Diabetes Management
Balancing Diabetes and Nutrition: The Power of Superfoods
2 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 17 April 2024
Share this article
0
0 like
.jpg?tr=q-80)
Diabetes management isn't just about taking your prescribed medication, it's also about embracing a balanced diet. Certain foods, often dubbed as "diabetes superfoods," can play a pivotal role in managing your blood sugar levels. So what are diabetes superfoods? Diabetes superfoods are nutritionally dense foods that come packed with fibre, protein, antioxidants and healthy fats. They can slow down sugar absorption, stabilise blood sugar levels and provide essential nutrients to ward off diabetes complications. Here's a rundown of these nutritional powerhouses and how they can help in your diabetes management routine.
Diabetes Superfoods
- Beans: Beans are loaded with fibre, protein and vital minerals like magnesium, potassium and folate. Being low in fat and carbohydrates, they can help manage blood sugar levels.
- Dark green leafy vegetables: Leafy vegetables like spinach, kale and cabbage are low in carbohydrates and calories but rich in vitamins A, C, E, K, calcium, iron, potassium and protein. They can assist in managing blood sugar levels whilst providing essential nutrients for overall health.
- Fish: Salmon, sardines, mackerel, trout and albacore tuna are high in omega-3 fatty acids. Packed with protein and healthy fats, they aid in reducing the risk of heart disease and inflammation.
In the Fruit Basket
- Citrus fruits: Fruits such as oranges, lemons, limes and grapefruit are high in soluble fibre, vitamin C, folate and potassium. Consuming these fruits can slow down sugar absorption and regulate blood sugar levels.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries and blackberries are abundant in antioxidants, vitamins C and K, manganese, potassium and fibre. These fruits can satisfy sweet cravings whilst managing blood sugar levels.
Superfoods in Your Kitchen
- Sweet potatoes: This is a nutritious food that can satisfy your sweet tooth while offering essential nutrients like vitamins A and C, fibre and potassium.
- Tomato: This versatile fruit is non-starchy and has a low glycaemic index making it a suitable choice for people with diabetes. Tomatoes are high in vitamin C, vitamin E and potassium and can help manage blood sugar levels
- Whole grains: Whole oats, quinoa, whole grain barley and farro are rich in vitamins, minerals and fibre. These whole grains can assist in stabilising blood sugar levels.
- Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, flax seeds, cashews, pistachios and peanuts are high in protein, fibre, folate, minerals like magnesium and potassium, antioxidants, vitamin E and healthy fats. They can help manage blood sugar levels and provide essential nutrients for overall health.
While these superfoods are beneficial for people with diabetes, they should not replace a well-balanced diet and regular exercise regimen. It's all about achieving a balance by making these superfoods part of your diet along with regular physical activity.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
Diabetes Management
Manage Your Diabetes Like A Pro With Apollo 24|7's 12-Week EMPOWER Programme
Diabetes is one of the most common and widespread lifestyle diseases, affecting millions of people worldwide. Keeping the condition under control is a very challenging task. The Diabetes Management Programme by Apollo 24|7 can help you learn how to manage your condition on your own. Read on to learn how.
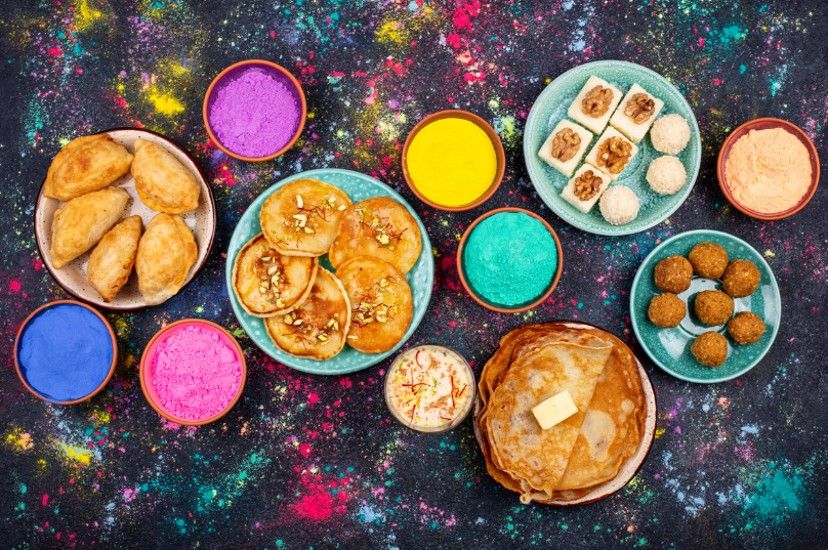

Diabetes Management
7 Diabetic-Friendly Recipes for a Healthy, Happy Holi
Celebrate Holi without compromising your health. Try these diabetic-friendly recipes that blend taste & nutrition. Enjoy savory Black Wheat Chaat Tartlets or protein-rich Chenna Kheer. For sweets, try Dates & Nuts Ladoo or sugar-free Sabudana Kheer (Recipe the blog). Remember, moderation is key! Relishing these treats, maintaining a balanced diet, & regularly tracking your blood glucose levels will help you enjoy Holi while effectively managing your diabetes.

Diabetes Management
Make These Simple Lifestyle Changes To Lower Your Risk of Diabetes
Reduce diabetes risk: limit refined carbs, choose high-fiber foods, and include lean proteins. Exercise aids weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Shed excess weight, quit smoking, control portions. Embrace a high-fiber diet, ensure enough vitamin D, cut processed foods and sugary drinks. Moderate healthy fats. These steps optimize blood sugar and lower diabetes risk.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Manage Your Diabetes Like A Pro With Apollo 24|7's 12-Week EMPOWER Programme
Diabetes is one of the most common and widespread lifestyle diseases, affecting millions of people worldwide. Keeping the condition under control is a very challenging task. The Diabetes Management Programme by Apollo 24|7 can help you learn how to manage your condition on your own. Read on to learn how.

Diabetes Management
7 Diabetic-Friendly Recipes for a Healthy, Happy Holi
Celebrate Holi without compromising your health. Try these diabetic-friendly recipes that blend taste & nutrition. Enjoy savory Black Wheat Chaat Tartlets or protein-rich Chenna Kheer. For sweets, try Dates & Nuts Ladoo or sugar-free Sabudana Kheer (Recipe the blog). Remember, moderation is key! Relishing these treats, maintaining a balanced diet, & regularly tracking your blood glucose levels will help you enjoy Holi while effectively managing your diabetes.

Diabetes Management
Make These Simple Lifestyle Changes To Lower Your Risk of Diabetes
Reduce diabetes risk: limit refined carbs, choose high-fiber foods, and include lean proteins. Exercise aids weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Shed excess weight, quit smoking, control portions. Embrace a high-fiber diet, ensure enough vitamin D, cut processed foods and sugary drinks. Moderate healthy fats. These steps optimize blood sugar and lower diabetes risk.

