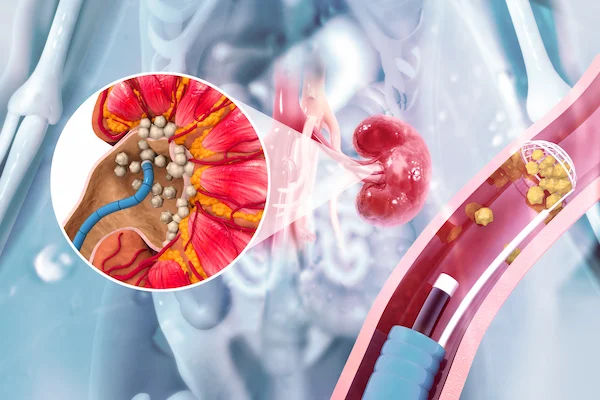
When hen calcium binds with oxalate in the kidneys, calcium oxalate crystals form in urine. These crystals can develop further into kidney stones and cause significant pain, discomfort, and health complications. Thus, managing oxalate levels is crucial for preventing stone formation and maintaining kidney health.
Learning about this condition may help individuals timely recognise symptoms, get help, and treat the condition before it leads to complications. Continue reading for more information on the management of calcium oxalate in urine.
Causes and Risk Factors of Calcium Oxalate in Urine
A person's diet significantly influences calcium oxalate levels in urine. It is very harmful to consume excessive oxalate-rich foods as it increases the risk of calcium oxalate crystal formation.
In this regard, here are a few dietary habits that should be avoided:
High intake of oxalate-rich vegetables (e.g., spinach, beets, rhubarb)
Excessive protein consumption as it leads to increased calcium excretion
Inadequate calcium intake, which prevents oxalate from binding in the gut
A high sodium diet as it increases calcium loss through urine
Excessive vitamin C supplementation, as the extra vitamin C converts to oxalate
Insufficient water intake leads to concentrated urine and crystal formation
High sugar consumption, which can promote kidney stone formation
Additionally, certain genetic factors and medical conditions can increase calcium oxalate formation. Here are a few such conditions:
Dehydration: Low fluid intake reduces urine volume, increasing stone risk
Medications: Some drugs, like diuretics, antacids, and certain antibiotics, may raise oxalate levels
Hormonal Changes: Conditions like hyperparathyroidism can elevate calcium excretion
Genetic Factors: Inherited conditions such as primary hyperoxaluria increase oxalate production
Digestive Disorders: Crohn’s disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and malabsorption disorders can lead to higher oxalate absorption
Bariatric Surgery Complications: Can alter digestion, increasing oxalate absorption
Chronic Kidney Disease: Impairs the body's ability to filter excess oxalate
Metabolic Disorders: Conditions affecting mineral metabolism may contribute to stone formation.
Symptoms and Implications of Calcium Oxalate in Urine
Early detection of high calcium oxalate levels helps prevent severe complications. Here are a few such symptoms that require attention:
Sharp pain in the lower back or sides
Frequent urination
Burning sensation during urination
Cloudy or dark urine
Blood in urine
Nausea and vomiting
Urinary urgency
Persistent high calcium oxalate levels can lead to serious health complications. They may lead to severe medical conditions like:
Kidney stone formation, which can cause intense pain and urinary blockage
Chronic kidney disease
Urinary tract damage caused by repeated stone formation and irritation
Recurrent infections, as bacteria thrive in an impaired urinary environment
Declining kidney function, leading to reduced filtration capacity
Permanent kidney scarring, increasing the risk of long-term complications
Consult Top Experts for Your Symptoms
Dietary Adjustments to Reduce Calcium Oxalate in Urine
Maintaining the right diet can play a crucial role in reducing calcium oxalate levels. Proper food selection and preparation can significantly minimise crystal formation risk. Individuals should focus on creating a balanced diet that supports kidney health and reduces oxalate absorption.
Foods that are mentioned below help manage oxalate levels and support overall urinary tract health:
Low-fat dairy products, which provide calcium without increasing stone risk
Lean proteins such as chicken, turkey, and fish, reducing excessive purine intake
White rice and pasta, which are lower in oxalates than whole grains
Low-oxalate vegetables, like cucumbers, zucchini, and cauliflower
Citrus fruits, which contain citrate that helps prevent stone formation
Egg whites are a good source of protein with minimal oxalates
Fresh herbs for flavouring without adding high-oxalate seasonings
Water-rich fruits, such as watermelon and cantaloupe, which support hydration
Certain foods contain high oxalate concentrations and can increase crystal formation risk. Such items can be avoided to minimise the risk:
Spinach and dark leafy greens
Nuts and nut-based products, particularly almonds and cashews
Chocolate and cocoa
Rhubarb
Beets and beet greens
Black tea
Soy products
Wheat bran
Sweet potatoes
Certain beans and legumes, such as navy beans and black beans
Proper food preparation can reduce oxalate content as well. Boiling high-oxalate vegetables removes some oxalates. However, combining calcium-rich foods with oxalate-containing foods helps bind oxalates in the digestive tract. This becomes harmful in the long term.
Hydration Management to Reduce Calcium Oxalate in Urine
Proper hydration is critical for managing calcium oxalate levels in urine. Adequate fluid intake helps dilute urine, preventing crystal formation and reducing kidney stone risk.
Key benefits of optimum fluid intake include:
Dilutes mineral concentration in urine
Reduces crystal formation likelihood
Supports kidney function
Helps flush out potential stone-forming substances
Maintains overall body hydration
Supports metabolic processes
Consistent fluid consumption requires strategic planning. Individuals should aim for steady hydration throughout the day. Following are some recommended hydration strategies:
Drink 2.5-3 litres of water daily
Spread fluid intake across daytime hours
Carry a water bottle for constant access
Monitor urine colour (pale yellow indicates good hydration)
Increase water intake during exercise and hot weather
Use smartphone apps to track water consumption
Consider herbal teas and water-rich foods, such as cucumbers, oranges, and melons, as alternative sources of hydration
Medical Treatments for Calcium Oxalate in Urine
Healthcare providers may prescribe targeted medications to manage calcium oxalate levels. These medications address underlying causes and prevent crystal formation.
Common prescription treatments include:
Thiazide diuretics
Potassium Citrate
Alpha-blockers
Calcium management drugs
Urine pH regulators
Metabolic disorder medications
Furthermore, certain over-the-counter supplements support kidney health and reduce oxalate levels. Consultation with healthcare professionals ensures safe and effective use.
Recommended supplements:
Magnesium citrate
Vitamin B6
Probiotics
Cranberry extract
Fish oil
Calcium supplements
Citrate-based formulations
Note - Supplement use requires medical supervision. Also, natural remedies should always complement conventional treatments.
Consult Top Doctors for Personalised Treatment
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Calcium Oxalate in Urine
Physical activity supports overall kidney health and metabolic processes. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces stone formation risk. The benefits of regular exercise include:
Improved metabolic function
Weight management
Enhanced circulation
Stress reduction
Hormonal balance
Improved mineral metabolism
Increased hydration awareness
Now, chronic stress impacts mineral balance and kidney function. Thus, implementing stress management strategies supports overall health and reduces stone formation risk.
Effective stress reduction methods include:
Meditation practices
Deep breathing exercises
Regular sleep schedule
Yoga
Mindfulness techniques
Time management
Professional counseling
Hobby engagement
Diagnostic Tests and Monitoring of Calcium Oxalate in Urine
Urine tests help diagnose calcium oxalate levels. Healthcare professionals analyse urine samples to assess crystal formation risks. Advanced testing provides detailed insights into metabolic factors affecting kidney stone development.
A 24-hour urine collection measures the following:
Mineral concentrations
pH level assessment
Crystal composition analysis
Calcium and oxalate concentration
Citrate and creatinine levels
Additionally, consistent medical monitoring can help prevent complications. Healthcare providers can track treatment effectiveness and adjust strategies as needed. The standard monitoring approach includes the following:
Quarterly urine and blood tests
Annual comprehensive metabolic screening
Regular kidney function assessments
Tracking dietary and lifestyle modifications
Reviewing medication effectiveness
Prevention Strategies for Calcium Oxalate in Urine
Preventing calcium oxalate accumulation requires proactive measures. Individuals can implement multiple strategies to reduce crystal formation risks:
Maintain consistent hydration
Balance calcium and oxalate intake
Control sodium consumption
Manage body weight
Practice portion control
Choose low-oxalate food options
Regular physical activity
Long-term management approaches include:
Develop a personalised nutrition plan
Regular medical consultations
Stress management techniques
Continuous lifestyle monitoring
Adaptive treatment strategies
Thorough knowledge of the condition
Conclusion
Calcium oxalate management requires comprehensive understanding and consistent effort. Individuals can significantly reduce kidney stone risks through dietary modifications, hydration, medical monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments. A holistic approach combining medical guidance, personal awareness, and proactive health strategies ensures effective prevention and long-term kidney wellness.
Consult Top Urologists
Consult Top Urologists

Dr. Aditendraditya Singh Bhati
Neurosurgeon
21 Years • MBBS(2004), DNB Neurosurgery(2014); MNAMS; Fellow Skull Base Endoscopy (Italy), Fellow Extended Skull Base ( Weill Cornell, USA), Fellow ZAP-X Radiosurgery. Member of American Association of Neurological Surgeons
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(100+ Patients)

Dr. Ganeshgouda Majigoudra
Neurologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD ( GENERAL MEDICINE) DM (NEUROLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(150+ Patients)

Dr Debnath Dwaipayan
Neurosurgeon
9 Years • MBBS, MS(Gen. Surgery), DrNB (Neurosurgery)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Anusha D
Neurologist
16 Years • MBBS, MD, DM (Neuro), DNB (Neuro)
Chennai
Apollo Speciality Hospitals OMR, Chennai
(125+ Patients)
Consult Top Doctors for Personalised Treatment

Dr. Aditendraditya Singh Bhati
Neurosurgeon
21 Years • MBBS(2004), DNB Neurosurgery(2014); MNAMS; Fellow Skull Base Endoscopy (Italy), Fellow Extended Skull Base ( Weill Cornell, USA), Fellow ZAP-X Radiosurgery. Member of American Association of Neurological Surgeons
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(100+ Patients)

Dr. Ganeshgouda Majigoudra
Neurologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD ( GENERAL MEDICINE) DM (NEUROLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(150+ Patients)

Dr Debnath Dwaipayan
Neurosurgeon
9 Years • MBBS, MS(Gen. Surgery), DrNB (Neurosurgery)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Anusha D
Neurologist
16 Years • MBBS, MD, DM (Neuro), DNB (Neuro)
Chennai
Apollo Speciality Hospitals OMR, Chennai
(125+ Patients)
Consult Top Experts for Your Symptoms

Dr. Aditendraditya Singh Bhati
Neurosurgeon
21 Years • MBBS(2004), DNB Neurosurgery(2014); MNAMS; Fellow Skull Base Endoscopy (Italy), Fellow Extended Skull Base ( Weill Cornell, USA), Fellow ZAP-X Radiosurgery. Member of American Association of Neurological Surgeons
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(100+ Patients)

Dr. Ganeshgouda Majigoudra
Neurologist
10 Years • MBBS, MD ( GENERAL MEDICINE) DM (NEUROLOGY)
Bengaluru
Apollo Clinic, JP nagar, Bengaluru

Dr. E Prabhakar Sastry
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
40 Years • MD(Internal Medicine)
Manikonda Jagir
Apollo Clinic, Manikonda, Manikonda Jagir
(150+ Patients)

Dr Debnath Dwaipayan
Neurosurgeon
9 Years • MBBS, MS(Gen. Surgery), DrNB (Neurosurgery)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Anusha D
Neurologist
16 Years • MBBS, MD, DM (Neuro), DNB (Neuro)
Chennai
Apollo Speciality Hospitals OMR, Chennai
(125+ Patients)
.webp)