Orthopedic Conditions
Shoulder Arthroscopy Surgery: Procedure and Recovery Time
7 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 25 August 2023, Updated on - 01 September 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
Shoulder arthroscopy, also known as arthroscopic shoulder surgery, is a minimally invasive procedure that allows doctors to diagnose and treat shoulder conditions. In India, shoulder arthroscopy is gaining popularity due to its effectiveness and less post-operative downtime compared with traditional open surgeries. This procedure has revolutionized the field of orthopaedics and has become the gold standard for many shoulder conditions. In this article, you will understand the procedure in detail, what to expect during and after surgery, recovery time, and other factors.
What Is Shoulder Arthroscopy?
Shoulder arthroscopy is a surgical procedure that allows doctors to examine and treat various shoulder conditions. The main goals of shoulder arthroscopy are to alleviate shoulder pain and improve overall quality of life. Shoulder Arthroscopy is conducted through:
- Preparation: The patient is positioned and given anaesthesia, often regional or general, to ensure comfort during the procedure.
- Incision: Small incisions, about the size of a buttonhole, are made around the shoulder joint. These incisions allow access to the arthroscope and surgical instruments.
- Arthroscope Insertion: An arthroscope, a small camera connected to a monitor, is inserted through one of the incisions. This provides a clear visual of the inside of the joint.
- Diagnostic Examination: The surgeon examines the joint's structures, including bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. Any abnormalities or issues are identified during this phase.
Indications for Shoulder Arthroscopy Surgery
Common Shoulder Conditions that Require Arthroscopy:
- Rotator cuff tears
- Shoulder impingement
- Shoulder instability
- Labral tears
Symptoms that may Indicate the Need for Surgery:
- Persistent pain that does not respond to conservative treatments
- Loss of range of motion in the shoulder
- Weakness or instability in the shoulder joint
- Difficulty performing daily activities or sports-related movements
- Recurring episodes of shoulder dislocation or subluxation.
Imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI scans and ultrasound may be used to aid in the diagnosis of shoulder conditions and determine the extent of the injury.
Medications to Avoid Before Surgery
Certain medications can interfere with the surgical process or increase the risk of complications. Here are some common medications that may need to be stopped temporarily:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Blood-thinning medications like warfarin or clopidogrel
- Herbal supplements such as ginkgo biloba, garlic, and ginger
Prior Tests and Examinations
Necessary tests and examinations prior to the procedure include the following:
- Blood tests
- X-rays
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
-
Physical examination
Shoulder Arthroscopy Procedure
Preparing for Shoulder Arthroscopy Surgery
Your doctor may ask you to fast for at least 6-8 hours before the surgery. Further, do not forget to inform your surgeon about any allergies or medications you are currently taking.
Anaesthesia Options
During shoulder arthroscopy surgery, the surgeon may use special instruments to repair damaged tissues, remove bone spurs or loose bodies. The procedure is typically performed under general anaesthesia or regional anaesthesia.
- General Anaesthesia: Under general anaesthesia, you will be completely unconscious throughout the surgery. This option allows for a painless and comfortable experience during the procedure.
- Regional Anaesthesia: Regional anaesthesia involves numbing only a specific area where the surgery will be performed. This can be achieved through a nerve block or an injection around the shoulder joint.
Regional anesthesia may have fewer risks compared with general anaesthesia, and can provide effective pain control during and after the surgery.
Surgical Steps of Shoulder Arthroscopy
The use of advanced technologies and techniques allows for shorter recovery times and better outcomes for patients. Specific steps involved in repairing common shoulder conditions include the following:
- Bankart repair for shoulder dislocation: In this procedure, the torn ligaments and tissues that cause recurrent shoulder dislocations are reattached to the bone. This helps stabilize the joint and prevent further dislocations.
- Rotator cuff repair for rotator cuff tear: When the tendons of the rotator cuff are torn, they can be repaired using arthroscopy.
- SLAP repair for labral tears: Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior or SLAP procedure repairs tears in the labrum. The torn labrum is reattached to the bone using sutures, helping to improve stability and reduce pain.
Potential Risks and Complications
Common risks and complications associated with shoulder arthroscopy include the following:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Nerve or blood vessel damage
- Stiffness
- Blood clots
To minimise the risks associated with shoulder arthroscopy, your doctor will take certain precautions, such as:
- Ensuring proper sterilisation techniques
- Using modern imaging techniques to visualise the shoulder joint accurately
- Employing skilled surgeons
- Providing clear post-operative instructions for wound care and rehabilitation exercises
With proper precautions and skilled medical professionals, the chances of complications can be significantly reduced.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Shoulder Arthroscopy Surgery
1. Pain Management Strategies
- Take prescribed pain medication as directed by your doctor.
- Apply ice packs to the shoulder for 20 minutes at a time, several times a day, to reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, if approved by your doctor.
2. Dressing Care and Incision Site Hygiene
- Keep the dressing clean and dry.
- Avoid getting the incision site wet until your doctor allows you to shower.
- Gently wash the area around the incision with mild soap and water, pat dry and cover with a clean bandage.
Rehabilitation Exercises and Physical Therapy
After undergoing shoulder arthroscopy surgery, rehabilitation exercises and physical therapy play a crucial role in your recovery.
1. Post-Operative Exercises
- Post-operative exercises help restore shoulder strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- They also aid in reducing pain and swelling, preventing stiffness, and promoting healing.
- Regular exercise can improve the success of your surgery and prevent complications.
2. Specific Exercises for Different Stages of Recovery
- In the initial phase, you may start with gentle range-of-motion exercises to prevent stiffness.
- As you progress, strengthening exercises targeting the rotator cuff muscles and other shoulder muscles are introduced.
3. Duration and Frequency of Physical Therapy Sessions
- The duration and frequency of physical therapy sessions depend on individual factors such as the extent of surgery, overall health, and progress.
- Initially, therapy sessions may be more frequent, gradually tapering off as you regain strength and mobility.
- On average, physical therapy sessions may last for several weeks to a few months.
Expected Recovery Time
On average, it may take around 3 to 6 months to fully recover.
Factors Affecting the Recovery Period
- The extent of the shoulder injury or condition being treated.
- Individual factors such as age, overall health, and adherence to post-operative care instructions.
- The presence of any underlying medical conditions that may impact healing.
Red Flags and Signs
- If you experience severe pain, increased swelling, redness, or warmth around the surgical site, it could indicate an infection or other complications.
- Numbness or tingling in your arm or hand, difficulty moving your fingers, or weakness could be signs of nerve damage.
- It is essential to report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider promptly.
Summary
If you are suffering from a shoulder condition, consult with your orthopedic specialist to determine if shoulder arthroscopy surgery is the right option for you. Remember, each case is unique, and your doctor will guide you through the entire process, ensuring the best possible outcome for your shoulder health.
If you have more doubts on the topic, consult our specialists.
FAQs
Q. Is shoulder arthroscopy a painful procedure?
Shoulder arthroscopy is performed under anesthesia, so you would not feel any pain during the surgery.
Q. Are there any risks or complications associated with shoulder arthroscopy?
Like any surgical procedure, shoulder arthroscopy carries some risks. These can include infection, bleeding, nerve injury, stiffness, and blood clots.
Q. Can I drive after shoulder arthroscopy?
It is generally recommended to avoid driving for at least a week after shoulder arthroscopy, or until you have regained full control and strength in your arm.
Q. Can I return to sports or heavy lifting after shoulder arthroscopy?
It depends on the type of sport or activity and the extent of your surgery. Your surgeon will guide you on when it is safe to resume these activities.
Q. How long do the effects of shoulder arthroscopy last?
The effects of shoulder arthroscopy can vary depending on the underlying condition being treated, as well as individual factors such as lifestyle and adherence to post-operative care.
Orthopedic Conditions
Consult Top Orthopaedicians
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
Orthopedic Conditions
Neck Rotation To Shoulder Shrugs, 7 Effective Exercises For Neck Pain Relief
Neck pain exercises are meant to alleviate pain and discomfort in the neck and shoulder area. These exercises can improve flexibility and strength of the neck and shoulder muscles, thereby, preventing future neck pain.

Orthopedic Conditions
Is Sciatica Causing the Sharp Pain in the Lower Back and Leg?
Any irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve can result in sharp pain and weakness in the lower back and the back of the leg, which is medically known as sciatica.
Orthopedic Conditions
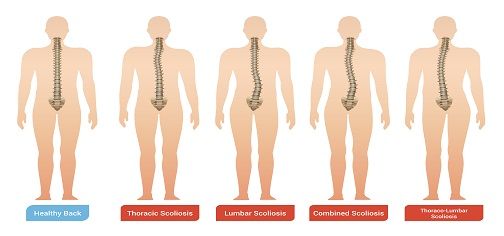
5 Facts About Scoliosis Every Parent Should Know
Scoliosis is the most prevalent among children and adolescents, usually occurring in children aged 10 to 15. While most scoliosis cases are mild, the condition can worsen and lead to respiratory issues.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

How to Keep Your Bones Strong and Healthy Naturally
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Orthopedic Conditions
Neck Rotation To Shoulder Shrugs, 7 Effective Exercises For Neck Pain Relief
Neck pain exercises are meant to alleviate pain and discomfort in the neck and shoulder area. These exercises can improve flexibility and strength of the neck and shoulder muscles, thereby, preventing future neck pain.

Orthopedic Conditions
Is Sciatica Causing the Sharp Pain in the Lower Back and Leg?
Any irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve can result in sharp pain and weakness in the lower back and the back of the leg, which is medically known as sciatica.

Orthopedic Conditions
5 Facts About Scoliosis Every Parent Should Know
Scoliosis is the most prevalent among children and adolescents, usually occurring in children aged 10 to 15. While most scoliosis cases are mild, the condition can worsen and lead to respiratory issues.



