Diabetes Management
Jaggery and Diabetes: Safe Substitute for Sugar?
2 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 17 July 2024
Share this article
0
0 like
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Managing diabetes involves careful attention to your diet, including choices about sweeteners. When managing diabetes, making informed decisions about sugar alternatives like jaggery is crucial. It's always best to be informed before making dietary changes, so let's delve deeper into this topic.
Understanding Jaggery and Its Effects on Blood Sugar
Jaggery, while often hailed as a healthier alternative to refined sugar, is not necessarily a safe option for individuals with diabetes. This is primarily due to its high Glycaemic Index (GI) of 84.4, which is akin to or even higher than refined sugar. Consuming high GI foods can lead to rapid spikes in blood glucose levels, posing a risk for diabetics.
Examining the Components of Jaggery
It's crucial to understand that jaggery is mainly composed of sucrose, similar to regular sugar. It contains about 65-85% sucrose that breaks down into glucose and fructose in our bodies. Moreover, jaggery is calorie-dense, offering around 375 calories per 100 grams.
Busting Misconceptions and Focusing on Blood Sugar Management
While it's true that jaggery contains minerals not found in refined sugar, the quantities are too minor to offer significant health benefits. Importantly, these minerals do not negate the impact of jaggery on blood glucose levels. For individuals with diabetes, the primary aim is to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Substituting sugar with jaggery doesn't assist in achieving this objective.
Considering Alternatives and Portion Control
If you still wish to consume jaggery, it should be taken infrequently and in small amounts. Always seek advice from your doctor or dietitian for personalised guidance. Instead of jaggery, you could consider natural sugar-free sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit extract, small quantities of low GI fruits for sweetness, and an overall balanced diet rich in fibre and protein.
Living well with diabetes is about making informed choices. Keeping this in mind, the Apollo Super 6 programme has been designed to help individuals manage type 2 diabetes through lifestyle modifications and personalised support. From the guidance received in this programme, you can make better dietary decisions and lead a healthier life.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
Diabetes Management
How To Bring Down The HbA1c Level?
To lower the HbA1c levels, diabetics should dollow a diet with low glycemic index foods and manage portion sizes. They should engage in regular exercise to manage weight and improve insulin sensitivity. Diabetics should also consume a fiber-rich diet to regulate blood sugar levels. Besides, taking prescribed oral hypoglycemic medications and monitoring blood glucose levels at home can bring down HbA1c levels.
Diabetes Management
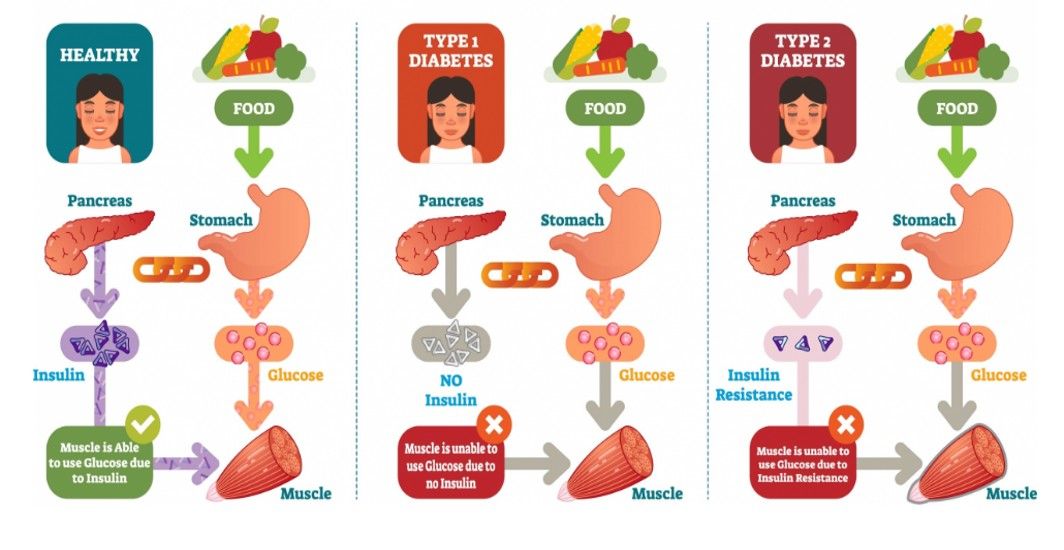
Understanding the Various Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant). Recognizing the type of diabetes you have and understanding its management strategy is crucial for effective control. Regular health check-ups, blood sugar monitoring, a healthy diet, and an active lifestyle form the bedrock of diabetes management. Empower yourself with the right knowledge and approach to live a healthy life with diabetes.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
What is the Difference between Diabetes Insipidus and Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes Insipidus is a rare condition where the body can't properly regulate fluid balance, leading to excessive thirst and urination. Diabetes Mellitus, on the other hand, is a more common condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insulin dysfunction, leading to various health complications. Both conditions share the name "diabetes" but have distinct causes and symptoms.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
How To Bring Down The HbA1c Level?
To lower the HbA1c levels, diabetics should dollow a diet with low glycemic index foods and manage portion sizes. They should engage in regular exercise to manage weight and improve insulin sensitivity. Diabetics should also consume a fiber-rich diet to regulate blood sugar levels. Besides, taking prescribed oral hypoglycemic medications and monitoring blood glucose levels at home can bring down HbA1c levels.

Diabetes Management
Understanding the Various Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant). Recognizing the type of diabetes you have and understanding its management strategy is crucial for effective control. Regular health check-ups, blood sugar monitoring, a healthy diet, and an active lifestyle form the bedrock of diabetes management. Empower yourself with the right knowledge and approach to live a healthy life with diabetes.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes Management
What is the Difference between Diabetes Insipidus and Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes Insipidus is a rare condition where the body can't properly regulate fluid balance, leading to excessive thirst and urination. Diabetes Mellitus, on the other hand, is a more common condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insulin dysfunction, leading to various health complications. Both conditions share the name "diabetes" but have distinct causes and symptoms.

