Fasting and Postprandial Sugar Explained
Understand the difference between fasting and postprandial blood sugar levels, what they mean for diabetes diagnosis and management, and how to keep them in a healthy range.


Fasting and Postprandial Sugar Explained
If you or a loved one has diabetes or is at risk of developing it, you may have heard the terms fasting blood sugar and postprandial blood sugar during doctor visits or lab tests. But what do these terms mean, and why are they important for your health?
In this article, we’ll break down these concepts in simple terms, explain why they matter, and share tips on how to keep your sugar levels in check.
What Are Fasting and Postprandial Blood Sugar Levels?
Here's an overview on Fasting and Postprandial blood sugar levels:
1. Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS)
This is the blood sugar level measured after not eating or drinking anything (except water) for at least 8hours, usually in the morning before breakfast.
- Normal range: 70–99 mg/dL
- Prediabetes range: 100–125 mg/dL
- Diabetes range: 126 mg/dL or higher
2. Postprandial Blood Sugar (PPBS)
This is the blood sugar level measured 2 hours after eating a meal. It shows how well your body processes sugar after food.
- Normal range: Below 140 mg/dL
- Prediabetes range: 140–199 mg/dL
- Diabetes range: 200 mg/dL or higher
Both tests help doctors understand how your body manages glucose (sugar) and whether you have diabetes or prediabetes.
Why Are These Tests Important?
Monitoring fasting and postprandial sugar levels helps:
- Detect diabetes early – Before complications arise.
- Manage diabetes better – If you already have it.
- Prevent complications – Like heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney problems.
High sugar levels over time can damage blood vessels and organs, so keeping them under control is crucial.
What Causes High Blood Sugar?
Several factors can lead to elevated fasting or postprandial sugar levels:
- 🔹 Insulin resistance – When your body doesn’t use insulin properly.
- 🔹 Insufficient insulin production – Common in Type 1 diabetes.
- 🔹 Unhealthy diet – Too many refined carbs, sugary foods, and processed snacks.
- 🔹 Lack of exercise – Physical activity helps control blood sugar.
- 🔹 Stress and poor sleep – These can raise sugar levels.
- 🔹 Certain medications – Like steroids or some blood pressure drugs
Consult a Top General Physician For More Health Benefits
How to Manage Your Blood Sugar Levels
This is how you should manage your blood sugar levels:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet
- Choose whole grains (brown rice, oats) over refined carbs (white bread, pasta).
- Include fiber-rich foods (vegetables, fruits, beans) to slow sugar absorption.
- Limit sugary drinks and sweets – Opt for water, herbal teas, or sugar-free options.
- Eat small, frequent meals – Helps avoid sugar spikes.
2. Stay Active
- Walk for 30 minutes daily – Even a short walk after meals helps.
- Try strength training – Build muscle, which improves insulin sensitivity.
3. Monitor Your Levels Regularly
- Check fasting and post-meal sugar levels as advised by your doctor.
- Keep a log to track patterns and adjust habits accordingly.
4. Manage Stress and Sleep Well
- Practice deep breathing, yoga, or meditation to lower stress.
- Aim for 7–8 hours of sleep – Poor sleep affects blood sugar control.
5. Take Medications as Prescribed
If your doctor has prescribed insulin or other diabetes medications, take them on time.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Consult a doctor if:
- Your fasting sugar is consistently above 100 mg/dL.
- Your post-meal sugar is often above 140 mg/dL.
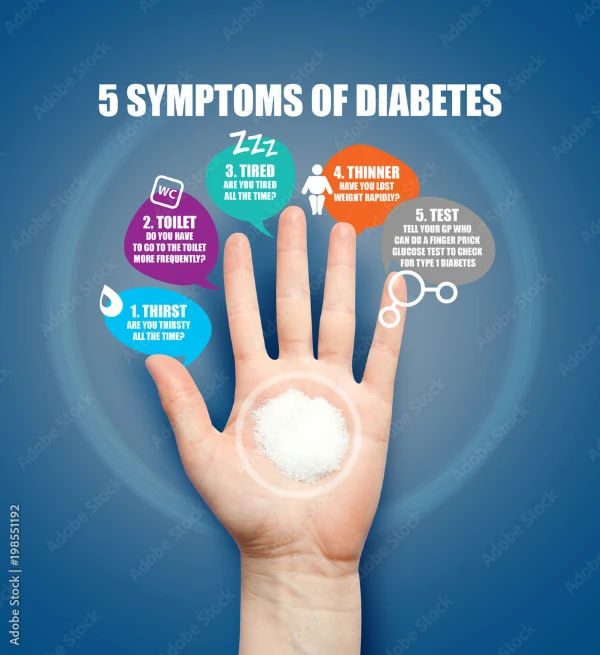
- You experience symptoms like frequent thirst, hunger, fatigue, or blurred vision.
Early detection and management can prevent complications.
Conclusion
Understanding your fasting and postprandial sugar levels is key to managing diabetes or preventing it. By making small, healthy changes in diet, exercise, and lifestyle, you can keep your blood sugar in check and stay healthier for longer.
If you need help monitoring your sugar levels or managing diabetes, consider booking a consultation with an expert on Apollo 24|7. Stay informed, stay healthy!
Consult a Top General Physician For More Health Benefits
Consult a Top General Physician For More Health Benefits

Dr. D Bhanu Prakash
General Practitioner
10 Years • MBBS, AFIH, Advanced certificate in critical care medicine, Fellowship in critical care medicine
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad

Dr D M Karthik
General Practitioner
4 Years • MBBS, Fellowship in Diabetes Mellitus, Advance certificate in Diabetes Mellitus, Derma Nutrition Certification
Visakhapatnam
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Andhra Pradesh, Visakhapatnam

Dr. Mohammed Kamran
General Practitioner
5 Years • MBBS, FIDM
Nashik
Apollo 24|7 Clinic - Maharashtra, Nashik

Dr. Suraja Nutulapati
General Physician/ Internal Medicine Specialist
10 Years • MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine)
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad
(875+ Patients)

Dr. Siri Nallapu
General Practitioner
5 Years • MBBS
Hyderabad
Apollo 24|7 Clinic, Hyderabad