Guide to Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Aub
Know about abnormal uterine bleeding, what it is, causes including palm-coein, signs, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options and more.

Written by Dr. Dhankecha Mayank Dineshbhai
Reviewed by Dr. J T Hema Pratima MBBS, Fellowship in Diabetes Mellitus
Last updated on 13th Jan, 2026
.webp?tr=q-80,f-webp,w-350,dpr-2,c-at_max 700w)
Introduction
Uterine bleeding is a natural part of the menstrual cycle for most women. But what happens when that bleeding becomes unpredictable, excessively heavy, or just doesn't feel right? You might be experiencing abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB), a common condition that affects a significant number of women at some point in their lives. This guide is designed to demystify abnormal uterine bleeding, empowering you with knowledge about its potential causes, from hormonal fluctuations and fibroids to more complex conditions. We will walk you through the common symptoms, explain how healthcare professionals diagnose the problem, and outline the range of treatment options available. Whether you're seeking answers for yourself or a loved one, understanding AUB is the first step toward taking control of your gynaecological health and finding a path to effective management. If your symptoms are causing concern, remember that consulting a doctor online with Apollo24|7 can be a convenient first step for personalised advice.
What is Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB)?
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) is a broad term used to describe any irregularity in the menstrual cycle concerning its
frequency, regularity, duration, or volume. It replaces older terms like "menorrhagia" (heavy bleeding) or
"metrorrhagia" (bleeding between periods) to provide a more precise and standardised framework for diagnosis. Essentially, AUB refers to any bleeding that differs from your typical menstrual pattern. It's crucial to understand that "normal" can vary from person to person, which is why tracking your cycle is so valuable. The International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) has established clear guidelines to help define what falls outside the norm, making it easier for patients and doctors to communicate effectively about symptoms.
Consult a Top Gynaecologist for Personalised Advice
Normal vs. Abnormal Bleeding: Knowing the Difference
To identify abnormal uterine bleeding, you first need a baseline for a normal menstrual cycle. A typical cycle lasts
between 24 and 38 days, with bleeding lasting 4 to 8 days. The average blood loss is about 30-40 millilitres (roughly 2-3
tablespoons). AUB is present if you experience any of the following:
- Bleeding between periods.
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding that soaks through one or more pads or tampons every hour for several consecutive hours.
- Menstrual periods lasting more than 8 days.
- Cycles that are shorter than 24 days or longer than 38 days.
- Bleeding after menopause.
Common Symptoms and Types of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
The symptoms of AUB can manifest in various ways, often impacting both physical and emotional well-being. The primary types of abnormal uterine bleeding are characterised by their timing and flow.
Common presentations include:
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (HMB): This involves losing more than 80 ml of blood per cycle (soaking a pad/tampon every 1-2 hours), passing large blood clots, or having a period that disrupts your normal activities due to flooding.
- Irregular Bleeding: This includes bleeding or spotting between your expected periods (intermenstrual bleeding) or having highly unpredictable cycles.
- Prolonged Bleeding: Menstrual bleeding that consistently lasts longer than eight days.
- Frequent Bleeding: Periods that occur more often than every 24 days (polymenorrhea).
- Infrequent Bleeding: Periods that occur less often than every 38 days (oligomenorrhea).
Many women with heavy bleeding may also experience symptoms of iron-deficiency anaemia, such as fatigue,
weakness, pale skin, and shortness of breath.
When Should You Be Concerned? Red Flag Symptoms
While AUB is often manageable, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. If you experience any of the
following red flag symptoms, it is crucial to seek prompt medical care:
- Vaginal bleeding after menopause.
- Soaking through a pad or tampon every hour for 2-3 hours in a row.
- Bleeding accompanied by severe pain, fever, or dizziness.
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded.
If symptoms like these persist, consulting a doctor promptly is essential. You can book a physical visit to a gynaecologist with Apollo24|7 for a thorough evaluation.
Unravelling the Causes: The PALM-COEIN System Explained
To systematically identify the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding, doctors use the FIGO PALM-COEIN classification
system. This acronym categorises causes into structural (things you can see, like fibroids) and non-structural (functional
or hormonal issues).
Structural Causes (PALM)
The "PALM" side of the system refers to causes that can be visually identified through imaging or pathology.
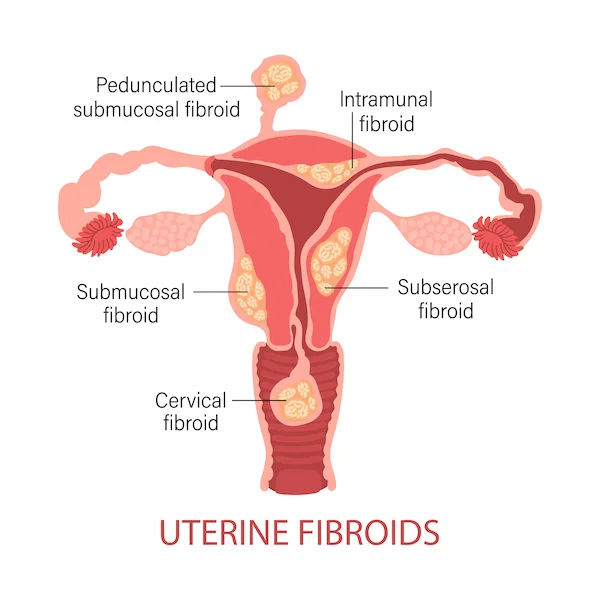
Polyps and Fibroids
- Polyps are small, benign (non-cancerous) growths on the inner wall of the uterus (endometrial polyps) or cervix.
- Fibroids (leiomyoma) are non-cancerous tumours made of muscle tissue that grow in or on the uterine wall. They are a
very common cause of heavy menstrual bleeding, especially in women over 30.
Adenomyosis
This condition occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus (endometrium) grows into the muscular wall of the
uterus. This can cause the uterus to enlarge and lead to heavy, painful periods.
Malignancy and Hyperplasia
Although less common, abnormal uterine bleeding can be a sign of precancerous conditions (endometrial hyperplasia)
or cancer of the uterus, cervix, or endometrium. This is why evaluation is critical, particularly for women over 45 or those with risk factors.
Non-Structural Causes (COEIN)
The "COEIN" side includes functional or systemic issues.
Coagulopathies and Ovulatory Dysfunction
- Coagulopathy: Underlying bleeding disorders, like von Willebrand disease, can cause heavy bleeding.
- Ovulatory Dysfunction: This is a frequent cause of irregular periods, often linked to conditions like Polycystic Ovary
Syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, obesity, extreme stress, or perimenopause. The body doesn't ovulate regularly, leading to hormonal imbalance and unpredictable bleeding.
Endometrial, Iatrogenic, and Not Yet Classified Causes
- Endometrial: This refers to issues with the uterine lining itself that are not explained by other categories.
- Iatrogenic: Bleeding caused by medical treatments, such as certain IUDs (especially the non-hormonal copper IUD),
blood thinners, or hormonal medications. - Not Yet Classified: Rare causes that don't fit elsewhere.
How is Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Diagnosed?
Diagnosing the cause of AUB is a detective-like process that begins with a detailed discussion of your medical history
and symptoms. Your doctor will likely ask you to describe your cycle pattern, flow, and any associated pain. A physical exam, including a pelvic exam, is usually the next step.
The Role of Pelvic Exams, Ultrasounds, and Blood Tests
- Pelvic Exam: To check the health of your reproductive organs.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: This is a key imaging test that uses sound waves to create pictures of your uterus, ovaries, and pelvis.
It can identify structural causes like fibroids or polyps. - Blood Tests: These are essential to check for anaemia (from blood loss), thyroid function, and hormone levels. A
pregnancy test is also standard. Apollo24|7 offers convenient home collection for these essential blood tests.
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures: When Are They Needed?
If initial tests are inconclusive, further procedures may be recommended:
- Hysteroscopy: A thin, lighted scope is inserted through the cervix to view the inside of the uterus directly.
- Endometrial Biopsy: A small sample of the uterine lining is taken to check for abnormalities like hyperplasia or cancer,
which is particularly important for women over 45. - Sonohysterography: Saline is injected into the uterus during an ultrasound to provide a clearer view of the endometrial
cavity.
Treatment Options for Managing AUB
Treatment is highly individualised and depends on the underlying cause, the severity of symptoms, your age, and
whether you wish to have children in the future.
Medications and Hormonal Therapies
For many women, the first line of treatment involves medication:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Like ibuprofen, can reduce blood loss and relieve menstrual cramps.
- Tranexamic Acid: A non-hormonal medication that helps reduce bleeding by promoting blood clotting.
- Hormonal Therapies: Combined oral contraceptives (birth control pills), progesterone-only pills, or hormonal IUDs (like
Mirena) are highly effective at regulating cycles and reducing bleeding. The Mirena IUD is often a first-choice
treatment for heavy bleeding.
Surgical and Minimally Invasive Procedures
If medications are ineffective or if a structural issue is identified, procedures may be necessary:
- Endometrial Ablation: A procedure that destroys the uterine lining to reduce or stop bleeding. This is not an option for
women who wish to become pregnant in the future. - Uterine Artery Embolisation (UAE): A procedure to shrink fibroids by blocking their blood supply.
- Myomectomy: Surgical removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus.
- Hysterectomy: The surgical removal of the uterus, which is a definitive cure for AUB but is a major surgery and
eliminates the possibility of pregnancy.
Living with AUB: Management and Self-Care Tips
While undergoing diagnosis and treatment, certain self-care strategies can help you manage the symptoms of abnormal
uterine bleeding:
- Track Your Cycle: Use a journal or an app to record the start and end dates of your period, flow heaviness, and any
symptoms. - Manage Iron Levels: If you have heavy bleeding, eat iron-rich foods (leafy greens, red meat, lentils) and consider an
iron supplement after consulting your doctor to prevent anaemia. - Manage Pain: Use a heating pad for cramps and take over-the-counter pain relievers as needed.
- Prioritise Rest: Fatigue is common; listen to your body and get adequate sleep.
When to See a Doctor: A Clear Guide
Don't hesitate to seek medical advice for abnormal uterine bleeding. It's better to be proactive. Schedule an appointment
with a gynaecologist if you experience:
- A consistent change in your menstrual pattern.
- Bleeding that interferes with your quality of life.
- Bleeding after sex or between periods.
- Any bleeding after menopause.
- A doctor can help determine if your irregular periods after 40 are a normal part of perimenopause or something that
needs further investigation.
Conclusion
Understanding abnormal uterine bleeding is the first and most crucial step toward regaining control over your health. While it can be a source of frustration and worry, it's important to remember that AUB is a common and highly treatable condition. The key is not to dismiss persistent changes in your cycle. By partnering with a healthcare provider, you can navigate the diagnostic process and find a treatment plan that works for your body and your life goals. If you recognise any of the symptoms discussed in this guide, take that proactive step. You can consult a doctor online with Apollo24|7 for an initial discussion or book an in-person appointment for a comprehensive evaluation. Your well-being is worth it.
Consult a Top Gynaecologist for Personalised Advice
Consult a Top Gynaecologist for Personalised Advice

Dr. Asawari Kesari Kapoor
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
23 Years • M.B.B.S, D.G.O(Mumbai) ,D.G.O (C.P.S), D.N.B (OBGY)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Akhila C
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
14 Years • MBBS , DGO , DNB - Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Sheshadripuram, Bengaluru

Dr Jaya Kumar Agarwal
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
25 Years • MBBS , DGO , DNB (obstetric and gynecology) DGE diploma in Gyne endoscopy (Germany )
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Surpreet Kaur Sandhu
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
20 Years • MBBS MS (OBS Gyn). Fellowship in Minimally Invasive Gynecology Surgery & Fellowship in Advanced Infertility Training (FOGSI)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(200+ Patients)

Dr Sangeetha Visweswar
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
23 Years • M. B.B.S., D.G.O., DNB ( OBG ) F.G.O.
Chennai
Apollo Speciality Hospitals, Teynampet, Chennai
Consult a Top Gynaecologist for Personalised Advice

Dr. Asawari Kesari Kapoor
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
23 Years • M.B.B.S, D.G.O(Mumbai) ,D.G.O (C.P.S), D.N.B (OBGY)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(25+ Patients)

Dr. Akhila C
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
14 Years • MBBS , DGO , DNB - Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Bengaluru
Apollo Hospitals Sheshadripuram, Bengaluru

Dr Jaya Kumar Agarwal
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
25 Years • MBBS , DGO , DNB (obstetric and gynecology) DGE diploma in Gyne endoscopy (Germany )
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi

Dr. Surpreet Kaur Sandhu
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
20 Years • MBBS MS (OBS Gyn). Fellowship in Minimally Invasive Gynecology Surgery & Fellowship in Advanced Infertility Training (FOGSI)
Delhi
Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, Delhi
(200+ Patients)

Dr Sangeetha Visweswar
Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
23 Years • M. B.B.S., D.G.O., DNB ( OBG ) F.G.O.
Chennai
Apollo Speciality Hospitals, Teynampet, Chennai
More articles from Uterine Bleeding
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the most common cause of abnormal uterine bleeding?
The most common cause varies by age. In adolescents and women in their 20s-30s, hormonal imbalances and ovulatory dysfunction (like PCOS) are frequent. In women in their 30s-40s, structural causes like fibroids and heavy bleeding become more common.
2. Can stress cause abnormal uterine bleeding?
Yes, high levels of physical or emotional stress can disrupt the hormonal signals from your brain to your ovaries, leading to ovulatory dysfunction and missed or irregular periods.
3. How do doctors treat heavy bleeding caused by fibroids?
Treatment depends on the size and location of the fibroids. Options include hormonal medications (like the Mirena IUD), minimally invasive procedures like uterine artery embolisation (UAE), or surgical options like myomectomy (fibroid removal) or hysterectomy.
4. Is abnormal uterine bleeding a sign of cancer?
While most cases of AUB are due to non-cancerous conditions, it can be a symptom of endometrial or uterine cancer, especially in postmenopausal women or those with specific risk factors. This is why a proper medical evaluation is essential to rule out serious causes.
5. Can I get pregnant if I have abnormal uterine bleeding?
.It depends on the underlying cause. Conditions like anovulation (not ovulating) can make conception difficult but are often treatable. Structural issues like large fibroids might also impact fertility. A gynaecologist can evaluate your specific situation and discuss your options.