Skin Care
Psoriasis: Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & Prevention
7 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 05 October 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
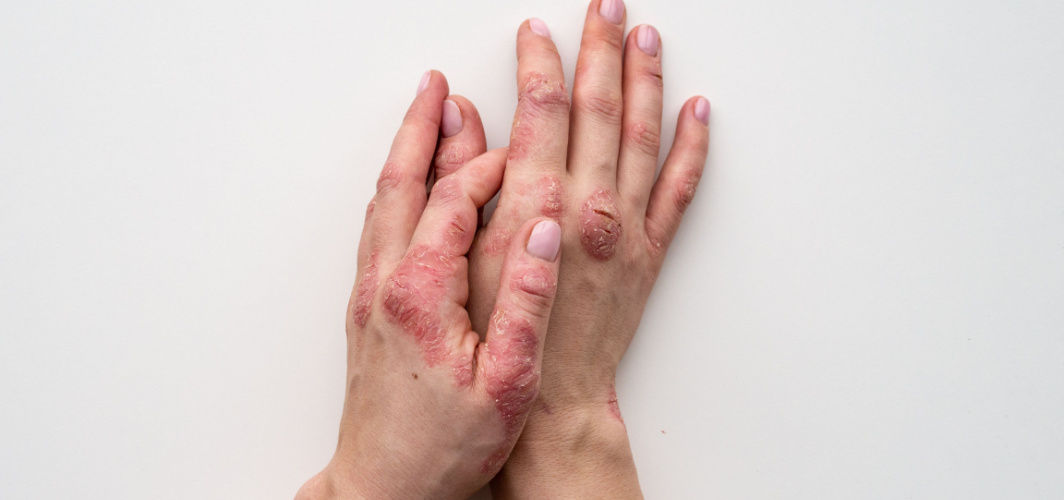
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterised by red, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin. The exact cause of psoriasis is still unknown, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disease, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. In this blog, we will delve into the multifaceted realm of Psoriasis, providing you with a deep understanding of its definition, underlying causes, wide-ranging symptoms, available psoriasis treatments, and effective prevention strategies to empower you in managing this complex skin condition.
Types of Psoriasis
In this section, we will delve into the different types of Psoriasis.
1. Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is the most common type, accounting for about 80% of all cases. It is characterised by raised, inflamed patches covered with silvery-white scales. These patches often develop on the elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp. Some symptoms of Plaque Psoriasis include:
- Red, raised patches covered with thick scales
- Itching and burning sensations
- Dry and cracked skin that may bleed
- Nail changes, such as pitting or ridges
2. Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate Psoriasis is a type of psoriasis that often appears as small, drop-shaped lesions on the skin. It is usually triggered by a bacterial or viral infection, such as strep throat. This type of psoriasis is more common in children and young adults but can affect people of all ages.
Symptoms of guttate psoriasis include small, red, scaly spots on the skin. These spots are typically found on the trunk, limbs, and scalp. They may be itchy and can sometimes be accompanied by a sore throat or fever if an infection is present.
3. Inverse Psoriasis
Inverse Psoriasis is a type of psoriasis that affects the skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts. Unlike other forms of psoriasis, it appears as smooth, red patches without the typical scaling. This can make it harder to diagnose and differentiate from other skin conditions.
The exact cause of Inverse Psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be related to an overactive immune system. Risk factors include obesity, family history of psoriasis, and certain medications. Some symptoms include:
- Smooth, red patches of skin in areas like armpits, groin, and under the breasts
- The skin may be shiny and appear moist
- Itching and discomfort in affected areas
- Increased sensitivity to friction and sweat
4. Pustular Psoriasis
Pustular Psoriasis is characterised by the presence of pus-filled blisters or pustules on the skin. The causes of Pustular Psoriasis can vary from person to person, but certain triggers may contribute to flare-ups. These triggers can include:
- Infections
- Certain medications, such as lithium or corticosteroids
- Exposure to certain chemicals or irritants
- Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or menopause
Symptoms of Pustular Psoriasis include:
- Pus-filled blisters or pustules
- Red and inflamed skin surrounding the pustules
- Itching or burning sensation
- Skin tightness or tenderness
- Flaking or scaling of the skin, which can lead to silver-white patches
5. Erythrodermic Psoriasis
Erythrodermic Psoriasis is a severe form of psoriasis that affects the entire body. It is a rare condition, accounting for only about 2% of all psoriasis cases. Certain factors can trigger or exacerbate flare-ups of erythrodermic psoriasis, including:
- Stress
- Infections
- Withdrawal from systemic corticosteroids
This type of psoriasis is characterised by widespread redness, scaling, and inflammation of the skin. The symptoms can be intense and may include:
- Itching
- Burning
- Pain
- Peeling of the skin
Common Triggers for Psoriasis Flare-ups
While the exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, several common triggers can lead to flare-ups. Understanding these triggers can help individuals manage their condition effectively.
1. Stress and Emotional Factors
Stress plays a major role in triggering psoriasis flare-ups. Emotional stress, such as anxiety or depression, can lead to increased inflammation and worsen the symptoms.
2. Cold Weather and Dry Skin
Psoriasis tends to worsen during cold weather due to low humidity levels. Cold temperatures and dry air can cause the skin to become dry and flaky, leading to an increase in psoriasis symptoms.
3. Infections and Illnesses
Certain infections, such as strep throat or respiratory infections, can trigger or worsen psoriasis flare-ups. It is important to promptly treat any infections to minimise the impact on psoriasis.
4. Certain Medications
Some medications, such as lithium, antimalarials, and beta-blockers, have been known to aggravate psoriasis symptoms. It is important to discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
5. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can affect the immune system and trigger psoriasis flare-ups. Women with psoriasis need to be aware of these hormonal changes and work closely with their healthcare provider to manage their condition effectively.
Managing Psoriasis Symptoms and Flare-ups
Treating and managing psoriasis symptoms and flare-ups typically involves a multidisciplinary approach.
1. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defence in managing scalp psoriasis symptoms. These medications can be applied directly to the affected areas of the skin. Common types of topical treatments include:
- Corticosteroids
- Vitamin D analogues
- Coal tar preparations
- Salicylic acid
These treatments help reduce inflammation, alleviate itching, and slow down the growth of skin cells.
2. Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under medical supervision. There are different types of phototherapy, including UVB therapy and PUVA therapy.
Phototherapy helps slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation. It can be an effective treatment option for individuals with moderate to severe psoriasis.
3. Systemic Medications
Systemic medications are taken orally or by injection. They work throughout the body to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system's response that triggers psoriasis. Examples of systemic medications for scalp psoriasis include:
- Methotrexate
- Cyclosporine
- Acitretin
4. Biologic Drugs
Biologic drugs are a newer class of medications that target specific parts of the immune system involved in psoriasis. They are usually given by injection or infusion.
Biologics can be highly effective in managing moderate to severe psoriasis symptoms when other treatments have failed.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Psoriasis
In addition to medical psoriasis treatments prescribed by your doctor, making certain lifestyle changes can also be beneficial.
1. Dietary Suggestions
Some dietary adjustments to manage psoriasis are:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of psoriasis and can worsen symptoms.
- Include Anti-inflammatory Foods: Incorporate foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet to reduce inflammation in the body.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can trigger psoriasis flare-ups, so it's best to drink in moderation or avoid it altogether.
- Reduce Processed Foods: These can contribute to inflammation in the body, so try to minimise their intake.
2. Regular Exercise and Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity can contribute to overall well-being.
- Engage in Low-impact Exercises: Activities like swimming, yoga, or walking can help reduce stress and inflammation.
- Maintain a Regular Exercise Routine: Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days of the week to improve overall health and manage stress levels.
3. Stress Management Techniques
Stress is a common trigger for psoriasis flare-ups.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate practices like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or mindfulness techniques into your daily routine to manage stress.
- Engage in Hobbies or Activities: Doing things that bring you joy can help distract from psoriasis-related stressors.
- Seek Support: Connect with others who have psoriasis through support groups or online communities to share experiences and coping strategies.
Preventing Psoriasis Flare-ups and Promoting Overall Skin Health
In this section, we will delve into how you can prevent psoriasis flare-ups and promote overall skin health.
1. General Skin Care Tips
Some general skin care tips include:
- Keep your skin moisturised by using a good quality moisturiser regularly.
- Avoid harsh soaps and opt for gentle, fragrance-free cleansers.
- Use a humidifier in your home to add moisture to the air.
2. Avoiding Triggers
Identify and avoid triggers that can worsen your psoriasis symptoms. Protect your skin from injuries, such as cuts and scrapes, as they can trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
3. Regular Check-ups with a Dermatologist
Visit your dermatologist regularly for check-ups and to discuss any concerns or changes in your condition. Stay updated on the latest treatment options and guidelines for managing scalp psoriasis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that can cause physical discomfort and impact quality of life. Understanding the causes, recognising the symptoms, and seeking proper psoriasis treatment can greatly improve the management of this condition. By adopting a holistic approach that includes medical interventions and lifestyle modifications, individuals with psoriasis can lead fulfilling lives while keeping their symptoms under control.
Skin Care
Consult Top Dermatologists
View AllFrequently Asked Questions
Can psoriasis be cured?
Can psoriasis be cured?
Is psoriasis contagious?
Is psoriasis contagious?
Can psoriasis affect other parts of the body besides the skin?
Can psoriasis affect other parts of the body besides the skin?
Can stress worsen psoriasis symptoms?
Can stress worsen psoriasis symptoms?
How is psoriasis treated?
How is psoriasis treated?
Leave Comment
Recommended for you

Skin Care
Can Your Deodorant Cause Dark Underarms?
Dark underarms is a common skin problem that becomes bothersome during summers when you wear those cut-sleeves. However, it is possible to get rid of them effectively.
Skin Care
Is Your Derma Roller Really Effective?
A derma roller is a handheld skin care device that contains multiple rows of tiny needles. The article explores its uses and benefits in detail below.

Skin Care
Are Hypoallergenic Cosmetic Products Good For You?
Hypoallergenic cosmetic products contain substances that are less likely to cause allergic reactions. Read to know more.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Recommended for you

Skin Care
Can Your Deodorant Cause Dark Underarms?
Dark underarms is a common skin problem that becomes bothersome during summers when you wear those cut-sleeves. However, it is possible to get rid of them effectively.

Skin Care
Is Your Derma Roller Really Effective?
A derma roller is a handheld skin care device that contains multiple rows of tiny needles. The article explores its uses and benefits in detail below.

Skin Care
Are Hypoallergenic Cosmetic Products Good For You?
Hypoallergenic cosmetic products contain substances that are less likely to cause allergic reactions. Read to know more.

