Diabetes Management
Can Diabetes Cause Digestive Issues?
2 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 31 October 2023, Updated on - 22 February 2024
Share this article
0
0 like
Diabetes is a complex metabolic disorder that might affect blood sugar regulation, cardiovascular health, and nerve damage, it's important to recognise that diabetes can also have a significant impact on the digestive system. Although diabetes doesn’t have any direct impact on the digestive system, they are related to each other. Let’s try and understand some of the most common digestive issues associated with diabetes.
Gastroparesis:
One of the most prominent digestive issues associated with diabetes is gastroparesis. This condition affects the normal motility of the stomach, leading to delayed emptying. Normally, the stomach contracts to mix food with digestive juices and then moves the mixture into the small intestine for further digestion. In individuals with diabetes, high and unstable blood sugar levels can damage the vagus nerve, which controls these contractions. As a result, food remains in the stomach longer than it should, causing symptoms such as bloating, nausea, vomiting, and poor appetite.
Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes, can also affect the digestive system. This condition results from nerve damage caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels. When neuropathy affects the nerves controlling digestion, it can lead to a range of gastrointestinal problems. These may include diarrhoea, constipation, or a combination of both, making it challenging to maintain regular bowel movements.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Some studies suggest a link between diabetes and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). IBS is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterised by symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits. While the exact connection between diabetes and IBS is not fully understood, it's thought that the impact of diabetes on gut motility and sensation might contribute to the development or exacerbation of IBS symptoms in some individuals.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, commonly known as GERD, is another digestive problem that can co-occur with diabetes. GERD occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the oesophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn and regurgitation. While diabetes itself does not directly cause GERD, uncontrolled diabetes and delayed stomach emptying (common in gastroparesis) can increase the risk of GERD.
Conclusion
While diabetes primarily affects blood sugar regulation, it may affect the digestive system too. Conditions like gastroparesis, diabetic neuropathy, IBS, and GERD may arise or worsen in individuals with diabetes. To address and manage these digestive issues, individuals with diabetes should work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive care plan.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Debunking 5 Common Myths About Diabetes
Family history increases risk of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle factors like obesity, prediabetes, PCOS, gestational diabetes, and age above 45 also contribute. To lower type 2 diabetes risk, maintain a healthy weight through exercise and a balanced diet.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
The Role of Hydration in Blood Sugar Management
Managing diabetes involves more than just diet and medicine; hydration plays a crucial role as well. Staying well-hydrated can prevent dehydration caused by high blood sugar, and may even reduce the risk of diabetes. Incorporating adequate hydration into your lifestyle is a practical step towards effective diabetes management. To receive holistic support in your diabetes management journey, consider enrolling in the Apollo Super 6 programme.
Diabetes Management
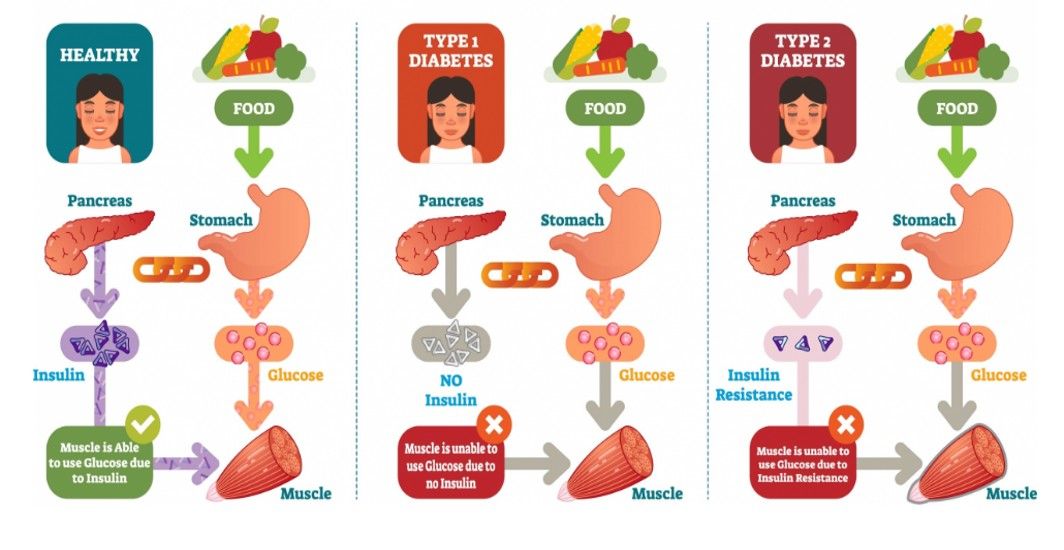
Understanding the Various Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant). Recognizing the type of diabetes you have and understanding its management strategy is crucial for effective control. Regular health check-ups, blood sugar monitoring, a healthy diet, and an active lifestyle form the bedrock of diabetes management. Empower yourself with the right knowledge and approach to live a healthy life with diabetes.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Debunking 5 Common Myths About Diabetes
Family history increases risk of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle factors like obesity, prediabetes, PCOS, gestational diabetes, and age above 45 also contribute. To lower type 2 diabetes risk, maintain a healthy weight through exercise and a balanced diet.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
The Role of Hydration in Blood Sugar Management
Managing diabetes involves more than just diet and medicine; hydration plays a crucial role as well. Staying well-hydrated can prevent dehydration caused by high blood sugar, and may even reduce the risk of diabetes. Incorporating adequate hydration into your lifestyle is a practical step towards effective diabetes management. To receive holistic support in your diabetes management journey, consider enrolling in the Apollo Super 6 programme.

Diabetes Management
Understanding the Various Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant). Recognizing the type of diabetes you have and understanding its management strategy is crucial for effective control. Regular health check-ups, blood sugar monitoring, a healthy diet, and an active lifestyle form the bedrock of diabetes management. Empower yourself with the right knowledge and approach to live a healthy life with diabetes.


