General Health
Sweating Profusely? Hyperhidrosis Could be the Reason
4 min read
By Apollo 24/7, Published on - 22 October 2021, Updated on - 04 May 2023
Share this article
0
47 likes
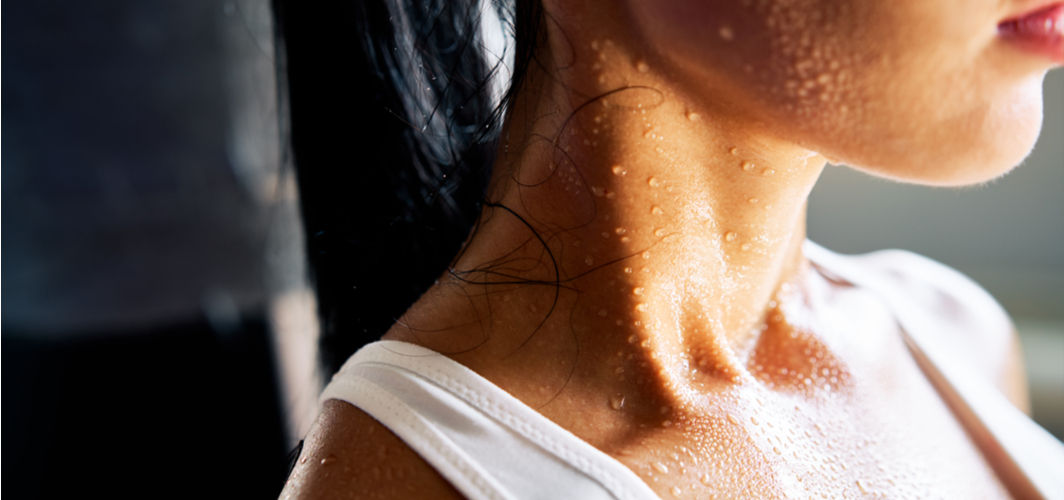
The human body has around 2 to 4 million sweat glands that release sweat to maintain body temperature. There are two types of sweat glands: eccrine and apocrine sweat glands. While the eccrine glands open directly on top of the skin surface, the apocrine glands open into the hair follicle. It is normal to sweat in hot weather or after a session of vigorous exercise. However, if one sweats excessively even when their body is at rest, it may indicate an underlying condition called hyperhidrosis.
Signs of hyperhidrosis
People suffering from hyperhidrosis may experience excessive sweating under the arms, around the back and neck or entire body. The person may need to change their clothes often due to extreme sweating. Other symptoms may include:
- Itching and inflammation in the areas with excessive sweat release
- Bad body odour due to mixing of bacteria with the sweat
- Pale, discoloured, cracked or wrinkled skin
- Soggy and soft skin (maceration of skin)
- Sweating even during sleep
Types of hyperhidrosis
There are two different types of hyperhidrosis - primary focal hyperhidrosis and secondary/ generalized hyperhidrosis.
- Primary focal hyperhidrosis: Focal hyperhidrosis does not indicate an underlying medical condition and begins developing during childhood or adolescence. It usually occurs due to mutation (change) in some genes and therefore, can be passed onto future generations. In this type of hyperhidrosis, the person experiences sweating in limited parts of the body such as underarms, hands, feet, or forehead.
- Secondary/generalized hyperhidrosis: Generalized hyperhidrosis is usually seen in adulthood. It is characterized by profuse sweating from the entire body, which occurs either due to an underlying medical condition or due to a side effect of some medication.
What causes excessive sweating?
The causes of primary focal hyperhidrosis include:
- Foods with strong odour such as lemon, coffee, chocolate, peanut butter and strong spices
- Stress and anxiety
- A hot and humid atmosphere
The causes of generalized hyperhidrosis include:
- Infectious diseases such as tuberculosis
- Chronic metabolic conditions such as obesity, hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland), diabetes, hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), pituitary disease and gout
- Physiologic changes such as menopause
- Medications such as some antidepressants, hypoglycemics (insulin), and selective estrogen receptor modulators
- Tumours and cancers such as pheochromocytoma (a tumour in the adrenal glands), carcinoid (slow-growing cancers), leukaemia and lymphomas
- Excessive use of alcohol
- Neurologic diseases such as Arnold-Chiari malformation, Parkinson disease, and dysautonomia
How is hyperhidrosis managed?
There is no cure for focal hyperhidrosis but the treatment aims at reducing the symptoms. The treatment of secondary hyperhidrosis depends on the underlying cause. Some of the common treatment measures include:
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe certain medicines such as anticholinergic drugs to improve the effectiveness of antiperspirants and antidepressants. These medicines decrease the production of sweat by reducing stress.
- Botox injections: In this therapy, botulinum toxin (botox) is injected into an overactive nerve to stop the production of sweat for a limited period.
- Iontophoresis: In this therapy, a weak electric current is passed through the water onto a wet pad to reduce the activity of sweat glands.
- Surgery: In severe cases when other treatments do not provide relief, doctors may surgically remove the overactive sweat glands.
- Homecare: Selfcare measures that may help manage hyperhidrosis include:
- Avoid wearing tight and synthetic clothes such as nylon and lycra. Instead, opt for breathable fabric such as cotton clothing.
- Shower as soon as you sweat profusely.
- Wear loose-fitted clothes to allow air to pass through, thereby reducing sweating.
- Avoid wearing shoes that enclose the feet as they can increase sweating.
- Wear cotton socks and foot powders as they help absorb moisture and keep the feet dry. Change them at least twice a day if required.
- Avoid consumption of alcohol and spicy foods as it makes the sweating worse.
- Rather than using deodorants, use strong antiperspirants.
- Use armpit or sweat shields to protect the spoiling of clothes.
- Do not use harsh soaps that contain fragrance. Use milder soaps with oils to keep the moisture of the skin intact.
Conclusion
Hyperhidrosis is the result of overactive sweat glands, which can occur due to medical conditions such as thyroid disorders, tuberculosis, and malignancies. It can result in excessive sweating, itching, bad odour, discoloured patches, wrinkles and cracks on the skin. The condition can be managed by wearing cotton clothes, using medicated antiperspirants, avoiding alcohol consumption, etc. to reduce or stop the release of sweat.
Consult a general physician if you are experiencing symptoms of hyperhidrosis.
General Health
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
.jpg?tr=q-80)
General Health
The Link Between UTI And Sexual Activity
Sexual activity can increase the risk of bacteria entering the urinary tract, potentially leading to an infection. UTIs are more prevalent in women, with approximately 1 in 5 adult women experiencing a UTI at some point. Women have a shorter urethra than men, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder due to their anatomy.
General Health
Top STD Test Packages For Couples
Explore top STD test packages for couples. Ensure safety and peace of mind with reliable, confidential, and comprehensive sexual health screenings.
General Health
Flu Vaccine: When Is The Right Time To Take It?
The common flu occurring in most people during the flu season can be prevented through the flu vaccine. The flu vaccine can be taken all through the year, particularly before or during the flu season, under a doctor's guidance.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Science-backed Home Remedies for Burns and Blisters
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you
.jpg?tr=q-80)
General Health
The Link Between UTI And Sexual Activity
Sexual activity can increase the risk of bacteria entering the urinary tract, potentially leading to an infection. UTIs are more prevalent in women, with approximately 1 in 5 adult women experiencing a UTI at some point. Women have a shorter urethra than men, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder due to their anatomy.

General Health
Top STD Test Packages For Couples
Explore top STD test packages for couples. Ensure safety and peace of mind with reliable, confidential, and comprehensive sexual health screenings.

General Health
Flu Vaccine: When Is The Right Time To Take It?
The common flu occurring in most people during the flu season can be prevented through the flu vaccine. The flu vaccine can be taken all through the year, particularly before or during the flu season, under a doctor's guidance.