Diabetes Management
A Step-By-Step Guide To Using A Glucometer
4 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 14 March 2023, Updated on - 14 November 2025
Share this article
0
2 likes

Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is a vital aspect of diabetes management. It can help you determine what kind of food and activities cause an increase in your blood sugar. It can also be beneficial in preventing any long-term complications. While you can get your blood sugar tested at a diagnostic lab, it can be quite inconvenient and expensive, especially if you have to do it frequently. This is where glucometers come in handy. A glucometer is a portable device that enables you to easily check your blood glucose levels at home. Read on to learn more about how to use a glucometer at home.
Supplies Required To Use A Glucometer
Before you start with the process of checking your blood sugar using a glucometer, make sure you have the necessary supplies within reach. These include:
- Soap and water or an alcohol prep pad
- A test strip
- A lancing device with a new lancet
- A notepad and pen to record results (in case your glucometer does not have the feature to store readings)
How To Use A Glucometer?
Every glucometer comes with its own instruction manual. However, these are some general steps you can follow to use almost all glucometers.
1. Clean your hand thoroughly using either soap and water or an alcohol prep pad. Make sure your skin dries completely before you begin as moisture can dilute the blood sample you take from your finger. Also, don’t blow on the fingers to dry them as this can introduce germs.

2. Turn your glucometer on by inserting a test strip. Check the glucometer's screen, which will alert you when it's time to add the blood sample to the strip.

3. Pierce the side of your fingertip, right next to your fingernail using the lancing device. Piercing this spot hurts less than piercing the pad of your finger. Squeeze the pierced spot to produce an adequately-sized blood drop.
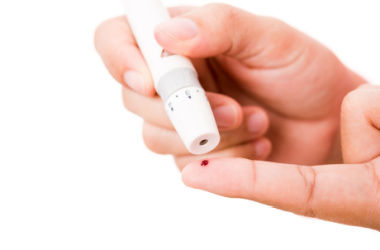
4. Place the blood sample on the test strip.
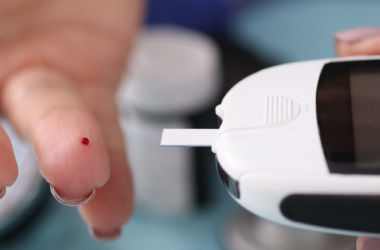
5. Use an alcohol pad to stop the bleeding by pushing it against the pierced skin and wait a few seconds for your glucometer to display the results.
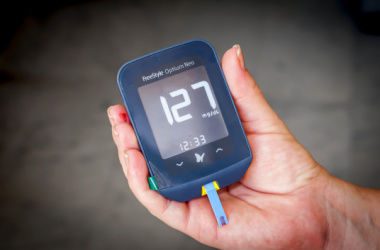
6. Record your results as it will make it easier for your doctor to create a suitable treatment plan. You can either note down the readings in a notepad or sync your glucometer to your smartphone app to record the readings. Some devices also come with a feature that lets you store the readings on the device itself.

7. Carefully dispose of the used test strips and lancet.
How To Minimise Lancet Pain?
If you feel that using a glucometer is painful, then you can try out the following tips to minimise the pain:
- Use a new lancet: While it’s essential to use a fresh lancet for hygiene purposes, that’s not the only reason. Repeatedly using the same lancet can dull it, making the pokes more painful.
- Change the lancet thickness: You can try modifying the lancet thickness and see if it works better for you. For instance, a 30-gauge lancet may work better for you than a 21-gauge lancet.
- Adjust the lancing device setting: You can change the settings of your lancing device to make the poke less deep. Try setting it to a 2 or 3 and work your way up to a setting that provides a good-size sample with minimal pain.
- Alternate positions: Keep changing the location of the pokes. Use the right side of a finger once then switch to the left side before moving on to another finger and so on. This will give a spot time to heal before you poke it again.
Using a glucometer is quite easy. You can always ask your healthcare provider for advice if you feel like something isn’t working right for you. Just make sure to follow the instructions given by your doctor regarding the frequency and timings of blood sugar checks. If you have more questions,
Consult Apollo's Expert Diabetologists
Medically reviewed by Dr Sonia Bhatt.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Breastfeeding Tips for Mothers with Diabetes
Breastfeeding while managing diabetes need not be a daunting task. With careful planning, it can be a beneficial journey for both mother and baby. Regular meals, smart snacking, and consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels are key strategies for successful breastfeeding. Remember, every journey is unique, so personalised advice from doctors is crucial. And remember, even as you navigate through this phase, the Apollo Super 6 programme is here to help you lead an active and healthy lifestyle.

Diabetes Management
The Impact of Intermittent Fasting on Blood Sugar Control
Intermittent fasting, renowned for weight loss, reveals potential in blood sugar control. Studies indicate improved insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation, and weight loss benefits. Caution is vital, particularly for those with diabetes, necessitating professional consultation. Its impact varies, demanding personalised guidance. While promising blood sugar regulation, prudent consideration and individualised advice is crucial for safe implementation.
Diabetes Management
How to Test for Insulin Resistance
To test for insulin resistance as a diabetic, common methods include fasting glucose and insulin tests. These help assess how your body manages blood sugar. Pay attention to risk factors like age, family history, and lifestyle. If diagnosed, focus on lifestyle changes—adopt a balanced diet, engage in regular exercise, and monitor your blood sugar levels. Early detection is key to effective management, empowering you to make informed choices for better health. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalised guidance.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Breastfeeding Tips for Mothers with Diabetes
Breastfeeding while managing diabetes need not be a daunting task. With careful planning, it can be a beneficial journey for both mother and baby. Regular meals, smart snacking, and consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels are key strategies for successful breastfeeding. Remember, every journey is unique, so personalised advice from doctors is crucial. And remember, even as you navigate through this phase, the Apollo Super 6 programme is here to help you lead an active and healthy lifestyle.

Diabetes Management
The Impact of Intermittent Fasting on Blood Sugar Control
Intermittent fasting, renowned for weight loss, reveals potential in blood sugar control. Studies indicate improved insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation, and weight loss benefits. Caution is vital, particularly for those with diabetes, necessitating professional consultation. Its impact varies, demanding personalised guidance. While promising blood sugar regulation, prudent consideration and individualised advice is crucial for safe implementation.

Diabetes Management
How to Test for Insulin Resistance
To test for insulin resistance as a diabetic, common methods include fasting glucose and insulin tests. These help assess how your body manages blood sugar. Pay attention to risk factors like age, family history, and lifestyle. If diagnosed, focus on lifestyle changes—adopt a balanced diet, engage in regular exercise, and monitor your blood sugar levels. Early detection is key to effective management, empowering you to make informed choices for better health. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalised guidance.




