General Health
What is a Blood Culture Test and When Should You Take It?
9 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 09 October 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
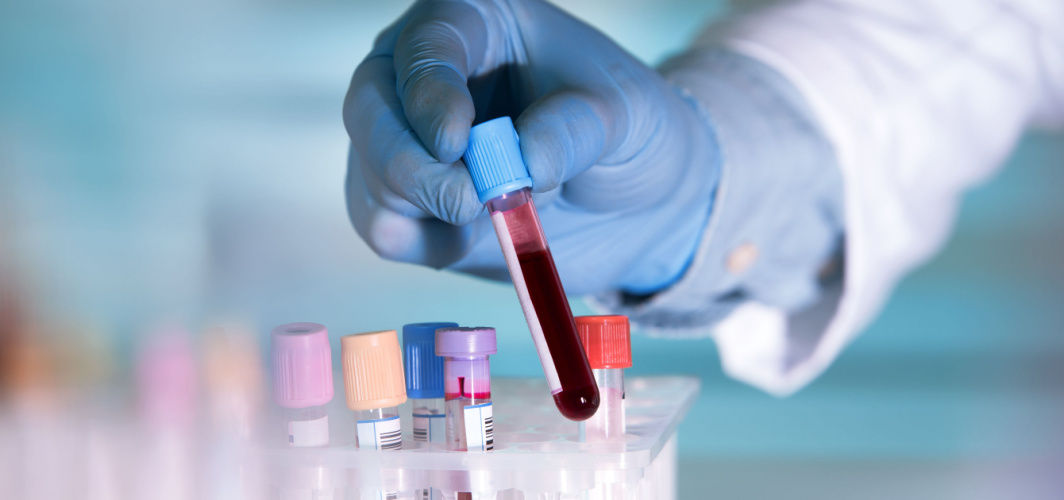
The blood culture test is a diagnostic procedure that helps identify the presence of bacteria or fungi in the bloodstream. The purpose of a blood culture test is to detect and diagnose bloodstream infections, also known as sepsis or bacteremia. Early detection and treatment of bloodstream infections are crucial to prevent serious complications. In the Indian healthcare context, where infectious diseases are prevalent, understanding what is blood culture test entails holds immense importance. Timely diagnosis can help healthcare professionals administer targeted antibiotic therapy, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.
What is a Blood Culture Test?
A blood culture test is a diagnostic procedure that involves taking a sample of blood to check for the presence of bacteria or fungi. It helps in identifying the specific organisms causing an infection in the bloodstream. The test is performed in a laboratory, where the blood sample is cultured or incubated under controlled conditions to allow the growth of any microorganisms present.
Indications for Blood Culture Test
A blood culture test is usually recommended when there is a suspicion of a bacterial infection in the body. The following signs and symptoms may warrant a blood culture test:
- High fever that persists or spikes suddenly
- Chills
- Rapid breathing or shortness of breath
- Rapid heart rate
- Severe headache
- Confusion
- Dizziness
These symptoms may indicate the presence of a bloodstream infection or sepsis, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Common Types of Infections Detected by Blood Culture Test
In this section, we will delve into some common types of infections detected by blood culture tests.
1. Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are a common cause of illness in India. The blood culture test is an effective way to detect and identify different types of bacterial infections. Some of the common bacterial infections are:
- Staphylococcus Aureus: Staphylococcus aureus is a type of bacteria that commonly causes skin infections, pneumonia, and bloodstream infections. It can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae: Streptococcus pneumoniae is a bacteria responsible for various respiratory infections such as pneumonia, sinusitis, and ear infections. It can also cause bloodstream infections.
- Escherichia Coli: Escherichia coli, commonly known as E.coli, is a type of bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections, gastrointestinal infections, and bloodstream infections.
2. Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are caused by fungi that can enter the bloodstream and cause serious health complications. Fungal infections can affect various parts of the body, including:
- Lungs
- Skin
- Nails
- Mucous membranes
In India, fungal infections such as candidiasis (caused by Candida species) and aspergillosis (caused by Aspergillus species) are commonly seen. These infections can occur due to weakened immunity, prolonged use of antibiotics or steroids, poor hygiene, or underlying medical conditions like diabetes.
3. Viral Infections
Viral infections are caused by viruses that can also be detected through blood culture testing. Common viral infections in India include:
- Dengue fever
- Hepatitis B and C
- Influenza
- HIV/AIDS
The blood culture test is not typically used as the primary method for diagnosing viral infections. Instead, specific tests for viral antigens or antibodies are used. However, in certain cases where the virus may be present in the bloodstream for a short period, a blood culture test may be utilised.
Procedure and Preparation of Blood Culture Test
When it comes to a blood culture test, proper preparation and understanding of the blood culture test procedure are essential. Let's take a closer look at what you should know:
1. How to Prepare for a Blood Culture Test?
Before undergoing a blood culture test, there are a few important preparations you need to keep in mind.
- First, inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are currently taking, as some medications can affect the accuracy of the test results such as antibiotics. You may be asked to temporarily stop taking certain medications before the test.
- It is also important to follow any fasting instructions given by your doctor. Fasting helps ensure that the blood sample obtained during the test is not affected by recent food intake. Typically, you will be asked to fast for a few hours before the test.
2. What to expect during the Procedure?
During a blood culture test procedure, a healthcare professional will collect a small sample of your blood for analysis. The procedure is relatively simple and involves inserting a needle into one of your veins, usually in your arm. The collected blood sample is then transferred to specialised bottles that contain nutrients to support bacterial or fungal growth.
These bottles are incubated at specific temperatures, and if there are any microorganisms present in the blood, they will multiply and can be identified through various techniques.
You may experience mild discomfort or a slight pinch when the needle is inserted, but the procedure is generally well-tolerated by most individuals. The entire process usually takes only a few minutes.
3. Potential Risks and Complications
While the blood culture test is considered safe, there are minimal risks associated with the procedure. These risks include:
- Minor bleeding at the puncture site
- Bruising
- Infection
However, these complications are rare and can be minimised by ensuring proper hygiene measures during sample collection.
When to Take a Blood Culture Test?
Knowing when to take a blood culture test is crucial in ensuring accurate results and timely treatment.
1. High-risk Individuals
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of developing bloodstream infections, making regular blood culture tests essential for early detection and prompt treatment.
- If you have a weakened immune system due to conditions like HIV/AIDS, cancer, or organ transplantation, it is advisable to discuss with your healthcare provider about regular blood culture testing.
- Additionally, individuals with implanted medical devices, such as central venous catheters or prosthetic heart valves, should also consider regular testing to detect any potential infections.
2. Specific Scenarios That Call for Testing
In some cases, immediate blood culture testing may be necessary.
- For instance, if you have a persistent fever with no identifiable cause, especially after surgery or other invasive procedures, your healthcare provider may recommend a blood culture test to identify any underlying infections.
- Similarly, if you show symptoms of severe sepsis or septic shock, an urgent blood culture test can help determine the causative organism and guide appropriate treatment.
Interpreting Blood Culture Results
Once the blood culture test is completed, it is important to understand and interpret the blood culture report and results accurately. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Positive Results
When your blood culture report comes back positive, it means that bacteria or fungi have been detected in your blood sample. The specific microorganism identified in the blood culture report helps healthcare providers determine the type of infection you have.
Positive blood culture results are crucial for guiding appropriate treatment decisions. It helps doctors choose the right antibiotics or antifungal medications to combat the infection effectively.
2. Negative Results
A negative blood culture report means that no microorganisms were detected in your blood sample. It suggests that you may not have a bloodstream infection at the time of testing.
However, it's important to note that a negative result doesn't completely rule out the possibility of infection. Sometimes, microorganisms may be present at low levels or may not be able to grow in the culture media used for testing.
3. Other Factors to Consider
At times during medical testing, errors occur when interpreting the results of a diagnostic test. These can be:
- False-positive Results: It occurs when a blood culture shows the presence of microorganisms, but they are contaminants from the skin or equipment used during sample collection. Factors such as inadequate skin disinfection, improper technique, or contamination during sample processing can lead to false-positive results.
- False-negative Results: It occurs when there is an actual infection, but the blood culture fails to detect it. This can happen if the organism causing the infection is present in low numbers, has an unusual growth pattern, or is difficult to cultivate in the laboratory.
Benefits and Limitations of Blood Culture Test
In this section, we will explore the benefits and limitations of a blood culture test.
1. Benefits of Early Detection
Early detection is crucial in effectively managing any medical condition, and bloodstream infections are no exception. The purpose of a blood culture test lies in identifying the presence of harmful bacteria or fungi in the bloodstream. By detecting these pathogens, healthcare providers can promptly administer appropriate treatment, such as antibiotics or antifungals, to combat the infection.
Timely treatment can help prevent the infection from spreading to other organs and causing severe complications. It also reduces the risk of developing antibiotic resistance, which is a growing concern in healthcare.
2. Limitations and Challenges
While blood culture tests are valuable diagnostic tools, they do have limitations.
- One limitation is that they may take time to produce results, typically ranging from 24 to 48 hours. During this waiting period, patients may already be receiving empirical treatment based on clinical symptoms.
- Additionally, blood culture tests may not always detect certain types of infections, such as those caused by fastidious organisms or viruses. False-negative results can occur due to various factors, including prior antibiotic use or low levels of pathogens in the bloodstream.
Prevention Strategies to Reduce the Risk of Bloodstream Infections
In this section, we will delve into some prevention strategies to reduce the risk of bloodstream infections.
1. Maintaining Good Hygiene Practices
Hygiene plays a crucial role in preventing bloodstream infections.
- It is essential to wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before meals and after using the restroom.
- Make sure to clean and disinfect surfaces regularly, particularly in high-traffic areas.
- Additionally, adopting proper respiratory hygiene, such as covering your mouth and nose while sneezing or coughing, can help limit the spread of infections.
2. Proper Wound Care and Infection Control
Proper wound care is vital in preventing bloodstream infections.
- Always clean wounds with antiseptics and cover them with sterile dressings.
- Avoid touching or scratching wounds unnecessarily to reduce the risk of introducing harmful bacteria.
- It's also crucial to follow infection control practices, such as using sterile medical equipment and ensuring their proper disposal after use.
3. Importance of Vaccination
Vaccination is an effective preventive measure against many infections that can lead to bloodstream infections. Keep your vaccinations up to date as recommended by healthcare professionals.
Vaccines help strengthen your immune system and protect you from various infectious diseases, reducing the risk of complications such as bloodstream infections.
4. Managing Underlying Medical Conditions Effectively
If you have any underlying medical conditions, it is important to manage them effectively to minimise the risk of bloodstream infections. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions regarding medications, lifestyle modifications, and regular check-ups.
By effectively managing these conditions, you can improve your overall health and reduce the likelihood of developing infections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have discussed what is blood culture test and its importance in diagnosing bloodstream infections. The purpose of blood culture test is to detect and identify the pathogens causing the infection, which helps in guiding appropriate treatment decisions. Remember, if you experience symptoms such as high fever, chills, rapid breathing, or signs of infection, consult your healthcare provider. They will determine if a blood culture test is necessary to diagnose a bloodstream infection. Early detection and appropriate treatment can make all the difference in your journey towards recovery.
General Health
Consult Top Haematologists
View AllFrequently Asked Questions
When should I take a Blood Culture Test?
When should I take a Blood Culture Test?
Does a positive blood culture always mean an infection?
Does a positive blood culture always mean an infection?
How is a Blood Culture Test performed?
How is a Blood Culture Test performed?
Are there any risks associated with a Blood Culture Test?
Are there any risks associated with a Blood Culture Test?
What can be determined from a Blood Culture Report?
What can be determined from a Blood Culture Report?
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
General Health
Sore Throat for More Than 5 Days? Get These Tests
Sore throat lasting more than 5 days? It could be more than just a viral bug. Learn about key tests like throat culture, CBC, and CRP to find the real cause and get the right treatment.

General Health
How To Choose The Right Omega-3 Supplement?
Unlock the secrets of Omega-3 oils and make informed choices. Learn how to select the ideal fish oil supplement for your well-being.

General Health
Electrolyte Imbalance: What It Is and How to Prevent It
Often, dehydration is a significant cause of an electrolyte imbalance. To resolve this, one must keep themselves hydrated with fluids that contain added electrolytes.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

The Best Exercises for Controlling Blood Sugar Levels
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

General Health
Sore Throat for More Than 5 Days? Get These Tests
Sore throat lasting more than 5 days? It could be more than just a viral bug. Learn about key tests like throat culture, CBC, and CRP to find the real cause and get the right treatment.

General Health
How To Choose The Right Omega-3 Supplement?
Unlock the secrets of Omega-3 oils and make informed choices. Learn how to select the ideal fish oil supplement for your well-being.

General Health
Electrolyte Imbalance: What It Is and How to Prevent It
Often, dehydration is a significant cause of an electrolyte imbalance. To resolve this, one must keep themselves hydrated with fluids that contain added electrolytes.
